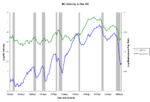
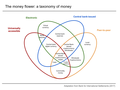
In macroeconomics, money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several...
48 KB (5,428 words) - 16:46, 12 December 2024
can be used as investable asset, but makes up the smallest part of the money supply. Float affects the amount of currency available to trade and countries...
5 KB (711 words) - 01:18, 18 January 2024
debts, public and private", in the case of the United States dollar. The money supply of a country comprises all currency in circulation (banknotes and coins...
57 KB (7,044 words) - 23:41, 30 November 2024
Money creation, or money issuance, is the process by which the money supply of a country, or an economic or monetary region, is increased. In most modern...
32 KB (3,690 words) - 08:06, 11 December 2024
monetary economics, the money multiplier is the ratio of the money supply to the monetary base (i.e. central bank money). If the money multiplier is stable...
36 KB (4,324 words) - 00:05, 22 July 2024
value of the money supply; in this case the money supply curve is perfectly elastic. The demand for money intersects with the money supply to determine...
36 KB (4,847 words) - 14:36, 19 November 2024
Monetary base (redirect from Narrow money supply)
base (also base money, money base, high-powered money, reserve money, outside money, central bank money or, in the UK, narrow money) in a country is...
7 KB (867 words) - 00:29, 13 November 2024
little of the supply of broad money is physical currency. For example, in December 2010 in the U.S., of the $8,853.4 billion of broad money supply (M2), only...
42 KB (4,796 words) - 17:09, 13 December 2024
Monetary policy (redirect from Money policy)
exchange rate system. A third monetary policy strategy, targeting the money supply, was widely followed during the 1980s, but has diminished in popularity...
80 KB (9,704 words) - 17:47, 20 December 2024
Deflation (section Money supply-side deflation)
happens when supply is high (when excess production occurs), when demand is low (when consumption decreases), or when the money supply decreases (sometimes...
68 KB (7,964 words) - 12:43, 20 December 2024
Fixed money wage rate, unemployed resources and constant returns to scale are assumed. Thus domestic price level is kept constant, and the supply of domestic...
25 KB (3,793 words) - 18:32, 2 October 2023
how many times money is changing hands. The concept relates the size of economic activity to a given money supply, and the speed of money exchange is one...
8 KB (1,034 words) - 15:27, 23 August 2024
Fractional-reserve banking (section Money supply)
liabilities are considered money in their own right (see commercial bank money), fractional-reserve banking permits the money supply to grow beyond the amount...
41 KB (4,848 words) - 17:09, 22 December 2024
of money is a stronger property than neutrality of money. It holds that not only is the real economy unaffected by the level of the money supply but...
13 KB (1,737 words) - 04:25, 15 November 2023
directly proportional to the amount of money in circulation (i.e., the money supply), and that the causality runs from money to prices. This implies that the...
41 KB (5,266 words) - 21:41, 5 December 2024
onwards, made much larger variations in the supply of money possible. Rapid increases in the money supply have taken place a number of times in countries...
122 KB (14,086 words) - 22:26, 22 December 2024
the money supply in the 1920s which led to an unsustainable credit-driven boom. In the Austrian view, it was this inflation of the money supply that...
186 KB (21,805 words) - 22:31, 15 December 2024
Demand deposit (redirect from Bank money)
usually considered money and form the greater part of the narrowly defined money supply of a country. Simply put, these are deposits in the bank that can be...
3 KB (362 words) - 03:13, 15 March 2024
Liquidity trap (redirect from Money gift)
liquidity trap are interest rates that are close to zero and changes in the money supply that fail to translate into changes in the price level. John Maynard...
20 KB (2,196 words) - 19:35, 13 August 2024
economics, broad money is a measure of the amount of money, or money supply, in a national economy including both highly liquid "narrow money" and less liquid...
5 KB (527 words) - 10:38, 22 December 2023
States), a money bill or supply bill is a bill that solely concerns taxation or government spending (also known as appropriation of money), as opposed...
19 KB (2,522 words) - 18:51, 5 November 2024
IS–LM model (section LM (liquidity-money) curve)
preference–money supply" (LM) curves illustrates a "general equilibrium" where supposed simultaneous equilibria occur in both the goods and the money markets...
29 KB (3,737 words) - 19:12, 30 November 2024
Reserve requirement (section Effects on money supply)
monetary authority as a tool in monetary policy, to influence the country's money supply by limiting or expanding the amount of lending by the banks. Monetary...
29 KB (2,696 words) - 12:12, 26 November 2024
official interest rate. The monetarist theory states that variations in the money supply have major influences on national output in the short run and on price...
26 KB (2,977 words) - 01:04, 22 December 2024
Modern monetary theory (redirect from Modern Money Theory)
control of the money supply will inevitably lead to hyperinflation. MMT's main tenets are that a government that issues its own fiat money: Can pay for...
64 KB (6,976 words) - 00:21, 7 December 2024
Stagflation (section Supply shock)
policies that simultaneously hinder industrial output and expand the money supply too rapidly. The stagflation of the 1970s led to a reevaluation of Keynesian...
43 KB (5,101 words) - 23:14, 17 December 2024
on which type of money supply one is discussing. M1 for example is commonly used to refer to narrow money, coins, cash, and other money equivalents that...
20 KB (3,043 words) - 11:24, 16 September 2024
The real demand for money is defined as the nominal amount of money demanded divided by the price level. For a given money supply the locus of income-interest...
20 KB (2,834 words) - 17:55, 31 October 2024
AD–AS model (redirect from Aggregate Demand-Aggregate Supply model)
targeting money supply as its central policy variable. In contrast, central banks since around 1990 have largely abandoned controlling money supply, instead...
22 KB (2,849 words) - 16:48, 2 September 2024
Digital currency (redirect from Electronic money)
inside an online game. Digital money can either be centralized, where there is a central point of control over the money supply (for instance, a bank), or...
52 KB (5,716 words) - 21:12, 1 December 2024