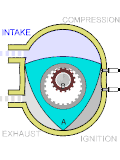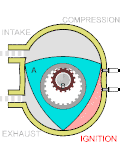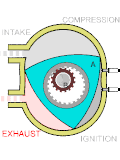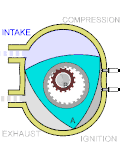
A hydrogen-cooled turbo generator is a turbo generator with gaseous hydrogen as a coolant. Hydrogen-cooled turbo generators are designed to provide a...
14 KB (1,732 words) - 02:01, 13 September 2024
Based on the air-cooled turbo generator, gaseous hydrogen first went into service as the coolant in a hydrogen-cooled turbo generator in October 1937, at...
10 KB (859 words) - 04:38, 31 October 2024
Combined cycle power plant (redirect from Hydrogen power plant)
cycle hydrogen power plant Combined cycle powered railway locomotive Cost of electricity by source Heat recovery steam generator Hydrogen-cooled turbo generator...
43 KB (5,515 words) - 20:31, 3 November 2024
Precooled jet engine (redirect from Pre-cooled turbojet)
saving. Air turborocket Compressor map Hydrogen-cooled turbo generator Intercooler Sloop, John (1978). Liquid hydrogen as a propulsion fuel, 1945–1959 (NASA...
7 KB (989 words) - 00:36, 18 April 2024
t/h. The generator produced 20 kV 50 Hz AC power. The generator's stator was cooled by water while its rotor was cooled by hydrogen. The hydrogen for the...
45 KB (4,403 words) - 10:58, 30 October 2024
Thermal power station (redirect from Steam electric generator)
generators may be cooled by air drawn through filters at the inlet, larger units generally require special cooling arrangements. Hydrogen gas cooling...
50 KB (6,690 words) - 17:07, 6 November 2024
third hydrogen-cooled turbo generator. Exhaust steam from the steam turbine flows to the air-cooled condenser. The condenser comprises 36 cooling fans...
7 KB (680 words) - 13:32, 1 June 2024
Capability curve (category Electrical generators)
the generator from the grid. The D-curve for a particular generator can be expanded by improved cooling. Hydrogen-cooled turbo generator's cooling can...
10 KB (1,184 words) - 11:14, 8 November 2023
Turboexpander (redirect from Turbo expander)
A turboexpander, also referred to as a turbo-expander or an expansion turbine, is a centrifugal or axial-flow turbine, through which a high-pressure gas...
19 KB (2,263 words) - 14:13, 25 February 2024
Mercury, Little Joe, as well as the turbo-pump gas generators for X-1, X-15, Jupiter, Redstone and Viking used hydrogen peroxide as a monopropellant. The...
92 KB (9,247 words) - 05:51, 20 November 2024
A hydrogen vehicle is a vehicle that uses hydrogen to move. Hydrogen vehicles include some road vehicles, rail vehicles, space rockets, forklifts, ships...
102 KB (9,411 words) - 22:00, 19 October 2024
Absorption refrigerator (redirect from Absorption cooling)
refrigerant cooling it via evaporative cooling and the resulting vapor is cooled via expansive cooling. (This is a combination of Joule-Thomson cooling and work...
17 KB (2,009 words) - 18:33, 21 November 2024
Turbopump (redirect from Turbo pump)
fire-fighting pumps.: 80 The V-2 rocket design used hydrogen peroxide decomposed through a Walter steam generator to power the uncontrolled turbopump: 81 produced...
13 KB (1,455 words) - 23:48, 22 November 2024
Air turborocket (redirect from Turbo-ramjet)
a form of combined-cycle jet engine. The basic layout includes a gas generator, which produces high pressure gas, that drives a turbine/compressor assembly...
9 KB (1,178 words) - 01:48, 15 November 2024
Mazda Wankel engine (section Turbo)
production of the engine. In 2023, Mazda reintroduced the engine as a generator for the 2023 MX-30 e-Skyactiv R-EV plug-in hybrid. Wankel engines can...
42 KB (5,528 words) - 02:53, 10 November 2024
Ramjet (redirect from Air Turbo Ramjet)
simultaneously heating the fuel and cooling the incoming air. This cooling is critical to efficient operation. The hydrogen then continues through a second...
36 KB (4,902 words) - 14:08, 17 November 2024
turbine (/ˈtɜːrbaɪn/ or /ˈtɜːrbɪn/) (from the Greek τύρβη, tyrbē, or Latin turbo, meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from...
21 KB (2,981 words) - 04:36, 31 October 2024
Marine propulsion (section Turbo-electric)
was the Russian tanker Vandal, launched in 1903. Turbo-electric transmission uses electric generators to convert the mechanical energy of a turbine (steam...
41 KB (4,957 words) - 12:43, 21 November 2024
Coolant (redirect from Cooling fluid)
machines susceptible to windage losses. Hydrogen-cooled turbogenerators are currently the most common electrical generators in large power plants. Inert gases...
16 KB (2,038 words) - 16:23, 2 August 2024
Cogeneration (section Heat recovery steam generators)
absorption refrigerators for cooling. The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator. The resulting low-temperature...
63 KB (7,080 words) - 06:04, 27 September 2024
Rocketdyne J-2 (category Rocket engines using the gas-generator cycle)
Built in the United States by Rocketdyne, the J-2 burned cryogenic liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, with each engine producing 1...
46 KB (5,784 words) - 16:17, 20 September 2024
Steam–electric power station (category Turbo generators)
which the electric generator is steam-driven: water is heated, evaporates, and spins a steam turbine which drives an electric generator. After it passes...
11 KB (1,379 words) - 03:59, 31 October 2024
Wankel engine (section Hydrogen fuel)
decreases in efficiency and performance. In small-displacement, charge-cooled rotor, air-cooled housing Wankel engines, that has been shown to reduce the maximum...
135 KB (16,650 words) - 15:35, 19 October 2024
Fastrac (rocket engine) (category Rocket engines using the gas-generator cycle)
then fed into the gas generator for mixing and thrust chamber for burning. The engine uses a gas generator cycle to drive the turbo-pump turbine, which...
11 KB (1,156 words) - 03:20, 15 July 2024
West Burton power stations (section Generator)
194 tons. The generator stator winding is water cooled at 2.155 m3/min (474 gal/min) and the stator core and rotor winding are cooled by hydrogen at 60 psig...
56 KB (7,756 words) - 14:53, 8 November 2024
January 1956. It comprised four Fraser and Chalmers / GEC 60 MW hydrogen cooled 11.8 kV turbo-alternators, these were supplied with steam at 62.1 bar and...
19 KB (1,776 words) - 20:41, 20 November 2024
turbogenerator. The Phase 1 generator is larger than Phase 2 so needs to be cooled by hydrogen gas. The terminal voltage of the generators is 15.75 kV. Electricity...
9 KB (829 words) - 11:20, 29 August 2023
and usable work. The fluid is then cooled, compressed and reused (closed cycle), or (less commonly) dumped, and cool fluid pulled in (open cycle air engine)...
42 KB (5,103 words) - 09:22, 20 November 2024
fuel cell, phosphoric acid fuel cell, and alkaline fuel cell require pure hydrogen as fuel, typically produced from external reforming of natural gas. However...
17 KB (1,980 words) - 19:53, 4 October 2023
transmission of AC power throughout the area, connecting the electricity generators with consumers. Grids can enable more efficient electricity markets. Although...
53 KB (6,825 words) - 23:35, 13 November 2024