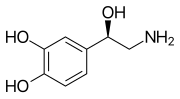
A catecholamine (/ˌkætəˈkoʊləmiːn/; abbreviated CA) is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl...
20 KB (2,075 words) - 08:55, 17 July 2024
Catecholamines up (Catsup) is a dopamine regulatory membrane protein that functions as a zinc ion transmembrane transporter (orthologous to ZIP7), and...
8 KB (759 words) - 14:59, 16 February 2024
Norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (redirect from Catecholamine releasing agent)
A norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (NDRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of norepinephrine (and epinephrine) and dopamine in the body...
7 KB (556 words) - 12:14, 10 December 2024
Monoamine-depleting agent (redirect from Catecholamine-depleting agent)
Monoamine-depleting agents are a group of drugs which reversibly deplete one or more of the monoamine neurotransmitters – serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine...
3 KB (252 words) - 06:58, 26 November 2024
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (redirect from Catecholamine O-methyltransferase)
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT; EC 2.1.1.6) is one of several enzymes that degrade catecholamines (neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine)...
29 KB (3,236 words) - 00:14, 10 July 2024
A norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) is a drug used for the treatment of clinical depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)...
6 KB (418 words) - 04:31, 25 July 2024
Monoamine precursor (redirect from Catecholamine precursors)
Monoamine precursors are precursors of monoamines and monoamine neurotransmitters in the body. The amino acids L-tryptophan and L-5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP;...
5 KB (357 words) - 09:42, 22 September 2024
Substituted phenethylamine (redirect from Catecholamine analogue)
citation needed] Numerous endogenous compounds – including hormones, catecholamines such as dopamine and noradrenaline, and many trace amines (e.g. adrenaline...
28 KB (701 words) - 15:15, 16 December 2024
Adrenaline (category Catecholamines)
work has been published using fluorimetric assays to measure total catecholamine concentrations, the method is too non-specific and insensitive to accurately...
57 KB (6,586 words) - 19:14, 15 November 2024
Monoaminergic activity enhancer (redirect from Catecholamine activity enhancer)
reduced activation of the enhancer regulation system and reduced brain catecholamine release with age. However, the key endogenous actors of the enhancer...
57 KB (5,873 words) - 22:03, 24 November 2024
Adrenal gland (section Catecholamines)
processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress...
49 KB (5,624 words) - 12:18, 14 December 2024
are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced...
33 KB (2,982 words) - 15:21, 27 November 2024
The catecholamines are a group of neurotransmitters composed of the endogenous substances dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), and adrenaline (epinephrine)...
68 KB (8,640 words) - 12:20, 23 October 2024
pathophysiology is not well understood, but a sudden massive surge of catecholamines such as adrenaline and norepinephrine from extreme stress or a tumor...
52 KB (5,864 words) - 09:23, 11 December 2024
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (redirect from Double tachycardia induced by catecholamines)
sudden death in response to exercise or stress. In those with CPVT, catecholamine release can lead to an abnormal heart rhythm or arrhythmia known as...
42 KB (4,764 words) - 15:55, 4 January 2024
catecholamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine. Concomitantly, adrenocortical cells secrete corticosteroids. These hormones (i.e., catecholamines...
22 KB (2,588 words) - 06:37, 28 November 2024
Chemical structures of the catecholamines Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic...
9 KB (891 words) - 19:06, 3 September 2024
Serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (redirect from Serotonin-catecholamine reuptake inhibitor)
antidepressant. Tetrabenazine, a similar agent to reserpine, which also depletes catecholamine stores, and to a lesser degree 5-HT, was shown to induce depression...
131 KB (15,715 words) - 14:19, 19 December 2024
doi:10.17744/mehc.26.4.w8u9h6uf5ybhapyl. Schildkraut JJ (1965). "The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders: A review of supporting evidence"...
57 KB (6,296 words) - 14:37, 17 December 2024
Cremaster muscle Cremasteric reflex Epinephrine Norepinephrine Catecholamine History of catecholamine research Limbic system Sympathetic ganglia Sympathetic trunk...
32 KB (3,734 words) - 09:06, 20 December 2024
maintain blood pressure. When urination begins, the PNS takes over, and catecholamine production changes. It may be the change in chemical production which...
3 KB (253 words) - 22:11, 1 December 2024
adrenal medulla. This causes the release of catecholamines. The chromaffin cells release catecholamines: ~80% of adrenaline (epinephrine) and ~20% of...
13 KB (1,403 words) - 12:24, 14 December 2024
These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they release catecholamines into the bloodstream which cause the most common symptoms, including...
151 KB (16,269 words) - 21:22, 3 December 2024
part of the adrenal gland, consisting of chromaffin cells that secrete catecholamines, including epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline)...
9 KB (929 words) - 16:33, 25 October 2024
L-DOPA (category Catecholamines)
(noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, l-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by...
16 KB (1,607 words) - 18:03, 18 December 2024
stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, leading to the release of catecholamines. This activation results in an increase in heart rate and blood pressure...
137 KB (14,249 words) - 23:27, 19 December 2024
Julius Axelrod (section Catecholamine research)
Nobel Committee honored him for his work on the release and reuptake of catecholamine neurotransmitters, a class of chemicals in the brain that include epinephrine...
17 KB (1,593 words) - 23:42, 11 December 2024
glucose levels: catabolic hormones (such as glucagon, cortisol and catecholamines) which increase blood glucose; and one anabolic hormone (insulin), which...
40 KB (4,146 words) - 07:03, 17 December 2024
provided evidence of selection for albinism as a means of increasing catecholamine levels, which promote adaptive feeding and sleep behaviors in Astyanax...
74 KB (8,245 words) - 02:13, 15 December 2024
oxidise monoamines (including catecholamines) and methylate the hydroxyl groups of the phenyl moiety of catecholamines. These enzymes can be targeted...
7 KB (757 words) - 22:26, 10 September 2024