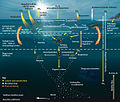
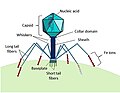
The microbial food web refers to the combined trophic interactions among microbes in aquatic environments. These microbes include viruses, bacteria, algae...
10 KB (1,308 words) - 22:31, 15 November 2024
webs, detrital food webs, marine food webs, aquatic food webs, soil food webs, Arctic (or polar) food webs, terrestrial food webs, and microbial food...
82 KB (8,605 words) - 07:53, 21 November 2024
foundation of the marine food web by supporting all other life in the ocean. The second central process in the marine food web is the microbial loop. This loop...
162 KB (16,694 words) - 05:55, 11 November 2024
Viral shunt (section Effect on the marine food web)
that is available for microbial re-consumption and offers an effective way to recycle key nutrients within the microbial food web. Data extracted from...
33 KB (4,098 words) - 23:21, 28 September 2024
Microorganism (redirect from Microbial)
single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from...
74 KB (7,752 words) - 01:23, 14 November 2024
classic food chain formed by phytoplankton-zooplankton-nekton. In soil systems, the microbial loop refers to soil carbon. The term microbial loop was...
27 KB (3,094 words) - 21:56, 15 November 2024
Marine microorganisms (redirect from Marine microbial)
Microbes Marine microbial symbiosis Microbial biogeography Microbial communities Microbial ecology Microbial food web Microbial loop Microbial oxidation of...
232 KB (21,388 words) - 09:31, 2 June 2024
profiled, or microbial biomass can be calculated by weighing the soil before and after fumigation. There are three different types of food web representations:...
27 KB (3,653 words) - 12:53, 6 June 2024
brackish habitats. The journal was originally established as Marine Microbial Food Webs by P. Bougis and F. Rassoulzadegan in 1985, and acquired its current...
2 KB (126 words) - 03:55, 14 July 2023
trophodynamics of the microbial food web in Chesapeake Bay Several established ecological models of marine microbial food webs have not included feeding...
19 KB (2,021 words) - 17:20, 16 May 2024
Microbiome (redirect from Microbial interaction)
plant health and food production and has received significant attention in recent years. Plants live in association with diverse microbial consortia, referred...
122 KB (12,348 words) - 21:57, 22 September 2024
flow of energy and the successive loss of energy as it travels up the food web are patterns in energy flow that are governed by thermodynamics, which...
31 KB (3,540 words) - 04:52, 14 September 2024
Pycnocline (section Microbial loop)
at other surface layers. The microbial loop is a trophic pathway in the marine microbial food web. The term "microbial loop" was coined by Azam et al...
11 KB (1,431 words) - 21:10, 21 September 2024
Invasive species (section By using them as food)
become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic...
128 KB (13,125 words) - 00:17, 12 November 2024
that use solar energy as a food source.[citation needed] Detritivores and scavengers are rare in the photic zone. Microbial decomposition of dead organisms...
25 KB (2,955 words) - 19:32, 8 November 2024
phytoplankton." Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them. Microalgae biomass...
16 KB (1,604 words) - 20:41, 14 October 2024
fungus gardens as the colony's primary food source. While the fungus itself does not digest cellulose, a microbial community containing a diversity of bacteria...
69 KB (7,869 words) - 11:25, 2 November 2024
global biological diversity." Criterion 8: "it is an important source of food for fishes, spawning ground, nursery and/or migration path on which fish...
8 KB (781 words) - 00:22, 18 October 2024
critical role in the mobilization of nutrients in ecosystems. Within the microbial food web they include the most important bacterivores. In part, they facilitate...
52 KB (5,212 words) - 05:40, 27 October 2024
Marine prokaryotes (section Roles in marine food webs)
geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. Microbial mat fossils have been found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone in Western...
136 KB (12,705 words) - 16:07, 22 October 2024
vents may occur where chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web. A marine coastal ecosystem is a marine ecosystem which occurs where the...
15 KB (2,910 words) - 22:31, 16 August 2024
bioluminescent bacteria in a light bulb. In 2011, Philips launched a microbial system for ambience lighting in the home. An iGEM team from Cambridge...
75 KB (8,136 words) - 04:03, 25 November 2024
Plankton (section Food chain)
Vázquez-Domínguez, E.; Vaqué, D.; Gasol, JM. (2010). "Warming effects on marine microbial food web processes: how far can we go when it comes to predictions?". Philosophical...
62 KB (6,471 words) - 20:01, 24 November 2024
cascade effect across the food chain, ultimately increasing overall ecosystem productivity. Biomass (ecology) Community ecology Food web Agricultural productivity...
22 KB (2,276 words) - 10:09, 13 July 2024
system, such as algae and the microbial breakdown of aquatic particulate organic carbon, are autochthonous. In aquatic food webs, the portion of biomass derived...
28 KB (3,128 words) - 00:07, 9 September 2024
and ending at, the same species.": 185 An example of this is the microbial food web in the ocean, where "bacteria are exploited, and controlled, by protozoa...
51 KB (5,269 words) - 10:59, 27 August 2024
blooms produce large quantities of mucus, leading to major changes in food webs in the ocean since few organisms feed on them. The organic carbon in mucus...
84 KB (9,152 words) - 02:18, 9 November 2024
trophic levels and complex microbial systems, it has many limitations. The KtW model represents an idealized microbial food web with mathematical parameters...
23 KB (2,553 words) - 21:49, 9 February 2024
implications for marine biogeochemical cycles, on the microbial loop and gas exchange, as well as the marine food web structure, the global dispersal of airborne...
91 KB (9,421 words) - 22:46, 15 November 2024
photochemical and microbial degradation represent the major sinks of DOC. Removal of refractory DOC in the ocean Phytoplankton production and food web dynamics...
79 KB (9,614 words) - 15:45, 19 April 2024