In electromagnetism and electronics, electromotive force (also electromotance, abbreviated emf, denoted E {\displaystyle {\mathcal {E}}} ) is an energy...
54 KB (6,921 words) - 19:05, 24 September 2024
Counter-electromotive force (counter EMF, CEMF, back EMF), is the electromotive force (EMF) manifesting as a voltage that opposes the change in current...
4 KB (499 words) - 20:15, 5 July 2023
magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (emf). This phenomenon, known as electromagnetic induction, is the...
44 KB (4,699 words) - 19:14, 28 September 2024
formula describe the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire (sometimes called Laplace force), the electromotive force in a wire loop moving through...
60 KB (8,548 words) - 21:18, 7 September 2024
Electrochemical gradient (redirect from Proton electromotive force)
across the membrane, then the difference in electric potential generates a force that drives ion diffusion until the charges are balanced on both sides of...
24 KB (2,770 words) - 23:32, 3 September 2024
Triboelectric effect (redirect from Contact electromotive force)
needed to understand how the triboelectric effect can generate an electromotive force. Generally, increased humidity (water in the air) leads to a decrease...
87 KB (9,334 words) - 14:24, 27 August 2024
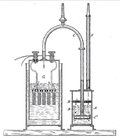
Voltaic pile (section Electromotive force)
by cloth or cardboard soaked in brine, which increased the total electromotive force. When the top and bottom contacts were connected by a wire, an electric...
17 KB (1,886 words) - 17:04, 12 May 2024
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field. Michael...
26 KB (2,885 words) - 21:36, 9 September 2024
the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in a generator). On a macroscopic...
25 KB (2,909 words) - 04:51, 27 September 2024
electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). One volt is defined as...
16 KB (1,834 words) - 10:15, 27 September 2024
magnetic flux passing through a loop of conductive wire will cause an electromotive force, and therefore an electric current, in the loop. The relationship...
10 KB (1,122 words) - 06:58, 22 August 2024
kinematic viscosity, electric current, electric charge, electric dipole, electromotive force (or electric potential difference), electrical resistance, capacitance...
84 KB (1,627 words) - 18:23, 15 September 2024
well as of permanent magnet motors. Back electromotive force (EMF) is also known as the counter-electromotive force. It is the voltage that occurs in electric...
17 KB (1,979 words) - 13:33, 17 September 2024
name, that is: Electromotive force = Current × Resistance Ohm brought into order a host of puzzling facts connecting electromotive force and electric current...
163 KB (20,960 words) - 15:03, 5 September 2024
Standard electrode potential (redirect from Electromotive series)
IUPAC "Gold Book" defines it as; "the value of the standard emf (electromotive force) of a cell in which molecular hydrogen under standard pressure is...
8 KB (1,169 words) - 10:34, 11 September 2024
imagine that we attach, in series with impedance Ze, a source with electromotive force E equal to Vθ but directed to oppose Vθ, as shown in Figure 2b. No...
23 KB (2,901 words) - 11:11, 21 June 2024
state, the electromotive force is proportional to the current produced. "That is, that the resistance, the ratio of the applied electromotive force (or voltage)...
47 KB (6,036 words) - 21:21, 6 October 2024
Electromagnetism (redirect from Electromagnetic force)
electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules...
38 KB (4,150 words) - 20:01, 3 October 2024
magnetostatics, the force of attraction or repulsion between two current-carrying wires (see first figure below) is often called Ampère's force law. The physical...
17 KB (2,912 words) - 22:58, 6 October 2023
machine or force in a linear machine. The second role is to generate an electromotive force (EMF). In the armature, an electromotive force is created...
10 KB (1,328 words) - 13:44, 31 July 2024
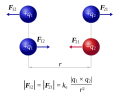
Coulomb's law (redirect from Electric force)
of force between two electrically charged particles at rest. This electric force is conventionally called the electrostatic force or Coulomb force. Although...
42 KB (6,758 words) - 17:30, 21 September 2024
Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), approved the volt as the unit for electromotive force, the ampere as the unit for electric current, and the coulomb as...
8 KB (940 words) - 17:13, 16 September 2024
angular impulse by Maxwell). E is called the electromotive force by Maxwell. The term electromotive force is nowadays used for voltage, but it is clear...
36 KB (3,941 words) - 01:45, 29 August 2024
magnetomotive force was coined by Henry Augustus Rowland in 1880. Rowland intended this to indicate a direct analogy with electromotive force. The idea of...
6 KB (741 words) - 19:26, 14 January 2024
Electric Currents. Fleming described the orientation of the induced electromotive force by referencing the motion of the conductor and the direction of the...
16 KB (2,089 words) - 04:18, 15 September 2024
active source. An active network contains one or more sources of electromotive force. Practical examples of such sources include a battery or a generator...
10 KB (1,238 words) - 09:27, 23 January 2024
is exactly balanced by a counter-electromotive force so that no current flows. If this counter-electromotive force is increased, the cell becomes an...
8 KB (904 words) - 13:27, 28 May 2024
Galvani incorrectly thought the source of electricity (or source of electromotive force (emf), or seat of emf) was in the animal, Volta incorrectly thought...
22 KB (3,000 words) - 01:34, 6 October 2024
the sign of their Seebeck coefficients. The Seebeck effect is the electromotive force (emf) that develops across two points of an electrically conducting...
29 KB (3,859 words) - 05:40, 26 September 2024
_{\mathbf {B} }}{\mathrm {d} t}},} which indicates that the induced electromotive force E {\displaystyle {\mathcal {E}}} and the rate of change in magnetic...
10 KB (1,151 words) - 17:57, 20 September 2024