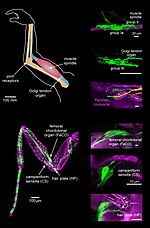
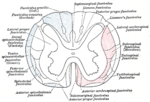
The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. Proprioceptive...
13 KB (1,434 words) - 15:06, 4 March 2024
Spinal cord (redirect from Spinal cord tract)
travels up the spinal cord in the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Also known as the anterior spinocerebellar tract, sensory receptors take in the information...
41 KB (4,971 words) - 17:09, 29 June 2024
column and medial to the posterior spinocerebellar tract. Axons in the lateral corticospinal tract weave out of the tract and into the anterior horns of the...
5 KB (560 words) - 16:48, 18 February 2024
maintenance. It consists of the following fiber tracts entering cerebellum: Posterior spinocerebellar tract: unconscious proprioceptive information from...
4 KB (386 words) - 13:54, 5 March 2022
Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition...
37 KB (2,946 words) - 13:44, 18 May 2024
pathways include the anterior spinocerebellar and tectocerebellar tracts. The fibers of the anterior spinocerebellar tract originate in Clarke's column...
4 KB (467 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2023
proprioception is communicated primarily via the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and ventral spinocerebellar tract, to the cerebellum. A nonconscious reaction is...
56 KB (6,836 words) - 18:51, 26 June 2024
anterior pituitary anterior root anterior spinal artery anterior spinocerebellar tract anterior superior alveolar artery anterior tibial artery anterior...
55 KB (4,460 words) - 17:52, 17 June 2024
the contralateral cerebral cortex. They may also arise within the spinocerebellar tract whose origin is located in the ipsilateral spinal cord. Most of...
32 KB (3,180 words) - 13:52, 26 May 2024
compromised anterior and lateral corticospinal tract, anterior grey matter and spinocerebellar tract. There is also a loss in nociception and thermosensation...
28 KB (3,033 words) - 00:49, 9 December 2023
Tract of the Anterolateral System. Bilateral (both sides) ataxia may also occur if the ventral spinocerebellar tract and dorsal spinocerebellar tract...
13 KB (1,698 words) - 19:04, 17 May 2024
nucleus. It also contains afferent tracts, most prominent of which is the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Other afferent tracts are the trigeminothalamic fibers...
4 KB (465 words) - 13:37, 28 February 2021
body and anterior spinocerebellar tract. It receives input from the ipsilateral posterior external arcuate fibers (cuneocerebellar tract) and the dorsal...
4 KB (394 words) - 12:03, 10 June 2024
projections from neurons in this nucleus give rise to the dorsal spinocerebellar tract which ascends ipsilaterally through the spinal cord and ends as...
5 KB (562 words) - 09:06, 12 June 2024
proprioception (joint sense). Lateral corticospinal tract dysfunction produces spasticity and dorsal spinocerebellar tract dysfunction causes ataxia.[citation needed]...
9 KB (912 words) - 22:28, 24 February 2024
Spinothalamic tract Lateral spinothalamic tract Anterior spinothalamic tract Spinomesencephalic tract Spinocerebellar tract Spino-olivary tract Spinoreticular...
21 KB (1,695 words) - 23:13, 27 May 2024
corticospinal tract (also called the ventral corticospinal tract, "Bundle of Turck", medial corticospinal tract, direct pyramidal tract, or anterior cerebrospinal...
4 KB (386 words) - 16:46, 18 February 2024
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder, which, like other spinocerebellar ataxias, is characterized by neurological...
85 KB (10,375 words) - 02:05, 21 May 2024
in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, the dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts. Vision Vestibular apparatus Crucially, the brain can obtain sufficient...
11 KB (1,276 words) - 07:55, 14 April 2024
"Messages Conveyed by Spinocerebellar Pathways During Scratching in Cat .2. Activity of Neurons of Ventral Spinocerebellar Tract". Brain Research. 151...
16 KB (2,254 words) - 17:59, 7 May 2023
input from the dorsal columns of the spinal cord (including the spinocerebellar tract) and from the trigeminal nerve, as well as from visual and auditory...
23 KB (2,598 words) - 06:54, 7 March 2024
cells of (the paravermal cortex of) the spinocerebellum Anterior spinocerebellar tract (via restiform body of inferior cerebellar peduncle) Contralateral...
3 KB (250 words) - 07:44, 30 April 2024
input from the dorsal columns of the spinal cord (including the spinocerebellar tract) and from the cranial trigeminal nerve, as well as from visual and...
94 KB (11,573 words) - 13:22, 12 June 2024
(Ventral/anterior spinocerebellar tract→ SCP → Cerebellar vermis) upper limb → 1° (Golgi tendon organ) → 2° (Rostral spinocerebellar tract → ICP → Cerebellum)...
2 KB (199 words) - 18:13, 23 November 2023
the crossed and uncrossed corticospinal tracts to the legs and fasciculus gracilis. The spinocerebellar tract is involved to a lesser extent. Neuronal...
36 KB (3,347 words) - 19:00, 17 April 2024
causes a polyglutamine tract in a specific gene to become too long. Important examples of polyglutamine diseases are spinocerebellar ataxia and Huntington's...
4 KB (448 words) - 06:25, 16 June 2024
afferent pathways to the cerebellum are the dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts. They are involved in the cerebellar regulation of movement.[citation...
10 KB (970 words) - 11:18, 12 June 2024
optic, auditory, posterior columns and gracile and cuneate nuclei, spinocerebellar tracts, motor neurons of cranial nerves and anterior horns, and muscle...
28 KB (3,575 words) - 20:49, 13 June 2024
to supraspinal structures via spinothalamic, spinoreticular, and spinocerebellar tracts. The so-called natural gaits, in increasing order of speed, are...
36 KB (4,877 words) - 16:42, 5 June 2024
Ataxin-2 (section Spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2))
that in humans is encoded by the ATXN2 gene. Mutations in ATXN2 cause spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2). Ataxin-2 contains the following protein domains:...
12 KB (1,550 words) - 05:39, 25 December 2023