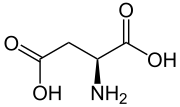
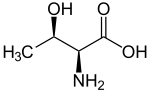
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its...
27 KB (2,690 words) - 10:20, 3 September 2024
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. The word "proteinogenic" means "protein...
38 KB (1,631 words) - 14:51, 30 August 2024
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far...
98 KB (10,151 words) - 03:53, 21 October 2024
nine essential amino acids for humans, accounting for 35% of the essential amino acids in muscle proteins and 40% of the preformed amino acids required...
29 KB (3,420 words) - 20:54, 29 August 2024
all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids. Most amino acids...
31 KB (3,929 words) - 13:49, 28 June 2024
occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded...
19 KB (1,699 words) - 08:58, 7 November 2024
Essential amino acids (EAAs) are amino acids that are necessary to build proteins in an organism. The source of complete EAAs are both animal and plant-based...
6 KB (445 words) - 23:26, 4 June 2024
Valine (redirect from 2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid)
side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. Valine is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it; it must be...
14 KB (1,188 words) - 12:26, 29 October 2024
An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromatic ring. Among the 20 standard amino acids, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine...
11 KB (1,066 words) - 00:48, 10 September 2024
Phenylalanine (redirect from 2-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid)
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula C 9H 11NO 2. It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl...
28 KB (2,386 words) - 21:26, 25 July 2024
Leucine (redirect from 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid)
or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which...
27 KB (4,132 words) - 00:11, 7 September 2024
Protein metabolism (redirect from Amino acid metabolism)
code for a specific amino acid. Ribosomes translate the codons to their respective amino acids. In humans, non-essential amino acids are synthesized from...
27 KB (2,828 words) - 23:11, 3 November 2024
Methionine (redirect from 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid)
Met or M) (/mɪˈθaɪəniːn/) is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile...
30 KB (3,080 words) - 18:02, 28 October 2024
Protein quality is the digestibility and quantity of essential amino acids for providing the proteins in correct ratios for human consumption. There are...
33 KB (1,799 words) - 01:22, 25 October 2024
Histidine (redirect from 2-Amino-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid)
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated...
24 KB (2,533 words) - 17:14, 12 October 2024
Lysine (redirect from Amino acid K)
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+3 form...
68 KB (7,547 words) - 20:48, 20 October 2024
Threonine (redirect from 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid)
chain containing a hydroxyl group, making it a polar, uncharged amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be...
16 KB (1,370 words) - 13:48, 29 October 2024
digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) is a method of evaluating the quality of a protein based on both the amino acid requirements of humans...
15 KB (1,700 words) - 17:20, 27 August 2024
Complete protein (section Amino acid profile)
protein that contains an adequate proportion of each of the nine essential amino acids necessary in the human diet. People who eat a varied diet generally...
7 KB (574 words) - 17:38, 20 November 2024
8 or 9 essential amino acids. The consensus seems to lean towards 9 since histidine is not synthesized in adults. There are five amino acids which humans...
46 KB (5,128 words) - 05:45, 5 November 2024
Tryptophan (redirect from (2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid)
tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Tryptophan is named after the digestive enzymes trypsin, which were...
52 KB (5,315 words) - 22:39, 7 October 2024
Tyrosine (redirect from 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid)
one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group...
26 KB (2,535 words) - 10:13, 21 October 2024
biochemistry, non-coded or non-proteinogenic amino acids are distinct from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids (21 in eukaryotes), which are naturally encoded...
27 KB (2,864 words) - 19:08, 10 October 2024
Isoleucine (category Essential amino acids)
branched-chain, aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it. Essential amino acids are necessary in the human...
15 KB (1,404 words) - 19:31, 15 November 2024
Nutrient (redirect from Essential nutrient)
water. Essential nutrients for animals are the energy sources, some of the amino acids that are combined to create proteins, a subset of fatty acids, vitamins...
40 KB (4,001 words) - 02:42, 14 November 2024
Taurine (redirect from 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid)
Taurine (/ˈtɔːriːn/), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a non-proteinogenic naturally occurring amino sulfonic acid that is widely distributed in animal tissues...
29 KB (3,081 words) - 19:17, 11 November 2024
vegetarian and vegan foods may provide an insufficient amount of some essential amino acids, making protein combining with multiple complementary foods necessary...
21 KB (2,604 words) - 03:44, 18 November 2024
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that are required by humans and other animals for normal physiological function that cannot be synthesized...
24 KB (2,951 words) - 01:14, 14 November 2024
Proline (category Alpha-Amino acids)
it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is...
23 KB (2,240 words) - 05:28, 11 November 2024
A ketogenic amino acid is an amino acid that can be degraded directly into acetyl-CoA, which is the precursor of ketone bodies and myelin, particularly...
7 KB (821 words) - 23:32, 6 September 2024