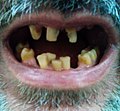
Pulp necrosis is a clinical diagnostic category indicating the death of cells and tissues in the pulp chamber of a tooth with or without bacterial invasion...
25 KB (3,364 words) - 05:27, 23 August 2024
Teeth with pulp necrosis undergo a root canal or extraction to prevent further spread of the infection, which may lead to an abscess. Necrosis may be symptomatic...
36 KB (4,342 words) - 18:35, 26 September 2024
Dental trauma (section Pulpal necrosis)
eruption sequence. Potential sequelae can involve pulpal necrosis, pulp obliteration and root resorption. Necrosis is the most common complication and an assessment...
43 KB (4,139 words) - 10:00, 14 September 2024
causing the pulp to die. Exposure of the pulp causes pulpitis (an inflammation which can become irreversible, leading to pain and pulp necrosis, and necessitating...
29 KB (3,540 words) - 11:57, 9 December 2024
the occurrence of pulpal strangulation and necrosis in response to inflammation Pulp polyps are characterised by overgrowth of the pulp tissue outside the...
5 KB (703 words) - 16:31, 1 July 2021
Tooth discoloration (section Pulp necrosis)
the pulp. The blood is then decomposed gradually and a blue-brown discoloration develops. Teeth may turn grey following trauma-induced pulp necrosis (death...
22 KB (2,393 words) - 09:13, 23 July 2024
evaginatus or dens invaginatus were the second most common etiology of pulp necrosis in immature teeth. Dens evaginatus is more common between these 2 dental...
44 KB (5,670 words) - 16:52, 3 February 2024
sequela in the natural history of tooth decay, irreversible pulpitis and pulpal necrosis. Other causes can include occlusal trauma due to 'high spots' after...
11 KB (945 words) - 09:00, 3 October 2024
There is a small risk of pulp necrosis. If root canal treatment is attempted it can be difficult or impossible on a tooth with pulp canal obliteration. Internal...
3 KB (297 words) - 19:40, 8 November 2023
Root resorption most commonly occurs due to inflammation caused by pulp necrosis, trauma, periodontal treatment, orthodontic tooth movement and tooth...
17 KB (1,818 words) - 00:47, 26 August 2024
associated with pulp necrosis may be able to conduct electric current next to infected and hypersensitive pulp tissue Inflamed pulp tissue may still...
25 KB (3,485 words) - 05:16, 23 August 2024
when compared with vital pulp, pulp with partial necrosis will not be stimulated as extensively. In the case of partial necrosis, access to and into dentine...
22 KB (2,949 words) - 18:05, 19 January 2025
Tooth replantation (section Pulp necrosis)
increasing the likelihood of complications such as ankylosis, infection and pulp necrosis. Avulsed teeth should be replanted within the hour to increase the likelihood...
16 KB (2,008 words) - 15:53, 2 November 2024
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
70 KB (7,952 words) - 07:47, 30 December 2024
pulpitis (toothache) to occur in the same region, and this may cause pulp necrosis and the formation of a periapical abscess associated with either tooth...
29 KB (3,089 words) - 14:17, 13 January 2025
originating, but not always. If the crack propagates into the pulp, irreversible pulpitis, pulpal necrosis and periapical periodontitis may develop, with the respective...
14 KB (1,596 words) - 15:47, 17 January 2024
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
23 KB (2,264 words) - 07:14, 22 October 2024
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
9 KB (968 words) - 07:03, 8 January 2025
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
10 KB (1,056 words) - 15:21, 26 November 2024
mucous membrane with loss of surface tissue and the disintegration and necrosis of epithelial tissue. A mucosal ulcer is an ulcer which specifically occurs...
37 KB (4,264 words) - 14:28, 20 January 2025
ischemic necrosis. In rare cases, oral involvement causes complications such as osteonecrosis, tooth loss, periodontitis (gum disease), pulp calcification...
80 KB (8,861 words) - 13:41, 3 January 2025
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
3 KB (228 words) - 04:30, 19 January 2024
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
23 KB (2,474 words) - 07:34, 29 September 2024
textbook description of Koplik spots is ulcerated mucosal lesions marked by necrosis, neutrophilic exudate, and neovascularization. They are described as appearing...
5 KB (610 words) - 12:26, 10 May 2024
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
12 KB (1,284 words) - 23:08, 19 September 2023
Pulp stones (also denticles or endoliths) are nodular, calcified masses appearing in either or both the coronal and root portion of the pulp organ in teeth...
13 KB (1,585 words) - 20:34, 3 December 2023
irreversibly progress to pulpal necrosis due to compression of the venous microcirculation and tissue ischemia, and reversible when the pulp is still capable...
27 KB (3,298 words) - 02:57, 19 October 2024
treated by teeth cleaning alone, and are at a high risk of spreading into the pulp of the tooth, leading to the loss of vitality and need for extraction or...
88 KB (9,276 words) - 13:00, 15 January 2025
contact Premature eruption Neonatal teeth Pulp calcification Pulp stone Pulp canal obliteration Pulp necrosis Pulp polyp Pulpitis Regional odontodysplasia...
35 KB (3,703 words) - 18:58, 10 October 2024