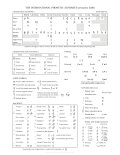
In phonetics, a homorganic consonant (from homo- "same" and organ "(speech) organ") is a consonant sound that is articulated in the same place of articulation...
5 KB (585 words) - 19:24, 10 December 2023
Place of articulation (section Homorganic consonants)
instance of assimilation, operates in many languages, where a nasal consonant must be homorganic with a following stop. We see this with English intolerable but...
22 KB (2,268 words) - 04:22, 24 September 2024
instead of the intended characters. Click consonants, or clicks, are speech sounds that occur as consonants in many languages of Southern Africa and in...
70 KB (6,903 words) - 22:09, 23 November 2024
voiceless stop homorganic to the nasal. For speakers without this feature, the word is pronounced without the /k/. Final clusters of four consonants, as in angsts...
19 KB (2,237 words) - 09:05, 20 October 2024
Convention of the IPA recommended that for other taps and flaps, a homorganic consonant, such as a stop or trill, should be used with a breve diacritic:...
15 KB (1,673 words) - 20:16, 21 October 2024
Lenition (section Consonant gradation)
involving homorganic consonants. This is colloquially known as 'blocked lenition', or more technically as 'homorganic inhibition' or 'homorganic blocking'...
33 KB (3,063 words) - 11:47, 25 October 2024
Japanese language (section Consonants)
syllables are allowed as long as the two consonants are the moraic nasal followed by a homorganic consonant. Japanese also includes a pitch accent, which...
90 KB (10,160 words) - 22:25, 24 November 2024
Russian phonology (redirect from Consonant clusters in Russian)
between these consecutive consonants at word boundaries, the major exception being clusters of homorganic consonants. Consonant cluster simplification in...
99 KB (8,971 words) - 13:37, 21 October 2024
English phonology (redirect from English consonants)
complex set of phonological features that distinguish fortis and lenis consonants (stops, affricates, and fricatives). Phonological analysis of English...
116 KB (12,239 words) - 08:04, 1 November 2024
The first palatalization affected single consonants and sequences of a nasal consonant followed by a homorganic voiced stop. The palatalization depended...
85 KB (6,558 words) - 07:00, 25 November 2024
Zulu language (section Consonants)
must always end in a vowel. Consonant clusters consist of any consonant, optionally preceded by a homorganic nasal consonant (so-called "prenasalisation"...
61 KB (5,118 words) - 18:16, 6 November 2024
International Phonetic Alphabet (redirect from Non-pulmonic consonant)
u}; ⟨D⟩ for the conflated flapped middle consonant of American English writer and rider; ⟨N⟩ for the homorganic syllable-coda nasal of languages such as...
166 KB (16,108 words) - 05:49, 22 November 2024
Hmong language (section Consonants)
Languages specifically describes lateral release as involving a homorganic consonant. White 2020, p. 220. White 2020, p. 214. Examples taken from: Heimbach...
97 KB (7,070 words) - 08:27, 24 November 2024
Catalan phonology (redirect from Catalan consonants)
Catalan), obstruents fail to surface word-finally when preceded by a homorganic consonant (e.g. /nt/ → [n̪]). Complex codas simplify only if the loss of the...
100 KB (8,256 words) - 16:40, 13 November 2024
Tsonga language (section Consonants)
dental [n̪] appear in homorganic consonant clusters. Unlike some of the Nguni languages, Tsonga has very few words with click consonants, and these vary in...
46 KB (3,365 words) - 01:41, 21 October 2024
considered separately from manner, as being independent parameters. Homorganic consonants, which have the same place of articulation, may have different manners...
14 KB (1,720 words) - 06:34, 22 May 2024
Abugida (redirect from Consonant stacking)
repeated consonants need not be represented, homorganic nasals may be ignored, and in Baybayin and Makasar script, the syllable-final consonant was traditionally...
44 KB (4,763 words) - 20:22, 12 November 2024
Marshallese language (section Consonants)
Only homorganic consonant sequences are allowed in Marshallese, including geminate varieties of each consonant, except for glides. Non-homorganic clusters...
93 KB (7,370 words) - 21:37, 10 November 2024
[d] is inaudible. A consonant is shortened when it is before an identical consonant, such as in "big game" or "top post". A homorganic voiceless stop may...
24 KB (2,873 words) - 17:21, 9 November 2024
Finnish phonology (section Consonant gradation)
exceeding 3 consonants (except in loan words) stop + nasal labial stop + non-labial stop non-dental stop + semivowel nasal + non-homorganic obstruent (except...
40 KB (4,659 words) - 19:04, 11 November 2024
Burmese alphabet (section Stacked consonants)
vowel "a" would apply to the မ (i.e., *ကမဘာ kamabha). Stacked consonants are always homorganic (pronounced in the same place in the mouth), which is indicated...
44 KB (2,213 words) - 12:33, 15 November 2024
Tamil script (section Basic consonants)
Aṉuvara, is the Anusvara. It was traditionally used as a homorganic nasal when in front of a consonant, and either as a bilabial nasal (m) or alveolar nasal...
57 KB (2,857 words) - 20:27, 12 November 2024
through the ʼPhags-pa script, such as the relationships among the homorganic consonants, Chinese phonology played a major role. Besides the grouping of...
34 KB (4,086 words) - 14:18, 8 November 2024
Taa language (section Consonants)
allowing mixed voicing in its consonants. These have been analyzed as prevoiced, but also as consonant clusters. When homorganic, as in [dt], such clusters...
33 KB (3,052 words) - 11:57, 21 September 2024
Proto-Sámi language (section Consonant gradation)
Eastern-Western divide are: Denasalisation of clusters of nasal plus homorganic consonant to geminate voiced or partially voiced stops (all except Akkala,...
41 KB (3,696 words) - 09:12, 30 July 2024
Lule Sámi (section Consonant length and gradation)
article to describe these combinations for convenience. Stops before a homorganic nasal (pre-stopped nasals) are realised as unreleased stops. /v/ is realised...
20 KB (1,673 words) - 02:40, 6 November 2024
involving the historical or allophonic insertion of a very short stop consonant before a sonorant, such as a short [d] before a nasal [n] or a lateral...
8 KB (934 words) - 22:50, 12 November 2023
Proto-Malayic had a total of 19 consonants and 4 vowels. Palatals (except *y) and voiced plosives cannot end a word, while only homorganic nasal–stop or *ŋs sequences...
9 KB (806 words) - 00:35, 13 November 2024
No audible release (redirect from Unreleased consonant)
release, also known as an unreleased stop or an applosive, is a stop consonant with no release burst: no audible indication of the end of its occlusion...
9 KB (978 words) - 01:55, 24 June 2024
there may be several manners of articulation, and therefore several homorganic consonants. Normal human speech is pulmonic, produced with pressure from the...
29 KB (3,323 words) - 18:06, 7 October 2024