In the mathematical field of order theory, an element a of a partially ordered set with least element 0 is an atom if 0 < a and there is no x such that...
3 KB (361 words) - 01:40, 17 June 2024
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. The definition of the word "atom" has changed over the years...
70 KB (9,130 words) - 19:29, 25 August 2024
electrons. Atom(s) may also refer to: Atom (time), a medieval unit of time Atom (measure theory), a minimal measurable set Atom (order theory) Atomic formula...
4 KB (598 words) - 05:54, 14 May 2024
measure theory, an atom is a measurable set which has positive measure and contains no set of smaller positive measures. A measure which has no atoms is called...
9 KB (1,490 words) - 21:20, 16 July 2024
Bohr model (redirect from Bohr's theory of the hydrogen atom)
the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell model. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader...
66 KB (9,312 words) - 19:43, 7 September 2024
Era" Atomic scale, distances comparable to the dimensions of an atom Atom (order theory), in mathematics Atomic (cocktail), a champagne cocktail Atomic...
2 KB (244 words) - 14:16, 25 March 2024
century) and others, developed distinctive theories of atomism, for example, involving momentary (instantaneous) atoms (kalapas) that flash in and out of existence...
64 KB (7,654 words) - 19:50, 26 July 2024
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically...
125 KB (12,755 words) - 06:17, 26 August 2024
orthogonality in a component-based system Atomicity, in order theory; see Atom (order theory) Atom (disambiguation) This disambiguation page lists articles...
803 bytes (133 words) - 15:59, 9 March 2022
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral hydrogen atom contains a nucleus of a single positively charged proton...
39 KB (6,015 words) - 14:12, 30 August 2024
Plum pudding model (redirect from Thomson's theory of the atom)
composed of atoms. The structure of the atom was discussed, and by the end of the century the leading model: 175 was the vortex theory of the atom, proposed...
44 KB (6,215 words) - 20:15, 7 September 2024
century. In molecular orbital theory, electrons in a molecule are not assigned to individual chemical bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under...
22 KB (2,943 words) - 17:32, 23 June 2024
An exotic atom is an otherwise normal atom in which one or more sub-atomic particles have been replaced by other particles of the same charge. For example...
12 KB (1,482 words) - 18:32, 28 August 2024
number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers, Ronald Gillespie and...
45 KB (4,038 words) - 17:14, 16 August 2024
Urelement (redirect from Atom (set theory))
atoms. Aczel's anti-foundation axiom implies that there is a unique Quine atom. Other non-well-founded theories may admit many distinct Quine atoms;...
8 KB (995 words) - 13:02, 29 June 2024
of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds when a molecule is formed. In contrast, molecular orbital theory has orbitals that cover...
12 KB (1,576 words) - 07:10, 29 April 2024
Atomism or social atomism is a sociological theory arising from the scientific notion atomic theory, coined by the ancient Greek philosopher Democritus...
6 KB (662 words) - 23:21, 10 September 2022
In first-order logic, a first-order theory is given by a set of axioms in some language. This entry lists some of the more common examples used in model...
36 KB (5,269 words) - 04:45, 30 April 2024
hyperfine splitting in the hydrogen atom. Despite the simpler notation, perturbation theory applied to quantum field theory still easily gets out of hand....
22 KB (2,939 words) - 15:24, 18 July 2024
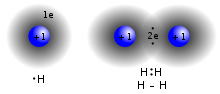
essence, means that the atoms share "valence", such as is discussed in valence bond theory. In the molecule H 2, the hydrogen atoms share the two electrons...
28 KB (3,654 words) - 19:53, 20 August 2024
Phonon (redirect from Atom vibrations)
phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids...
47 KB (6,853 words) - 16:17, 2 September 2024
chemistry, bond order is a formal measure of the multiplicity of a covalent bond between two atoms. As introduced by Linus Pauling, bond order is defined as...
9 KB (1,260 words) - 05:21, 12 February 2023
Atomic number (redirect from Atom number)
of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic...
15 KB (1,937 words) - 00:58, 28 August 2024
Big Bang (redirect from Primordial atom)
of dark energy, called phantom energy theories, suggest that ultimately galaxy clusters, stars, planets, atoms, nuclei, and matter itself will be torn...
150 KB (16,104 words) - 03:21, 2 September 2024
hydrogen atom, the quantum harmonic oscillator and the particle in a box, are too idealized to adequately describe most systems. Using perturbation theory, we...
70 KB (15,963 words) - 03:05, 20 July 2024
Octet rule (redirect from Lewis-Langmuir theory)
chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell...
22 KB (2,869 words) - 19:16, 11 May 2024
Energeticism – a theory that attempted to reinterpret all chemistry in terms of energy, rejecting the concept of atoms. Caloric theory – the theory that a self-repelling...
25 KB (2,944 words) - 15:11, 16 August 2024
Electron configuration (redirect from Orbital ordering)
of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2...
60 KB (6,147 words) - 11:00, 3 September 2024
Energy level (redirect from Quantized energy levels of atoms)
1913 by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in the Bohr theory of the atom. The modern quantum mechanical theory giving an explanation of these energy levels in...
22 KB (2,830 words) - 15:50, 25 July 2024
state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can...
79 KB (10,545 words) - 14:57, 19 August 2024