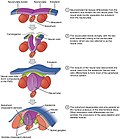
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural...
41 KB (4,610 words) - 23:01, 30 October 2024
Neural crest cells are multipotent cells required for the development of cells, tissues and organ systems. A subpopulation of neural crest cells are the...
37 KB (4,546 words) - 00:36, 30 November 2023
The trunk neural crest or truncal neural crest is one of the regions of neural crest in the embryo. The trunk neural crest lies between the vagal and sacral...
2 KB (271 words) - 11:30, 29 November 2023
create the neural tube. The figure demonstrates the development of the neural plate into the neural tube, which is where the neural crest cells are derived...
18 KB (2,461 words) - 04:22, 16 July 2024
Neurulation (redirect from Neural tube defect, folate-sensitive)
vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula. The process...
26 KB (3,288 words) - 21:36, 24 November 2024
migration of neural crest cells during embryonic development (though some of the genes involved also affect the neural tube). Neural crest cells are stem...
49 KB (5,792 words) - 18:24, 7 November 2024
The cranial neural crest is one of the four regions of the neural crest. The cranial neural crest arises in the anterior and populates the face and the...
3 KB (326 words) - 03:40, 26 August 2021
Germ layer (section Neural crest)
embryo's epiblast. The ectoderm develops into the surface ectoderm, neural crest, and the neural tube. The surface ectoderm develops into: epidermis, hair, nails...
14 KB (1,365 words) - 17:30, 16 October 2024
neural plate, which invaginates to form the neural tube and neural crest. The surface ectoderm gives rise to most epithelial tissues, and the neural plate...
16 KB (1,844 words) - 03:04, 1 September 2024
long after the closure of the neural plate. Development of the olfactory placode requires the presence underlying neural crest-derived mesenchymal tissue...
19 KB (2,059 words) - 11:42, 6 October 2024
has been disputed. Other research suggested that pleiotropic change in neural crest cell regulating genes was the common cause of shared traits seen in many...
35 KB (3,415 words) - 02:02, 12 December 2024
22q11 deletions (DiGeorge Syndrome). The neural crest, specifically a population known as the cardiac neural crest, directly contributes to the aorticopulmonary...
14 KB (1,596 words) - 15:29, 8 November 2023
Nociceptor (section Neural development)
(PNS). The neural-crest stem cells split from the neural tube as it closes, and nociceptors grow from the dorsal part of this neural-crest tissue. They...
23 KB (2,811 words) - 20:21, 17 October 2024
internally located neural tube The externally located epidermis The neural crest cells, which develop in the region between the neural tube and epidermis...
13 KB (1,522 words) - 20:50, 23 September 2024
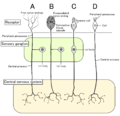
Nervous system (redirect from Neural)
called the neural tube, whereas the future PNS appears as two strips of tissue called the neural crest, running lengthwise above the neural tube. The sequence...
72 KB (9,249 words) - 21:36, 14 December 2024
differentiation from the neural crest. NRG1 plays important roles in the development of neural crest derivatives. It is required for neural crest cells to migrate...
19 KB (2,450 words) - 00:59, 1 November 2024
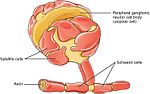
ganglion. The dorsal root ganglia develop in the embryo from neural crest cells, not neural tube. Hence, the spinal ganglia can be regarded as gray matter...
9 KB (1,019 words) - 15:07, 2 May 2024
the posterior and lateral area of the neural plate, the same region that the neural crest arises from. Neural crest defects were found to occur in mouse...
16 KB (1,951 words) - 10:50, 18 October 2024
Mesenchyme (section Neural mesenchyme)
skeletal muscle. Neural crest cells (NCCs) form from neuroectoderm, instead of the primary mesenchyme, from morphogenic signals of the neural crest. The EMT occurs...
18 KB (1,683 words) - 05:09, 30 November 2024
Eye development (section Neural crest)
fissure the blood vessels enter the eye. Several layers such as the neural tube, neural crest, surface ectoderm, and mesoderm contribute to the development...
16 KB (1,919 words) - 17:18, 12 July 2024
populations, cranial neural crest and ectodermal placodes. The components of the sensory nervous system of the head are derived from the neural crest and from an...
42 KB (4,693 words) - 18:54, 1 December 2024
formation of the neural crest cells and the neural tube, which arise from the joining of the neural folds. The formation of the neural fold is initiated...
14 KB (1,551 words) - 21:27, 15 May 2024
Adult stem cell (section Neural crest stem cells)
which appears to represent a remnant of the stem cells of the embryonic neural crest. Similar cells have been found in the gastrointestinal tract, sciatic...
52 KB (5,961 words) - 18:30, 27 November 2024
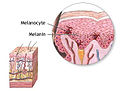
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer...
20 KB (2,278 words) - 01:49, 19 November 2024
neurulation stage—the neural folds close to form the neural tube, bringing together the neural crest cells at the neural crest. The neural crest runs the length...
169 KB (18,815 words) - 13:42, 21 December 2024
the midbrain, and the forebrain. The types of neuroectoderm include: Neural crest pigment cells in the skin ganglia of the autonomic nervous system dorsal...
2 KB (246 words) - 16:58, 8 May 2024
dural folds, or reflections. The dura mater is primarily derived from neural crest cells, with postnatal contributions from the paraxial mesoderm. The dura...
15 KB (1,713 words) - 15:46, 10 November 2024
Due to its embryonic derivation from paraxial mesoderm (as opposed to neural crest, from which many other craniofacial bones are derived), it has been posited...
14 KB (1,788 words) - 06:14, 30 October 2024
craniofacial malformations occur via: apoptosis of neural crest cells, interference with neural crest cell migration, as well as the disruption of sonic...
43 KB (4,771 words) - 08:52, 21 December 2024
by them. The ENS is nicknamed the "second brain". It is derived from neural crest cells. The enteric nervous system is capable of operating independently...
20 KB (2,198 words) - 22:39, 2 December 2024