The Vinča culture [ʋîːnt͜ʃa], also known as Turdaș culture, Turdaș–Vinča culture or Vinča-Turdaș culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast...
36 KB (3,554 words) - 11:17, 29 September 2024
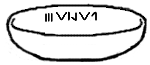
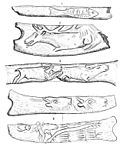
The Vinča symbols are a set of undeciphered symbols found on artifacts from the Neolithic Vinča culture and other "Old European" cultures of Central and...
19 KB (2,143 words) - 03:49, 30 September 2024
continuity at the Transition from the Starčevo to the Vinča culture group. From Starčevo to Vinča culture, Current problems of the Transition Period, Proceedings...
18 KB (1,873 words) - 15:02, 2 July 2024
archaeological site that gives its name to the Neolithic Vinča culture, is located in the village. Vinča is located on the confluence of the Bolečica river...
48 KB (5,528 words) - 19:37, 9 May 2023
Vinča-Belo Brdo (Serbian: Винча-Бело брдо) is an archaeological site in Vinča, a suburb of Belgrade, Serbia. The tell of Belo Brdo ('White Hill') is almost...
15 KB (1,494 words) - 18:28, 20 May 2024
Tărtăria tablets (category Vinča culture)
the account of their discovery which associates the tablets with the Vinča culture and on indirect radiocarbon evidence, some scientists propose that the...
15 KB (1,818 words) - 02:28, 4 September 2024
culture Lengyel culture Linear Pottery culture Sesklo culture Solnitsata Starčevo culture Tisza culture Vinča culture Old European script Carnac Stones -...
14 KB (1,361 words) - 10:58, 29 August 2024
Old Europe (archaeology) (redirect from Old European Culture)
Sesklo culture figurine Sesklo and Dimini culture ceramics Dimini culture ceramic vessel Vinča culture figurine Vinča culture ceramics Vinča culture, Tartaria...
27 KB (2,295 words) - 14:22, 4 October 2024
excavations confirmed the existence of two distinct Neolithic settlements (Vinča culture), separated by around 200 meters. The earlier settlement (Fafos I) featured...
3 KB (205 words) - 15:44, 12 October 2024
stelae Butmir culture Vinča culture Beaker culture Baden culture Botai culture Khvalynsk culture Mamai-Hora Samara culture Sintashta culture Yersinia pestis...
68 KB (7,012 words) - 21:48, 13 October 2024
Narva culture, the Funnelbeaker culture, the Linear Pottery culture, the Cardium pottery culture, the Vinča culture, the early Helladic culture, and the...
79 KB (9,140 words) - 04:49, 15 October 2024
Southeastern Europe Proto-Indo-Europeans Samara culture Sredny Stog culture Varna culture Vinča culture Yamnaya culture "7,000 years ago, Neolithic optical art...
104 KB (11,333 words) - 22:15, 8 October 2024
culture Cycladic art History of Bulgaria Old Europe Prehistoric art Prehistory of Southeastern Europe Prehistoric Romania Varna culture Vinča culture...
7 KB (541 words) - 20:06, 17 June 2024
Belgrade (category Starčevo–Körös–Criș culture)
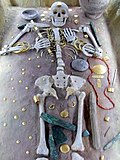
prehistoric Europe. Also associated with the Vinča culture are anthropomorphic figurines such as the Lady of Vinča, the earliest known copper metallurgy in...
199 KB (17,165 words) - 16:57, 15 October 2024
Neolithic (redirect from Neolithic American culture)
northwestern Europe by around 4500 BC. The Vinča culture may have created the earliest system of writing, the Vinča signs, though archaeologist Shan Winn believes...
78 KB (7,974 words) - 14:40, 5 October 2024
Kerma culture was an early civilization centered in Kerma, Sudan. It flourished from around 2500 BC to 1500 BC in ancient Nubia. The Kerma culture was based...
34 KB (3,959 words) - 12:01, 29 September 2024
region during the First Temperate Neolithic was developed further by the Vinča culture. It was noted for dark-burnished pottery, and fuelling a population...
44 KB (5,251 words) - 06:56, 30 September 2024
findings suggest an ancestor cult with preserved skulls of the dead. The Vinča culture may have created the earliest system of writing. The megalithic temple...
55 KB (5,870 words) - 10:04, 12 October 2024
The Capsian culture was a late Mesolithic and Neolithic culture centered in the Maghreb that lasted from about 8,000 to 2,700 BC.[is this date calibrated...
10 KB (1,000 words) - 03:30, 3 October 2024
prehistoric period on the territory of modern-day Serbia are the Starčevo and Vinča cultures dating back to 6400–6200 BC. Serbia's strategic location between two...
24 KB (2,255 words) - 20:10, 3 August 2024
The Funnel(-neck-)beaker culture, in short TRB or TBK (German: Trichter(-rand-)becherkultur, Dutch: Trechterbekercultuur; Danish: Tragtbægerkultur; c...
38 KB (3,931 words) - 00:03, 24 September 2024
Vinca (/ˈvɪŋkə/; Latin: vincire "to bind, fetter") is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, native to Europe, northwest Africa and southwest...
16 KB (1,327 words) - 18:38, 5 January 2024
48 °F). The oldest traces of human activity in Săliștea date back to the Vinča culture of the Middle Neolithic. The Tărtăria tablets dated 5300 BC were discovered...
8 KB (966 words) - 20:17, 14 February 2024
back to at least 5700 BC. One of the largest prehistoric cultures of Europe, the Vinča culture, evolved from the Belgrade area in the 6th millennium BC...
59 KB (5,667 words) - 06:01, 14 August 2024
Miloje Vasić (section Vinča)
river, site of Vinča-Belo Brdo is one of the most important prehistoric localities in Europe. It gave name, Vinča culture, to the culture of the late Neolithic...
22 KB (2,010 words) - 02:32, 12 October 2024
Kurgan hypothesis (redirect from Kurgan culture)
Cucuteni–Trypillia culture. Repercussions of the migrations extend as far as the Balkans and along the Danube to the Vinča culture in Serbia and Lengyel culture in Hungary...
34 KB (3,818 words) - 02:41, 26 August 2024
in Hungary. It was a continuation of the Starčevo culture and strongly influenced by the Vinča culture. Some of the archeological sites where artifacts...
7 KB (719 words) - 05:19, 3 April 2024
of the La Tène culture Vinča, Belgrade, Serbia, of the Vinča culture Abri de la Madeleine (Dordogne, France), of the Magdalenian culture Le Moustier (Dordogne...
5 KB (452 words) - 18:56, 16 October 2024