In astronomy, aberration (also referred to as astronomical aberration, stellar aberration, or velocity aberration) is a phenomenon where celestial objects...
60 KB (8,016 words) - 01:45, 18 October 2024
In physics, relativistic aberration is the relativistic version of aberration of light, including relativistic corrections that become significant for...
3 KB (335 words) - 03:41, 2 May 2024
(optical telescopes). Visible-light astronomy is part of optical astronomy,[clarification needed] and differs from astronomies based on invisible types of light...
11 KB (1,339 words) - 14:51, 28 September 2024
James Bradley (category Savilian Professors of Astronomy)
from 1742. He is best known for two fundamental discoveries in astronomy, the aberration of light (1725–1728), and the nutation of the Earth's axis (1728–1748)...
15 KB (1,651 words) - 17:08, 4 September 2024
Apparent place (redirect from Diurnal aberration)
cause the apparent position to differ from the mean position: Annual aberration – a deflection caused by the velocity of the Earth's motion around the...
4 KB (588 words) - 17:43, 16 February 2023
of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. Astronomy is...
161 KB (18,470 words) - 07:25, 24 November 2024
Optical telescope (section The five Seidel aberrations)
parabolic mirrors (primarily a reduction of spherical aberration with elimination of chromatic aberration) led to several proposed designs for reflecting telescopes...
58 KB (8,133 words) - 23:45, 21 July 2024
Astronomical unit (redirect from AU (astronomy))
of 8.83″ in 1864. Another method involved determining the constant of aberration. Simon Newcomb gave great weight to this method when deriving his widely...
53 KB (5,370 words) - 18:29, 22 November 2024
Geocentric model (redirect from Ptolemaic astronomy)
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of...
75 KB (8,799 words) - 00:26, 15 November 2024
different configurations to correct for image orientation and types of aberration. Because the image was formed by the bending of light, or refraction,...
35 KB (3,717 words) - 10:54, 1 November 2024
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for...
24 KB (3,437 words) - 16:15, 24 November 2024
The following is a timeline of Solar System astronomy and science. It includes the advances in the knowledge of the Earth at planetary scale, as part...
129 KB (13,493 words) - 20:15, 24 October 2024
spherical aberration at two wavelengths, rather than one as in an achromat. Telescope objective lenses for wide-band digital imaging in astronomy must have...
7 KB (708 words) - 21:34, 20 November 2024
This is a timeline of astronomy. It covers ancient, medieval, Renaissance-era, and finally modern astronomy. Mayan astronomers discover an 18.7-year cycle...
45 KB (5,788 words) - 22:52, 22 November 2024
Telescope (redirect from Telescopic observational astronomy)
advantages of using parabolic mirrors—reduction of spherical aberration and no chromatic aberration—led to many proposed designs and several attempts to build...
42 KB (3,941 words) - 08:33, 25 November 2024
Galileo Galilei (redirect from Father of modern observational astronomy)
Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the father of observational astronomy, modern-era classical physics, the scientific method, and modern science...
129 KB (15,815 words) - 16:21, 21 November 2024
of multiple-element lens for correcting spherical aberration and coma, but not chromatic aberration. His studies on dielectrics led to important results:...
4 KB (325 words) - 20:33, 4 October 2024
features new sections on generalised coordinate transformations, nutation, aberration, and selenographic coordinates. The fourth edition, coauthored by Jonathan...
4 KB (380 words) - 18:43, 11 August 2023
optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and...
28 KB (3,113 words) - 05:11, 22 June 2024
suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for...
33 KB (3,918 words) - 14:30, 23 November 2024
position due to the effects of light-time correction and aberration is known as planetary aberration. By convention, light-time correction is not applied...
3 KB (432 words) - 23:19, 15 December 2023
angle so it can be viewed with an eyepiece. They are free of chromatic aberration found in refracting telescopes. Newtonian telescopes are usually less...
17 KB (1,937 words) - 15:42, 13 November 2024
Celestial spheres (redirect from Orb (astronomy))
Mathematical Astronomy, vol. 2, pp. 677–85. Lloyd, "Heavenly aberrations," p. 173. Neugebauer, History of Ancient Mathematical Astronomy, vol. 2, pp....
44 KB (5,784 words) - 22:54, 20 May 2024
Doppler effect (redirect from Aberration redshift)
effect for electromagnetic waves such as light is of widespread use in astronomy to measure the speed at which stars and galaxies are approaching or receding...
34 KB (4,313 words) - 22:06, 4 November 2024
Eyepiece (section Chromatic aberration)
dispersion glass may also be used to reduce chromatic aberration. Longitudinal chromatic aberration is a pronounced effect of optical telescope objectives...
47 KB (6,470 words) - 04:52, 11 May 2024
In astronomy, air mass or airmass is a measure of the amount of air along the line of sight when observing a star or other celestial source from below...
35 KB (5,390 words) - 21:31, 23 September 2024
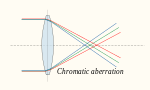
Achromatic lens (section Removing other aberrations)
lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths (typically red...
13 KB (1,740 words) - 03:27, 7 September 2024
Robert Stawell Ball (category Lowndean Professors of Astronomy and Geometry)
trigonometry and the celestial sphere, considering atmospheric refraction and aberration of light, and introducing basic use of a generalised instrument.[citation...
14 KB (1,253 words) - 10:00, 6 June 2024
History of the telescope (category History of astronomy)
in the main mirror. The achromatic lens, which greatly reduced color aberrations in objective lenses and allowed for shorter and more functional telescopes...
74 KB (9,260 words) - 17:07, 17 November 2024
The position of Savilian Professor of Astronomy was established at the University of Oxford in 1619. It was founded (at the same time as the Savilian...
50 KB (2,903 words) - 19:02, 22 November 2024