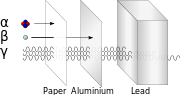
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable...
95 KB (9,826 words) - 07:36, 11 November 2024
In nuclear science a decay chain refers to the predictable series of radioactive disintegrations undergone by the nuclei of certain unstable chemical...
46 KB (3,963 words) - 13:37, 20 November 2024
Radionuclide (redirect from Radioactive isotopes)
The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay...
31 KB (2,660 words) - 10:05, 14 November 2024
from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often proceeds via a sequence of steps (decay chain). For example, 238U decays to 234Th which decays to 234mPa...
4 KB (428 words) - 13:45, 4 November 2024
Gamma ray (redirect from Gamma decay)
a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic...
60 KB (7,399 words) - 22:06, 21 October 2024
in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable atoms survive. The term is also used more generally...
17 KB (2,180 words) - 14:06, 20 November 2024
decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or "decays"...
19 KB (2,542 words) - 20:56, 19 November 2024
Decay heat is the heat released as a result of radioactive decay. This heat is produced as an effect of radiation on materials: the energy of the alpha...
13 KB (1,574 words) - 17:00, 23 August 2024
Radiometric dating (redirect from Radioactive dating)
naturally occurring radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay. The use of radiometric...
46 KB (5,770 words) - 19:20, 7 November 2024
Atom (section Radioactive decay)
or a beta particle. Thus, gamma decay usually follows alpha or beta decay. Other more rare types of radioactive decay include ejection of neutrons or...
126 KB (12,933 words) - 22:22, 13 November 2024
more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide (a radioactive atom). By virtue of its radioactive decay, it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical...
19 KB (2,378 words) - 18:50, 31 October 2024
Alpha particle (section Alpha decay)
particles have a net spin of zero. When produced in standard alpha radioactive decay, alpha particles generally have a kinetic energy of about 5 MeV and...
33 KB (4,134 words) - 15:56, 24 November 2024
The decay energy is the energy change of a nucleus having undergone a radioactive decay. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus...
5 KB (651 words) - 21:26, 24 December 2023
Stable nuclide (section Still-unobserved decay)
produce a radioactive emission. The nuclei of such isotopes are not radioactive and unlike radionuclides do not spontaneously undergo radioactive decay. When...
28 KB (3,289 words) - 18:41, 22 November 2024
Nuclear fission (section Radioactive decay)
a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay. Nuclear fission was discovered by chemists Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann...
74 KB (9,714 words) - 03:03, 25 November 2024
Beta particle (section Beta decay modes)
emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and β+ decay, which produce electrons...
14 KB (1,522 words) - 15:16, 13 September 2024
Positron emission (redirect from Beta plus decay)
Positron emission, beta plus decay, or β+ decay is a subtype of radioactive decay called beta decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide nucleus is...
9 KB (1,138 words) - 03:51, 13 November 2024
In nuclear physics, double beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which two neutrons are simultaneously transformed into two protons, or vice versa...
38 KB (3,793 words) - 18:16, 6 November 2024
some shielding; and high-level waste (HLW), which is highly radioactive and hot due to decay heat, thus requiring cooling and shielding. In nuclear reprocessing...
113 KB (12,846 words) - 01:35, 11 November 2024
Forbidden mechanism (section In radioactive decay)
seconds, compared to less than a microsecond for decay via permitted transitions. In some radioactive decay systems, multiple levels of forbiddenness can...
14 KB (1,847 words) - 19:22, 17 November 2024
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron)...
58 KB (6,987 words) - 12:18, 1 November 2024
nature. Potassium-40 undergoes three types of radioactive decay. In about 89.28% of events, it decays to calcium-40 (40Ca) with emission of a beta particle...
8 KB (868 words) - 18:21, 28 September 2024
Different types of radioactive decay are characterized by their changes in mass number as well as atomic number, according to the radioactive displacement law...
8 KB (1,101 words) - 14:24, 4 October 2024
Radiocarbon dating (redirect from Radioactive carbon dating)
amount of 14 C it contains begins to decrease as the 14 C undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the proportion of 14 C in a sample from a dead plant or...
104 KB (13,826 words) - 21:01, 9 November 2024
Iodine-131 (redirect from Radioactive iodine therapy)
Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with nuclear energy...
38 KB (4,377 words) - 09:05, 2 November 2024
Radiation (redirect from Radioactive radiation)
naturally occurring radioactive isotopes, particularly potassium-40 (40K), which emit ionizing radiation when undergoing radioactive decay, the levels of such...
48 KB (6,161 words) - 02:36, 4 November 2024
physics, is a rule governing the transmutation of elements during radioactive decay. It is named after Frederick Soddy and Kazimierz Fajans, who independently...
2 KB (277 words) - 15:28, 22 October 2023
radionuclide that undergoes radioactive decay to a different state, the number of atoms in the original state follows exponential decay as long as the remaining...
17 KB (2,597 words) - 17:30, 4 October 2024
Decay correction is a method of estimating the amount of radioactive decay at some set time before it was actually measured. Researchers often want to...
5 KB (802 words) - 09:26, 2 June 2024
Secular equilibrium (redirect from Radioactive Equilibrium)
quantity of a radioactive isotope remains constant because its production rate (e.g., due to decay of a parent isotope) is equal to its decay rate. Secular...
3 KB (446 words) - 19:03, 1 April 2024