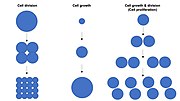
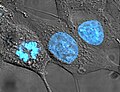
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which...
41 KB (4,763 words) - 21:20, 21 January 2025
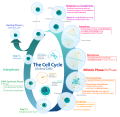
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These...
78 KB (9,079 words) - 16:48, 22 January 2025
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane; many cells contain...
60 KB (6,269 words) - 16:45, 2 January 2025
Mitosis (redirect from Mitotic cell division)
part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives...
70 KB (7,275 words) - 03:33, 10 February 2025
An asymmetric cell division produces two daughter cells with different cellular fates. This is in contrast to symmetric cell divisions which give rise...
30 KB (3,691 words) - 02:37, 10 June 2024
cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle...
37 KB (4,869 words) - 09:19, 17 May 2024
come from the division of pre-existing cells. Viruses are not considered in cell biology – they lack the characteristics of a living cell and instead are...
41 KB (5,252 words) - 13:40, 31 January 2025
DNA in the cell nucleus. It has been shown to be a potent tumor suppressor gene, meaning that its primary role is to control cell division. Since this...
52 KB (5,913 words) - 20:45, 30 May 2024
multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely...
102 KB (11,741 words) - 15:55, 9 February 2025
increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at...
5 KB (646 words) - 22:07, 8 February 2025
Cleavage (embryo) (redirect from Eight-cell stage)
cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with...
26 KB (2,959 words) - 13:07, 2 December 2024
Tubulin (section Cell division)
drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division.[citation needed] In...
32 KB (3,392 words) - 02:56, 13 January 2025
method of cell division involving the formation of a cell plate or phragmoplast that separates the new daughter cells. Plant cells have cell walls composed...
19 KB (2,232 words) - 12:17, 8 January 2025
of the cell cycle. During the prophase in the process of cell division called mitosis, the centrosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell. The mitotic...
24 KB (2,616 words) - 01:32, 30 January 2025
Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after development, that multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate...
52 KB (5,961 words) - 18:30, 27 November 2024
Hayflick limit (section The belief in cell immortality)
number of times a normal somatic, differentiated human cell population will divide before cell division stops. The concept of the Hayflick limit was advanced...
16 KB (1,840 words) - 10:38, 14 January 2025
Gene (section DNA replication and cell division)
replication and cell division. The growth, development, and reproduction of organisms relies on cell division; the process by which a single cell divides into...
100 KB (11,198 words) - 02:57, 29 January 2025
(TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer....
30 KB (3,409 words) - 03:26, 14 November 2024
Epithelium (redirect from Epithelial cell)
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost...
32 KB (2,908 words) - 09:23, 27 December 2024
non-differentiated somatic cells form the germ line and, in Cnidaria, differentiated somatic cells are the source of the germline. Mitotic cell division is only seen...
15 KB (1,793 words) - 18:18, 6 February 2025
cell nucleus (from Latin nucleus or nuculeus 'kernel, seed'; pl.: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually...
88 KB (9,965 words) - 18:00, 4 December 2024
all cells come from pre-existing cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure in all living organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. Cell theory...
26 KB (3,347 words) - 00:27, 16 November 2024
means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to induce DNA damage (so that DNA repair can augment chemotherapy)...
155 KB (17,536 words) - 10:20, 28 January 2025
Meiosis (redirect from Reduction division)
reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It...
76 KB (8,978 words) - 18:05, 11 February 2025
Biology (section Cell structure)
individual cells have all the characteristics of life, although they opposed the idea that (3) all cells come from the division of other cells, continuing...
133 KB (13,826 words) - 14:38, 26 January 2025
plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation,...
18 KB (1,978 words) - 05:33, 11 December 2024
Caenorhabditis elegans (redirect from P4 cell)
daughter cells of the first cell division are called the AB cell (containing PAR-6 and PAR-3) and the P1 cell (containing PAR-1 and PAR-2). A second cell division...
95 KB (10,941 words) - 18:45, 18 December 2024
daughter cell A cell resulting from the division of an initial progenitor, known as the parent cell. Generally two daughter cells are produced per division. Denoising...
321 KB (29,858 words) - 04:58, 16 February 2025
Aneuploidy (redirect from Aneuploid cell)
cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. About 68% of human solid tumors are aneuploid. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the...
37 KB (3,585 words) - 01:37, 12 January 2025
Hypha (section Classification based on cell division)
the cells. Yeasts form pseudohyphae. They are the result of a sort of incomplete budding where the cells elongate but remain attached after division. Some...
15 KB (1,585 words) - 22:40, 14 November 2024