Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far...
94 KB (10,035 words) - 17:56, 13 April 2025
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its...
27 KB (2,693 words) - 06:58, 9 March 2025
Amino acid biosynthesis is the set of biochemical processes (metabolic pathways) by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes...
31 KB (3,932 words) - 13:25, 23 December 2024
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation from RNA. The word "proteinogenic" means...
38 KB (1,633 words) - 22:41, 12 March 2025
A branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) is an amino acid having an aliphatic side-chain with a branch (a central carbon atom bound to three or more carbon atoms)...
29 KB (3,409 words) - 18:33, 18 March 2025
biochemistry, non-coded or non-proteinogenic amino acids are distinct from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids (21 in eukaryotes), which are naturally encoded...
27 KB (2,864 words) - 05:44, 3 March 2025
An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromatic ring. Among the 20 standard amino acids, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine...
11 KB (1,092 words) - 15:10, 29 January 2025
digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) is a method of evaluating the quality of a protein based on both the amino acid requirements of humans...
15 KB (1,700 words) - 17:20, 27 August 2024
D-Amino acids are amino acids where the stereogenic carbon alpha to the amino group has the D-configuration. For most naturally-occurring amino acids,...
13 KB (1,589 words) - 09:16, 7 November 2024
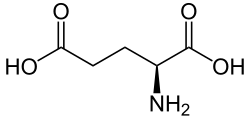
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis...
36 KB (3,308 words) - 20:38, 25 March 2025
Amino acid replacement is a change from one amino acid to a different amino acid in a protein due to point mutation in the corresponding DNA sequence....
25 KB (1,451 words) - 07:20, 22 May 2024
Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) is a protein quality method proposed in March 2013 by the Food and Agriculture Organization to replace...
14 KB (1,216 words) - 02:36, 4 March 2025
A ketogenic amino acid is an amino acid that can be degraded directly into acetyl-CoA, which is the precursor of ketone bodies and myelin, particularly...
7 KB (821 words) - 23:32, 6 September 2024
Peptide (redirect from Amino acid chain length)
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have...
22 KB (2,438 words) - 10:54, 4 April 2025
Protein metabolism (redirect from Amino acid metabolism)
biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism. The steps of...
27 KB (2,828 words) - 15:30, 9 January 2025
amino acid, sulfur-containing amino acid, or SAA is an amino acid containing element sulfur. Common sulfur amino acids include: Proteinogenic amino acids...
1 KB (180 words) - 22:36, 12 April 2025
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC or AAAD), also known as DOPA decarboxylase (DDC), tryptophan decarboxylase, and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase...
17 KB (1,946 words) - 13:59, 4 January 2025
Protein primary structure (redirect from Amino acid sequence)
linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end...
21 KB (2,603 words) - 22:06, 23 November 2024
A glucogenic amino acid (or glucoplastic amino acid) is an amino acid that can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis. This is in contrast to...
5 KB (520 words) - 15:37, 29 April 2024
Glycine (redirect from Amino acetic acid)
amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids....
41 KB (3,776 words) - 21:18, 15 April 2025
The Strecker amino acid synthesis, also known simply as the Strecker synthesis, is a method for the synthesis of amino acids by the reaction of an aldehyde...
10 KB (1,093 words) - 12:49, 6 February 2025
Genetic code (section Non-standard amino acids)
links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA...
74 KB (8,070 words) - 00:43, 4 April 2025
Biochemistry (section Nucleic acids)
inorganic (for example, water and metal ions) or organic (for example, the amino acids, which are used to synthesize proteins). The mechanisms used by cells...
59 KB (6,459 words) - 16:17, 15 March 2025
aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other...
56 KB (6,064 words) - 02:51, 13 April 2025
Protein structure (redirect from Amino acid residue)
arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers...
38 KB (4,246 words) - 13:59, 17 January 2025
properties of a specific amino acid. In glycine, the simplest amino acid, the R group is a hydrogen atom, but in all other amino acids it is contains one or...
47 KB (5,963 words) - 19:19, 14 March 2025
Beta-peptide (redirect from Beta amino acid)
β-amino acids, in which the amino group is attached to the β-carbon (i.e. the carbon two atoms away from the carboxylate group). The parent β-amino acid...
8 KB (879 words) - 02:30, 19 November 2024
Biosynthesis (redirect from Biosynthesis of amino acids)
Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production...
61 KB (6,770 words) - 20:03, 8 March 2025
biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms...
105 KB (10,954 words) - 06:09, 7 April 2025
Methionine (redirect from 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid)
or M) (/mɪˈθaɪəniːn/) is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile...
30 KB (3,083 words) - 04:36, 29 March 2025