Bhāskara II ([bʰɑːskərə]; c.1114–1185), also known as Bhāskarāchārya (lit. 'Bhāskara the teacher'), was an Indian polymath, mathematician, astronomer and...
33 KB (3,688 words) - 14:40, 20 September 2024
Bhāskara (c. 600 – c. 680) (commonly called Bhāskara I to avoid confusion with the 12th-century mathematician Bhāskara II) was a 7th-century Indian mathematician...
11 KB (1,346 words) - 21:12, 25 October 2024
satellites are named after the ancient Indian mathematicians Bhāskara I and Bhāskara II. Bhaskara-I, weighing 444 kg at launch, was launched on 7 June 1979...
4 KB (267 words) - 10:26, 6 September 2024
Līlāvatī is a treatise by Indian mathematician Bhāskara II on mathematics, written in 1150 AD. It is the first volume of his main work, the Siddhānta...
7 KB (833 words) - 16:19, 25 October 2024
Bhaskar (disambiguation) Bhaskara's formula, another name (after Bhaskara II) for the quadratic formula Bhaskara's formula or Bhāskara I's sine approximation...
1 KB (169 words) - 05:24, 27 August 2023
History of algebra (section Bhāskara II)
and Indian syncopation may be derived from a common Babylonian source. Bhāskara II (1114 – c. 1185) was the leading mathematician of the 12th century. In...
121 KB (17,011 words) - 16:59, 12 November 2024
manuscript) Brahmagupta's mathematical advances were carried on further by Bhāskara II, a lineal descendant in Ujjain, who described Brahmagupta as the...
44 KB (5,849 words) - 12:17, 2 November 2024
mathematician and astronomer, and the author of the Maha-Siddhanta. The numeral II is given to him to distinguish him from the earlier and more influential Āryabhaṭa I...
4 KB (427 words) - 17:11, 25 October 2024
"Crown of treatises") is the major treatise of Indian mathematician Bhāskara II. He wrote the Siddhānta Śiromaṇi in 1150 when he was 36 years old. The...
4 KB (295 words) - 13:54, 3 April 2024
important contributions were made by scholars like Aryabhata, Brahmagupta, Bhaskara II, Varāhamihira, and Madhava. The decimal number system in use today was...
116 KB (14,798 words) - 16:00, 11 November 2024
(1060–1130) Pavuluri Mallana (11th century CE) Hemachandra (1087–1172 CE) Bhaskara II (1114–1185 CE) Someshvara III (1127–1138 CE) Śārṅgadeva (1175-1247) Thakkar...
10 KB (961 words) - 02:51, 23 September 2024
In mathematics, Bhāskara I's sine approximation formula is a rational expression in one variable for the computation of the approximate values of the trigonometric...
12 KB (1,754 words) - 19:25, 28 October 2024
{\displaystyle 92x^{2}+1=y^{2}} in his Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta circa 628. Bhaskara II in the 12th century and Narayana Pandit in the 14th century both found...
48 KB (6,613 words) - 19:47, 5 October 2024
were the most significant Sanskrit mathematics treatises after those of Bhaskara II, other than the Kerala school.: 52 He wrote the Ganita Kaumudi (lit...
5 KB (519 words) - 12:00, 7 November 2024
Bhāskara's wheel was a hypothetical perpetual-motion machine design created around 1150 CE by the Indian mathematician Bhāskara II. The wheel consisted...
2 KB (233 words) - 13:33, 14 September 2024
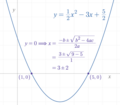
on algebra quoted by Bhāskara II. The modern quadratic formula is sometimes called Sridharacharya's formula in India and Bhaskara's formula in Brazil. The...
35 KB (5,783 words) - 20:49, 13 November 2024
Pāṭīgaṇita-sāra, he was probably a Shaivite Hindu. He was mentioned by Bhāskara II (12th century), and made apparent reference to Brahmagupta (7th century)...
7 KB (701 words) - 18:05, 10 November 2024
was found by Fermat and his contemporaries, and also by Jayadeva and Bhaskara II before them.) He also studied quadratic forms in full generality (as...
86 KB (10,828 words) - 14:51, 11 November 2024
Āryabhata, Brahmagupta, and Bhāskara I. His works were followed by later astronomers Śrīpati, Vateśvara, and Bhāskara II. Lalla also authored the Siddhāntatilaka...
64 KB (7,418 words) - 14:12, 15 October 2024
History of gravitational theory (section Bhāskara II)
direction you may throw them away, and never rise upwards from the earth. Bhāskara II (c. 1114 – c. 1185), another Indian mathematician and astronomer, describes...
88 KB (10,802 words) - 17:45, 15 November 2024
Chakravala method (redirect from Bhaskara lemma)
quadratic equations, including Pell's equation. It is commonly attributed to Bhāskara II, (c. 1114 – 1185 CE) although some attribute it to Jayadeva (c. 950 ~...
16 KB (3,302 words) - 15:51, 11 November 2024
(IAST: Bījagaṇita) was treatise on algebra by the Indian mathematician Bhāskara II. It is the second volume of his main work Siddhānta Shiromani ("Crown...
4 KB (352 words) - 09:55, 19 September 2024
Calculus (redirect from Calculus II)
and fourth powers allowed him to calculate the volume of a paraboloid. Bhāskara II (c. 1114–1185) was acquainted with some ideas of differential calculus...
74 KB (8,584 words) - 13:29, 1 November 2024
between 1976 and 1997 (Pick catalog). 1984 USSR stamp featuring Bhaskara-I, Bhaskara-II and Aryabhata satellites Illustration of Aryabhata spacecraft on...
8 KB (495 words) - 07:04, 10 November 2024
Varahamihira, ninth century Lalla, eleventh century Sripati and Bhaskara. The texts of Bhaskara have dedicated chapters on instruments and he calls them Yantra-adhyaya...
21 KB (2,180 words) - 13:28, 14 November 2024
jyotisha (astrology and astronomy) by Bhaskara II, a mathematician-astronomer from present-day India. Bhaskara II wrote Karana-kutuhala (literally, "Calculation...
5 KB (419 words) - 13:54, 3 April 2024
12th-century treatise, Lilavati, written by the Indian mathematician Bhāskara II wherein problems in arithmetic, algebra, geometry, etc. are discussed...
5 KB (523 words) - 20:21, 8 August 2024
Mathematics Mathematics Sanskrit Bhāskara II 1114 - 1185 C.E Karnataka Lilavati Mathematics Mathematics Sanskrit Bhāskara II 1114 - 1185 C.E Karnataka Bijaganita...
38 KB (256 words) - 10:42, 7 November 2024
himself a native of Kusumapura or Pataliputra (present day Patna, Bihar). Bhāskara I describes Aryabhata as āśmakīya, "one belonging to the Aśmaka country...
42 KB (4,761 words) - 04:06, 8 November 2024
Brahmagupta, and Bhāskara I. In turn, he influenced later generations of astronomers, including Āryabhaṭa II, Śrīpati, Vaṭeśvara, and Bhāskara II (who later...
5 KB (574 words) - 13:09, 31 August 2024