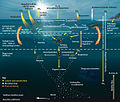
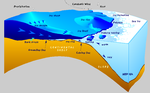
A marine food web is a food web of marine life. At the base of the ocean food web are single-celled algae and other plant-like organisms known as phytoplankton...
158 KB (16,553 words) - 04:16, 17 September 2024
webs, detrital food webs, marine food webs, aquatic food webs, soil food webs, Arctic (or polar) food webs, terrestrial food webs, and microbial food...
84 KB (8,765 words) - 23:53, 26 August 2024
Fishing down the food web is the process whereby fisheries in a given ecosystem, "having depleted the large predatory fish on top of the food web, turn to increasingly...
25 KB (2,734 words) - 16:29, 26 April 2024
These impact marine ecosystems and food webs and may result in consequences as yet unrecognised for the biodiversity and continuation of marine life forms...
96 KB (10,600 words) - 05:09, 2 September 2024
the general foundation of the ocean food chain, particularly phytoplankton which are key primary producers. Marine invertebrates exhibit a wide range of...
304 KB (29,025 words) - 10:22, 26 September 2024
foundation of the marine food web, polynyas are a critical food source for a variety of organisms such as fish, birds, and marine mammals. Listed below...
17 KB (1,977 words) - 20:32, 11 September 2024
Viral shunt (section Effect on the marine food web)
on food webs across marine environments as well as on a more macro scale on the global carbon budget. Viral shunt influences carbon cycling in marine environments...
33 KB (4,090 words) - 19:08, 14 June 2024
Plankton (redirect from Marine plankton)
provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish, and baleen whales. Marine plankton include bacteria...
62 KB (6,470 words) - 14:07, 8 September 2024
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically...
18 KB (2,034 words) - 00:37, 16 September 2024
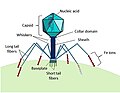
bacteriophages which infect and destroy marine bacteria and control the growth of phytoplankton at the base of the marine food web. Bacteriophages are harmless to...
88 KB (9,234 words) - 19:15, 14 June 2024
conditions, and survive wherever they are." Marine microorganisms serve as "the foundation of all marine food webs, recycling major elements and producing...
232 KB (21,388 words) - 09:31, 2 June 2024
microbial food webs maintain higher trophic levels. Thus, these webs are crucial for energy flow and nutrient cycling in both freshwater and marine ecosystems...
10 KB (1,308 words) - 02:15, 27 September 2024
ocean food chains. When pesticides are incorporated into the marine ecosystem, they quickly become absorbed into marine food webs. Once in the food webs, these...
79 KB (11,112 words) - 17:19, 4 August 2024
Zooplankton (section Role in food webs)
levels in marine food webs, zooplankton also play an important role as “recyclers” of carbon and other nutrients that significantly impact marine biogeochemical...
77 KB (7,077 words) - 07:14, 27 September 2024
Ramsar site (section Marine/coastal wetlands)
Permanent: (A) Permanent shallow marine waters: Less than 6m deep at low tide; including sea bays and straits (B) Marine subtidal aquatic beds: Underwater...
8 KB (781 words) - 15:22, 8 April 2024
scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account...
64 KB (6,650 words) - 03:41, 22 September 2024
The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how...
27 KB (3,653 words) - 12:53, 6 June 2024
Aquatic ecosystem (section Marine ecosystems)
chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web. A marine coastal ecosystem is a marine ecosystem which occurs where the land meets the ocean...
15 KB (2,913 words) - 22:31, 16 August 2024
Bioluminescence (redirect from Marine Phosphorescence)
organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms...
75 KB (8,096 words) - 09:16, 17 August 2024
shifting baselines in 1995 and authored the seminal paper, Fishing down marine food webs, in 1998. For working to protect the environment, he earned a place...
17 KB (1,690 words) - 17:08, 8 September 2024
of climate-active marine aerosols. The diagram on the right shows links among the ocean's biological pump and the pelagic food web and the ability to...
140 KB (12,943 words) - 00:56, 12 August 2024
important is because it plays a prominent role when interwoven with other food webs. Most of the solar energy reaching the Earth is in the range of visible...
25 KB (2,955 words) - 08:17, 23 May 2024
Rachel; Cole, Matthew (2018-01-01). "Chapter 11 - Microplastics in Marine Food Webs". In Zeng, Eddy Y. (ed.). Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments...
161 KB (19,124 words) - 03:25, 2 September 2024
toxic to either one or many members of the marine food web. This page focuses on phycotoxins produced by marine microalgae; however, freshwater algae and...
27 KB (2,521 words) - 15:56, 11 July 2024
Trophic level (category Food chains)
trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. Within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms...
26 KB (3,071 words) - 16:51, 27 August 2024
Phytoplankton form the lowest trophic level of marine food webs and thus capture light energy and materials to provide food and energy for hundreds of thousands...
72 KB (8,392 words) - 00:23, 7 April 2024
Thysanoessa is a genus of the krill that play critical roles in the marine food web. They're abundant in Arctic and Antarctic areas, feeding on zooplankton...
10 KB (1,104 words) - 19:28, 17 September 2024
world have made their way to the Arctic marine food web. This poses a health risk to people who eat "country food" (traditional Inuit foodstuffs). As whales...
12 KB (1,085 words) - 16:11, 9 July 2024
to their small size and position in the lower trophic level of many marine food webs, the levels of methylmercury they bioaccumulate are very low, reducing...
8 KB (982 words) - 21:34, 22 September 2024
Ocean (redirect from Marine (ocean))
ocean food chains. When pesticides are incorporated into the marine ecosystem, they quickly become absorbed into marine food webs. Once in the food webs, these...
127 KB (16,965 words) - 18:02, 20 August 2024