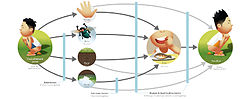
In medicine, public health, and biology, transmission is the passing of a pathogen causing communicable disease from an infected host individual or group...
36 KB (4,072 words) - 15:35, 22 September 2024
conditions are affected as a result of monetary policy decisions Pathogen transmission, the passing of a disease from an infected host individual or group...
4 KB (418 words) - 14:25, 20 August 2024
virus. Some pathogens which have more than one mode of transmission are also anisotropic, meaning that their different modes of transmission can cause different...
32 KB (3,483 words) - 21:54, 17 December 2024
patients already combating another condition. Infectivity involves pathogen transmission through direct contact with the bodily fluids or airborne droplets...
41 KB (4,224 words) - 09:04, 25 December 2024
Cross-species transmission (CST), also called interspecies transmission, host jump, or spillover, is the transmission of an infectious pathogen, such as a...
33 KB (3,985 words) - 17:25, 19 March 2024
A human pathogen is a pathogen (microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus) that causes disease in humans. The human physiological...
14 KB (1,579 words) - 07:05, 30 June 2024
Infection (section Primary pathogens)
This may be due high pathogen load favoring avoidance of other groups, which may reduce pathogen transmission, or a high pathogen load preventing the creation...
118 KB (12,826 words) - 19:55, 3 January 2025
Epidemic (section Changes in transmission)
established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is...
32 KB (3,290 words) - 22:50, 27 September 2024
Christian Gospels Pathogen transmission in medicine and biology This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Oral transmission. If an internal...
324 bytes (68 words) - 14:01, 13 September 2022
Fecal–oral route (redirect from Fecal-oral transmission)
route or orofecal route) describes a particular route of transmission of a disease wherein pathogens in fecal particles pass from one person to the mouth...
15 KB (1,420 words) - 21:16, 19 October 2024
sylvatic cycle, also enzootic or sylvatic transmission cycle, is a portion of the natural transmission cycle of a pathogen. Sylvatic refers to the occurrence...
3 KB (282 words) - 12:12, 30 May 2023
Spillover infection (redirect from Pathogen spillover)
further human-to-human transmission, as occurs, for example, with rabies, anthrax, histoplasmosis or hydatidosis. Other zoonotic pathogens are able to be transmitted...
22 KB (2,493 words) - 20:52, 17 September 2024
– transmission, entry/invasion after evading/overcoming defense, establishment, and replication of disease-causing microscopic organisms (pathogens) inside...
45 KB (5,250 words) - 20:42, 6 November 2024
relative. Other negative effects may include the increased risk of pathogen transmission as the encounter rate of hosts increases. Cannibalism, however,...
42 KB (5,091 words) - 23:11, 20 November 2024
Argas persicus (section Pathogen Transmission)
infected membrane. This was tested using artificial inoculation. If the pathogen infects humans due to A. persicus, it would likely be as an incidental...
10 KB (1,466 words) - 22:28, 1 October 2024
better suited for the research into the contagious pathogens due to the reduced risk of transmission afforded by a remote or isolated location. The basic...
4 KB (401 words) - 15:25, 3 January 2025
between the habitat patches, which can lead to reduced gene flow and pathogen transmission between patches. Animals such as the bobcat are particularly sensitive...
74 KB (8,249 words) - 22:53, 23 December 2024
Zoonosis (redirect from Transmission of pathogens from animals to humans)
(rabies). In contrast, transmission can also occur via an intermediate species (referred to as a vector), which carry the disease pathogen without getting sick...
82 KB (7,184 words) - 18:55, 1 January 2025
intensive, have the potential to provide valuable insights into pathogen transmission dynamics. The structure of the host contact network significantly...
62 KB (6,946 words) - 22:22, 30 December 2024
needle and syringe method (needlestick). Less waste, eliminate pathogen transmission, and injuries. At least 300,000 needlestick related injuries occurred...
33 KB (3,824 words) - 08:20, 2 October 2024
Plant pathology (redirect from Seed transmitted pathogen)
caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Plant pathology involves the study of pathogen identification...
13 KB (1,291 words) - 19:47, 20 September 2024
Natural reservoir (section Disease transmission)
specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces, or upon which the pathogen primarily depends for its survival. A reservoir...
21 KB (2,513 words) - 19:25, 28 October 2024
Respiratory droplet (redirect from Respiratory droplet transmission)
William D. (2011-01-01). "The role of particle size in aerosolised pathogen transmission: A review". Journal of Infection. 62 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.jinf...
20 KB (2,065 words) - 19:04, 27 November 2024
this creates a coevolutionary arms race between pathogen transmission and host avoidance. For a pathogen to move to a new host, it must exploit regions...
35 KB (4,151 words) - 05:46, 25 December 2024
Fomite (redirect from Fomite transmission)
(Toilet Plume). Many common objects can sustain a pathogen until a person comes in contact with the pathogen, increasing the chance of infection. The likely...
19 KB (2,087 words) - 16:40, 9 November 2024
certain epidemiologically important pathogens, which require additional control measures to effectively prevent transmission. Universal precautions are also...
55 KB (5,430 words) - 05:24, 30 December 2024
Plant disease (redirect from Plant pathogen)
Plant diseases are diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that...
27 KB (2,415 words) - 17:24, 6 November 2024
types of organisms can then be further classified as a pathogen based on its mode of transmission. This includes the following: food borne, airborne, waterborne...
14 KB (1,740 words) - 11:44, 9 October 2024
Wolbachia (section Step 3: Vertical transmission)
of mosquito-borne diseases, and it decreases their efficacy of pathogen transmission because older mosquitoes are more likely to have become carriers...
82 KB (8,675 words) - 14:17, 16 December 2024
Horizontal transmission is the transmission of organisms between biotic and/or abiotic members of an ecosystem that are not in a parent-progeny relationship...
8 KB (923 words) - 15:15, 2 May 2024