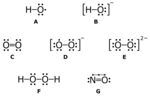
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (O2), water, and hydrogen peroxide....
70 KB (8,492 words) - 09:37, 20 November 2024
Radical (chemistry) (redirect from Oxygen radicals)
nervous system, while too much uric acid causes gout. Reactive oxygen species or ROS are species such as superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radical...
40 KB (4,613 words) - 06:59, 17 October 2024
Reactive nitrogen species act together with reactive oxygen species (ROS) to damage cells, causing nitrosative stress. Therefore, these two species are...
7 KB (787 words) - 06:24, 27 January 2024
the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the...
55 KB (6,161 words) - 22:43, 25 June 2024
All living cells produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a byproduct of metabolism. ROS are reduced oxygen intermediates that include the superoxide radical...
47 KB (5,571 words) - 20:10, 2 January 2024
triplet ground state of O2. In terms of its chemical reactivity, however, singlet oxygen is far more reactive toward organic compounds. It is responsible for...
29 KB (2,933 words) - 11:39, 5 November 2024
Antioxidant (redirect from Oxygen radical scavenger)
particularly during the Jurassic period – as chemical defences against reactive oxygen species that are byproducts of photosynthesis. Originally, the term antioxidant...
94 KB (10,255 words) - 23:25, 13 November 2024
Hydroperoxyl (category Reactive oxygen species)
formula HO2, also written HOO•. This species plays an important role in the atmosphere and as a reactive oxygen species in cell biology. The molecule has...
5 KB (409 words) - 15:15, 16 May 2024
addition to direct O2 formation, these processes often produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydroxyl radicals (OH•), superoxide (O2•-), and...
16 KB (1,561 words) - 22:19, 15 November 2024
oxidative phosphorylation is a vital part of metabolism, it produces reactive oxygen species such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, which lead to propagation...
88 KB (9,674 words) - 18:37, 5 November 2024
of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Current scientific consensus states that UCP2 and UCP3 perform proton transportation only when activation species are...
17 KB (1,876 words) - 06:54, 27 April 2024
Respiratory burst (or oxidative burst) is the rapid release of the reactive oxygen species (ROS), superoxide anion (O− 2) and hydrogen peroxide (H 2O 2),...
22 KB (2,555 words) - 10:14, 5 November 2023
Oxygen is a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal...
115 KB (11,930 words) - 07:22, 28 October 2024
of the phagosome and the lysosome produces a phagolysosome. The reactive oxygen species, superoxides and hypochlorite bleach within the phagolysosomes...
97 KB (9,827 words) - 07:13, 20 November 2024
thiosulfate. Reactive oxygen species Reactive nitrogen species Reactive carbonyl species Giles, GI; Jacob, C (2002). "Reactive sulfur species: an emerging...
1 KB (120 words) - 01:00, 19 March 2022
Photodynamic therapy (section Reactive oxygen species)
triplet oxygen (3O2) and produce radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS), crucial to the Type II mechanism. These species include singlet oxygen (1O2)...
79 KB (9,506 words) - 22:52, 7 November 2024
important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all...
39 KB (4,277 words) - 04:57, 2 November 2024
has since been expanded to encompass oxidative damage from other reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), or peroxynitrite (OONO−)...
25 KB (3,070 words) - 02:52, 24 May 2024
be the most effective treatment, but research is still ongoing. Reactive oxygen species are upregulated during inflammation as part of the immune response...
13 KB (1,458 words) - 17:59, 22 June 2024
Superoxide (category Reactive oxygen species)
formula O−2. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron...
15 KB (1,611 words) - 20:23, 10 August 2024
NADPH oxidase (redirect from NAD(P)H:oxygen oxidoreductase)
NADPH oxidases (NOXes) are one of the major sources of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), and they still are the focus of extensive research interest...
25 KB (2,841 words) - 14:26, 5 March 2024
antioxidants and protect cellular components from being oxidized by reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can form as a result of drought, injury, herbicides...
48 KB (5,242 words) - 20:43, 12 October 2024
multiple cell types and tissues. Proteases, integrins, pH, and reactive oxygen species are just few of the currently known factors that can activate TGF-β...
67 KB (8,184 words) - 20:48, 31 October 2024
inflammasome activation, with age, cellular components accumulate reactive oxygen species (ROS). These free radicals can damage DNA, lipid, and protein and...
26 KB (3,020 words) - 17:03, 14 May 2024
They perform key roles in lipid metabolism and the reduction of reactive oxygen species. Peroxisomes are involved in the catabolism of very long chain...
33 KB (3,863 words) - 06:13, 27 July 2024
dismutase and catalase activities which prevented injuries from reactive oxygen species, helping promote the livelihood of tissues. Pucheu, S.; Boucher...
1 KB (144 words) - 13:32, 4 February 2020
Α-O (redirect from Alpha-oxygen)
α-O (alpha-oxygen) is a reactive oxygen species formed from an oxygen-atom abstraction (OAT) from nitrous oxide (N2O) by alpha-iron (α-Fe) catalysts. The...
3 KB (388 words) - 18:42, 26 September 2023
molecularly diagnose pyruvate kinase deficiency. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are chemically reactive forms of oxygen. In human lung cells, ROS has been shown...
33 KB (4,042 words) - 02:51, 1 February 2024
MTORC1 (section Reactive oxygen species)
efficient, the unreduced oxygen molecules in the mitochondrial cortex may accumulate and begin to produce reactive oxygen species. It is important to note...
69 KB (7,807 words) - 19:19, 19 September 2024
Α-Ketoglutaric acid (section Reactive oxygen species)
and ammonia; reduce the cellular levels of potentially toxic reactive oxygen species; and synthesize the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid. It...
44 KB (5,479 words) - 18:49, 17 November 2024