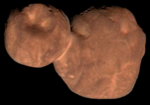
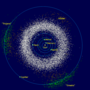
mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods...
97 KB (10,257 words) - 02:43, 21 November 2024
Tidal locking (redirect from Spin-orbit resonance)
include non-synchronous orbital resonances in which there is no further transfer of angular momentum over the course of one orbit (e.g. Mercury). In Mercury's...
47 KB (5,091 words) - 19:54, 18 December 2024
energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic...
60 KB (7,906 words) - 04:54, 14 December 2024
Resonant trans-Neptunian object (redirect from Resonance with Neptune)
object is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) in mean-motion orbital resonance with Neptune. The orbital periods of the resonant objects are in a simple integer...
31 KB (3,150 words) - 18:16, 1 January 2025
Neptune (redirect from Orbit of Neptune)
Retrieved 28 February 2008. Varadi, F. (1999). "Periodic Orbits in the 3:2 Orbital Resonance and Their Stability". The Astronomical Journal. 118 (5):...
147 KB (14,202 words) - 22:51, 1 January 2025
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals (with different energies,...
33 KB (3,178 words) - 20:06, 22 December 2024
Orbital Resonance is a science fiction novel by John Barnes. It is the first of four books comprising the Century Next Door series, followed by Kaleidoscope...
2 KB (113 words) - 15:57, 17 September 2024
Kirkwood gap (category Resonance with Jupiter)
would make three orbits for each orbit of Jupiter (hence, called the 3:1 orbital resonance). Other orbital resonances correspond to orbital periods whose...
9 KB (1,029 words) - 23:56, 24 November 2024
Musica universalis (section Orbital resonance)
mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods...
21 KB (2,656 words) - 22:58, 20 December 2024
belt object (KBO) that orbits beyond Neptune and is not controlled by an orbital resonance with Neptune. Cubewanos have orbits with semi-major axes in...
23 KB (2,362 words) - 03:01, 14 December 2024
Mercury (planet) (redirect from Mercury's orbit)
Mercury's orbital period, and proposed that the planet's orbital and rotational periods were locked into a 3:2 rather than a 1:1 resonance. Data from...
155 KB (15,927 words) - 20:20, 5 December 2024
Asteroid belt (section Orbits)
from these orbits. When the mean orbital period of an asteroid is an integer fraction of the orbital period of Jupiter, a mean-motion resonance with the...
83 KB (8,797 words) - 05:11, 30 December 2024
A secular resonance is a type of orbital resonance between two bodies with synchronized precessional frequencies. In celestial mechanics, secular refers...
3 KB (391 words) - 19:11, 10 October 2022
Pluto (redirect from Hadeocentric orbit)
orbital periods of all Pluto's moons are linked in a system of orbital resonances and near-resonances. When precession is accounted for, the orbital periods...
165 KB (14,266 words) - 23:46, 31 December 2024
radii ranging from 1.94 R⊕ to 2.85 R⊕. The planets orbit the host star in a rhythmic orbital resonance. The star, and related planetary system, is located...
15 KB (1,196 words) - 02:34, 17 November 2024
Angular momentum coupling (redirect from Orbit-orbit coupling)
with which it orbits another body. This is more commonly known as orbital resonance. Often, the underlying physical effects are tidal forces. Conservation...
17 KB (2,228 words) - 20:09, 21 February 2024
within Jupiter's orbit, in a 3:2 orbital resonance with Jupiter. The namesake is the asteroid 153 Hilda. Hildas move in their elliptical orbits in such a fashion...
11 KB (1,294 words) - 08:50, 9 September 2024
Moons of Pluto (section Resonances)
be in a 3-body Laplace orbital resonance with orbital periods in a ratio of 18:22:33. The ratios should be exact when orbital precession is taken into...
38 KB (3,597 words) - 20:22, 5 December 2024
Orcus (dwarf planet) (section Orbit and rotation)
Orcus is in a 2:3 orbital resonance with Neptune, having an orbital period of 245 years, and is classified as a plutino. Its orbit is moderately inclined...
40 KB (3,595 words) - 02:26, 14 December 2024
orbital resonance with Jupiter (2.502 AU), which results in their being close to a 1:4 resonance with Earth (2.520 AU). An object in this resonance has...
5 KB (410 words) - 05:45, 30 October 2024
Jupiter (redirect from Jovian orbit)
completes an orbit every 11.86 years. This is approximately two-fifths the orbital period of Saturn, forming a near orbital resonance. The orbital plane of...
174 KB (16,453 words) - 14:26, 19 December 2024
compounds are well described by resonance hybrids as well as by delocalised orbitals in molecular orbital theory. Resonance is to be distinguished from isomerism...
42 KB (5,094 words) - 15:41, 14 November 2024
Miranda (moon) (category Moons with a prograde orbit)
during a past time when it was in 3:1 orbital resonance with Umbriel. The resonance would have increased Miranda's orbital eccentricity to 0.1, and generated...
49 KB (5,655 words) - 20:19, 10 December 2024
molecular orbital is best characterized by that type. This method of quantifying orbital contribution as a linear combination of atomic orbitals is used...
23 KB (3,018 words) - 12:43, 22 October 2024
Mimas (category Moons with a prograde orbit)
Saturn's ring, named the Cassini Division, due to orbital resonance destabilising the particles' orbit there. Mimas was discovered by the astronomer William...
27 KB (2,621 words) - 17:01, 17 November 2024
1:2 resonance, dubbed twotinos, with a mean orbital radius of 47.7 AU and an eccentricity of 0.37. There are several objects in the 2:5 (mean orbital radius...
18 KB (2,407 words) - 08:01, 18 July 2024
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy...
17 KB (2,059 words) - 22:31, 24 October 2024
Ganymede (moon) (category Moons with a prograde orbit)
density compared to the three. Ganymede orbits Jupiter in roughly seven days and is in a 1:2:4 orbital resonance with the moons Europa and Io, respectively...
111 KB (10,623 words) - 05:24, 22 November 2024
perturbing their orbits. Later that year, Raúl and Carlos de la Fuente Marcos argued that two massive planets in orbital resonance were necessary to...
182 KB (19,427 words) - 14:03, 3 January 2025
Retrograde and prograde motion (redirect from Retrograde orbit)
spin–orbit resonance due to the eccentricity of its orbit. Mercury's prograde rotation is slow enough that due to its eccentricity, its angular orbital velocity...
40 KB (4,642 words) - 01:34, 27 August 2024