The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the...
77 KB (8,530 words) - 07:16, 15 November 2024
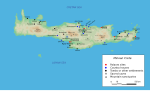
Salzburg and Graz. Hallstatt is known for its production of salt, dating back to prehistoric times, and gave its name to the Hallstatt culture, the archaeological...
24 KB (2,248 words) - 01:35, 7 November 2024
Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean...
45 KB (4,481 words) - 21:05, 5 November 2024
Celts (redirect from Ancient Celtic culture)
Age Hallstatt culture which followed it (c. 1200–500 BC), named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria, and with the following La Tène culture (c...
149 KB (16,668 words) - 16:48, 14 November 2024
Urnfield culture followed the Tumulus culture and was succeeded by the Hallstatt culture. Some linguists and archaeologists have associated this culture with...
104 KB (11,112 words) - 21:57, 2 October 2024
information regarding the material culture of the Celts, especially that of the La Tène culture and Hallstatt culture. However, the significance of these...
82 KB (9,432 words) - 09:00, 1 November 2024
a shared material culture, in which the Northern Bronze Age continued to exert cultural influence on the Celtic Hallstatt culture in the southern parts...
9 KB (933 words) - 20:39, 23 October 2024
particular archaeological culture or other typological unit, which is often named after it. For example, discoveries at La Tène and Hallstatt led scholars to divide...
5 KB (452 words) - 18:56, 16 October 2024
culture" specifically refers to the South German variant of the Bronze Age. In the table, Ha designates Hallstatt. Archaeological horizons Hallstatt A–B...
23 KB (2,077 words) - 20:21, 17 October 2024
Lusatian culture) to V of the Northern European chronological scheme. It has been associated or closely linked with the Nordic Bronze Age. Hallstatt influences...
14 KB (1,263 words) - 12:16, 13 September 2024
grouped with related Bosut culture, into the Bosut-Basarabi complex. The Basarabi culture is related to the Hallstatt culture of the Iron Age period that...
4 KB (378 words) - 04:07, 3 April 2024
Minoan civilization (redirect from Minoan culture)
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it...
119 KB (14,043 words) - 05:57, 3 November 2024
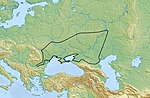
Sigynnae (section On the Hallstatt culture)
peoples of the Hallstatt culture, with a demarcation existing between the western parts of the Pannonian Basin inhabited by the sedentary Hallstatt farmers and...
37 KB (4,556 words) - 06:25, 29 October 2024
Catacomb culture. In addition to the Yamnaya culture, the Catacomb culture displays links with the earlier Sredny Stog culture, the Afanasievo culture and...
28 KB (3,353 words) - 14:11, 20 October 2024
to be Kerma Kush and the A-Group culture of ancient Nubia. While the stele-circled burial mounds of C-Group culture of Nubia are regarded as precursors...
98 KB (10,853 words) - 15:04, 25 October 2024
Central Europe the Urnfield culture had already given way to the Hallstatt culture. In north Italy the Villanovan culture is regarded as the start of...
32 KB (4,196 words) - 12:54, 8 July 2024
the Hallstatt culture – as supported by the known homelands of La Tène culture. The culture came to an end with the advent of the Hallstatt culture. Bronze...
6 KB (719 words) - 11:17, 17 October 2024
Age date near to the mines, which have made Hallstatt the type site for the important Hallstatt culture. The museum is close to the Hallstättersee, below...
11 KB (948 words) - 01:09, 5 November 2024
Cycladic culture (also known as Cycladic civilisation) was a Bronze Age culture (c. 3100–c. 1000 BC) found throughout the islands of the Cyclades in the...
13 KB (1,529 words) - 07:51, 14 October 2024
The Glazkov culture, Glazkovo culture, or Glazkovskaya culture (2200-1200 BCE), was an archaeological culture in the Lake Baikal area during the Early...
13 KB (1,283 words) - 23:22, 4 April 2024
the Iron Age in Central Europe, with the spread of the Proto-Celtic Hallstatt culture, and the Proto-Celtic language. The major Olmec site of San Lorenzo...
8 KB (953 words) - 19:24, 19 August 2024
Around 800 BC, the region was inhabited mostly by the people of the Hallstatt culture. Around 450 BC, they merged with the people of other areas in the...
15 KB (1,548 words) - 10:40, 22 August 2024
Celtic centres in Central Europe, particularly during the Iron Age Hallstatt culture period. Apart from the fortified citadel, there are extensive remains...
40 KB (4,534 words) - 12:03, 28 October 2024
The Karasuk culture (Russian: Карасукская культура, romanized: Karasukskaya kul'tura) describes a group of late Bronze Age societies who ranged from the...
31 KB (3,313 words) - 12:05, 15 November 2024
culture or Funnelbeaker culture. More frequently, they are named after the site at which the culture was first defined such as the Hallstatt culture or...
15 KB (1,838 words) - 21:33, 28 October 2024
Italic peoples (redirect from Italic culture)
Indo-European cultures. The burial characteristics relate the Proto-Villanovan culture to the Central European Urnfield culture and Celtic Hallstatt culture that...
25 KB (2,732 words) - 21:47, 26 September 2024
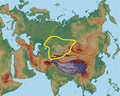
The Andronovo culture is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished c. 2000–1150 BC, spanning from the southern Urals to the...
63 KB (7,097 words) - 06:42, 7 November 2024
Villanovan culture to the Central European Urnfield culture (c. 1300–750 BCE) and Celtic Hallstatt culture that succeeded the Urnfield culture. It is not...
18 KB (1,531 words) - 12:47, 20 October 2024
Bronze Age Britain (section The Bell Beaker culture)
earlier than that, with some cultural practices developing in the Hallstatt culture. In 2021, a major archaeogenetics study uncovered a migration into...
28 KB (2,876 words) - 13:46, 23 September 2024
Kurgan hypothesis (redirect from Kurgan culture)
prehistoric cultures, including the Yamnaya (or Pit Grave) culture and its predecessors. In the 2000s, David Anthony instead used the core Yamnaya culture and...
34 KB (3,818 words) - 02:41, 26 August 2024