Marine protists Marine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans...
133 KB (10,590 words) - 01:51, 21 October 2024
A protist (/ˈproʊtɪst/ PROH-tist) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural...
140 KB (14,501 words) - 21:57, 25 November 2024
Marine life, sea life or ocean life is the collective ecological communities that encompass all aquatic animals, plants, algae, fungi, protists, single-celled...
306 KB (29,263 words) - 19:00, 17 November 2024
protists, but recent studies in marine environments found mixotrophic protests contribute a significant part of the protist biomass. Since protists are...
232 KB (21,388 words) - 09:31, 2 June 2024
water column. Marine snow is made up of a variety of mostly organic matter, including dead or dying animals and phytoplankton, protists, fecal matter...
22 KB (2,737 words) - 21:03, 24 June 2024
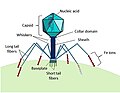
viruses affecting marine protists had been isolated and examined, most of them viruses of microalgae. The genomes of these marine protist viruses are highly...
91 KB (9,421 words) - 22:46, 15 November 2024
Microorganism (section Protists)
multicellular organisms as well as many unicellular protists and protozoans that are microbes. Some protists are related to animals and some to green plants...
74 KB (7,752 words) - 01:23, 14 November 2024
Ramsar site (section Marine/coastal wetlands)
Permanent: (A) Permanent shallow marine waters: Less than 6m deep at low tide; including sea bays and straits (B) Marine subtidal aquatic beds: Underwater...
8 KB (781 words) - 00:22, 18 October 2024
Coccolithophore shells Many protists have protective shells or tests, usually made from silica (glass) or calcium carbonate (chalk). Protists are a diverse group...
41 KB (3,843 words) - 18:33, 13 September 2024
Bioluminescence (redirect from Marine Phosphorescence)
organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms...
75 KB (8,136 words) - 04:03, 25 November 2024
Aquatic ecosystem (section Marine ecosystems)
microorganisms, phytoplankton, higher plants, invertebrates, fish, bacteria, protists, aquatic fungi, and more. These organisms are actively involved in multiple...
15 KB (2,910 words) - 22:31, 16 August 2024
"Molecular Phylogeny of the Widely Distributed Marine Protists, Phaeodaria (Rhizaria, Cercozoa)". Protist. 166 (3): 363–373. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2015.05...
19 KB (1,640 words) - 14:03, 19 November 2024
the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular...
16 KB (1,604 words) - 20:41, 14 October 2024
Plankton (redirect from Marine plankton)
bacteria, around 40,000 varieties of fungi, and hundreds of species of protists, algae, mosses and liverworts that live some part of their life cycle as...
62 KB (6,471 words) - 20:01, 24 November 2024
expanded his studies to include marine protists, helping to contribute to the description of the dinoflagellate protists. He first coined the terms "eukaryote"...
4 KB (305 words) - 23:29, 22 August 2024
Photosymbiosis (section Protists)
Sébastien; Foster, Rachel A. (2015), "Photosymbiosis in Marine Planktonic Protists", Marine Protists, Tokyo: Springer Japan, pp. 465–500, doi:10.1007/978-4-431-55130-0_19...
40 KB (4,041 words) - 06:34, 13 November 2024
Microbiome (section Marine)
microbiome researchers agree bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, and small protists should be considered as members of the microbiome. The integration of phages...
122 KB (12,348 words) - 21:57, 22 September 2024
aphotic zone is sometimes called the dysphotic zone. Ninety percent of marine life lives in the photic zone, which is approximately two hundred meters...
25 KB (2,955 words) - 19:32, 8 November 2024
Aquatic toxicology (redirect from Marine toxicology)
ecology and aquatic chemistry. This field of study includes freshwater, marine water and sediment environments. Common tests include standardized acute...
29 KB (3,537 words) - 20:44, 20 August 2024
Cyanobacteria (section Marine origins)
Decelle J, Colin S, Foster RA (2015). "Photosymbiosis in Marine Planktonic Protists". Marine Protists. pp. 465–500. doi:10.1007/978-4-431-55130-0_19. ISBN 978-4-431-55129-4...
180 KB (17,735 words) - 17:20, 13 November 2024
Microfossil (section Marine sediments)
animals, fungus, protists, bacteria and archaea. Terrestrial microfossils include pollen and spores. Marine microfossils found in marine sediments are the...
61 KB (6,338 words) - 22:11, 12 September 2024
In marine and freshwater ecology, a particle is a small object. Particles can remain in suspension in the ocean or freshwater. However, they eventually...
3 KB (388 words) - 14:01, 2 November 2024
(seaweeds) are technically marine protists since they are not true plants. Macroalgae Giant kelp is technically a protist since it is not a true plant...
82 KB (8,313 words) - 02:10, 27 August 2024
member of the family Astracanthidae. They are an unusual family of marine protists, but can be found across all oceans, from tropical to Arctic and Antarctic...
5 KB (456 words) - 00:49, 30 April 2024
Cercozoa (category Protist phyla)
"Molecular Phylogeny of the Widely Distributed Marine Protists, Phaeodaria (Rhizaria, Cercozoa)". Protist. 166 (3): 363–373. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2015.05...
20 KB (1,884 words) - 11:15, 24 April 2024
Picozoa, Picobiliphyta, Picobiliphytes, or Biliphytes are protists of a phylum of marine unicellular heterotrophic eukaryotes with a size of less than...
11 KB (1,167 words) - 13:28, 7 September 2024
multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic...
69 KB (7,869 words) - 11:25, 2 November 2024
(from Latin nanos 'tiny' and fila 'threads') is a genus of marine heterotrophic protists of the phylum Cercozoa. It is the only genus in the family Nanofilidae...
1 KB (128 words) - 22:45, 16 April 2024
catchments: connecting terrestrial carbon losses with aquatic metabolism". Marine and Freshwater Research. 52 (1): 101. doi:10.1071/mf00084. S2CID 11143190...
28 KB (3,128 words) - 00:07, 9 September 2024