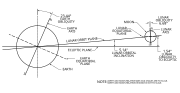
high Earth orbit is an geocentric orbit with an apogee farther than that of the geosynchronous orbit, which is 35,786 km (22,236 mi) away from Earth....
7 KB (602 words) - 19:24, 2 August 2024
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between 2,000...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 19:07, 10 August 2024
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less...
20 KB (2,226 words) - 04:42, 6 August 2024
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi), or 8.317 light-minutes, in a counterclockwise direction as viewed...
17 KB (1,837 words) - 03:18, 12 August 2024
Geocentric orbit: An orbit around the planet Earth, such as that of the Moon or of artificial satellites. Selenocentric orbit (named after Selene): An orbit around...
31 KB (3,471 words) - 19:19, 24 February 2024
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours...
32 KB (3,171 words) - 19:30, 12 March 2024
transfer orbit (GTO) or geosynchronous transfer orbit is a highly elliptical type of geocentric orbit, usually with a perigee as low as low Earth orbit (LEO)...
13 KB (1,801 words) - 19:57, 9 August 2024
The Moon orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the stars in about 27.32 days (a tropical...
37 KB (4,652 words) - 18:08, 16 April 2024
the existence of other moons of Earth—that is, of one or more natural satellites with relatively stable orbits of Earth, other than the Moon—have existed...
36 KB (3,942 words) - 04:16, 6 August 2024
above Earth's equator, 42,164 km (26,199 mi) in radius from Earth's center, and following the direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has...
49 KB (4,861 words) - 05:05, 11 June 2024
graveyard orbit, also called a junk orbit or disposal orbit, is an orbit that lies away from common operational orbits. One significant graveyard orbit is a...
8 KB (1,003 words) - 01:03, 3 May 2024
A geocentric orbit, Earth-centered orbit, or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA estimated...
17 KB (1,998 words) - 15:10, 9 August 2024
elliptical orbit (HEO) is an elliptic orbit with high eccentricity, usually referring to one around Earth. Examples of inclined HEO orbits include Molniya...
3 KB (307 words) - 19:21, 6 July 2024
over high latitudes. It is a highly elliptical orbit with an inclination of 63.4 degrees, an argument of perigee of 270 degrees, and an orbital period...
28 KB (3,094 words) - 12:32, 5 July 2024
Very low Earth orbit is a range of orbital altitudes below 400 km (250 mi), and is of increasing commercial importance in a variety of scenarios and for...
15 KB (1,854 words) - 06:10, 10 April 2024
would carry various radiation detectors in test flights to a very high Earth orbit that came nowhere near the Moon; Block II, which would try to accomplish...
116 KB (10,931 words) - 14:50, 13 August 2024
For example, it is possible to plot an orbit from high Earth orbit to Mars, passing close to one of the Earth's Trojan points.[citation needed] Collectively...
41 KB (5,821 words) - 11:16, 22 March 2024
to raise a satellite's orbit from low Earth orbit to geostationary orbit. In the idealized case, the initial and target orbits are both circular and coplanar...
27 KB (3,616 words) - 21:03, 18 June 2024
horseshoe orbit is a type of co-orbital motion of a small orbiting body relative to a larger orbiting body. The osculating (instantaneous) orbital period...
10 KB (1,341 words) - 08:44, 1 July 2023
orbit of Earth per sidereal day (relative to the stars, not the Sun). High Earth orbit: Geocentric orbits above the altitude of geosynchronous orbit 35...
57 KB (8,170 words) - 14:39, 18 July 2024
polar orbit is one in which a satellite passes above or nearly above both poles of the body being orbited (usually a planet such as the Earth, but possibly...
3 KB (416 words) - 15:33, 8 January 2024
thruster burns to keep the active craft in the same orbit as its target. For many low Earth orbit satellites, the effects of non-Keplerian forces, i.e...
14 KB (1,754 words) - 15:24, 26 May 2024
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given...
14 KB (1,629 words) - 00:10, 31 July 2024
operational, transited back to a high Earth orbit from lunar orbit on 22 November 2023 for continued scientific observations of Earth. On 22 July 2019, ISRO launched...
89 KB (7,087 words) - 19:58, 13 August 2024
on a spacecraft. Halo orbits exist in any three-body system, e.g., a Sun–Earth–orbiting satellite system or an Earth–Moon–orbiting satellite system. Continuous...
11 KB (1,104 words) - 16:53, 22 April 2024
Lagrange point (redirect from Lagrange orbit)
the orbital plane of the two large bodies. There are five Lagrange points for the Sun–Earth system, and five different Lagrange points for the Earth–Moon...
50 KB (5,703 words) - 04:44, 18 July 2024
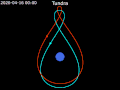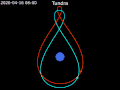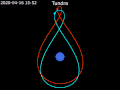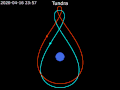
Tundra orbit (Russian: орбита «Тундра») is a highly elliptical geosynchronous orbit with a high inclination (approximately 63.4°), an orbital period of...
17 KB (1,703 words) - 18:00, 6 August 2023
Altitude (redirect from High altitude)
Geocentric orbits with altitudes at apogee higher than that of the geosynchronous orbit. A special case of high Earth orbit is the highly elliptical orbit, where...
26 KB (3,078 words) - 08:20, 29 July 2024
Boeing X-37 (redirect from Boeing X-37 Orbital Test Vehicle)
known as the Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV), is a reusable robotic spacecraft. It is boosted into space by a launch vehicle, then re-enters Earth's atmosphere...
82 KB (7,127 words) - 16:53, 3 August 2024
vehicle malfunction, the spacecraft could reach only Low Earth orbit, rather than the high Earth orbit that had been planned, and was only able to complete...
10 KB (1,117 words) - 17:12, 31 July 2024