the Tiszapolgár culture, although these objects appear at increasing frequency among the Bodrogkeresztúr culture. The Bodrogkeresztúr people appear to...
4 KB (455 words) - 00:41, 29 June 2024
BC Gold idol, Bodrogkeresztúr culture, c. 4000-3600 BC Copper ornaments, Tiszapolgar culture, c. 4000 BC Ceramic vessel, Baden culture, c. 4th millennium...
44 KB (5,251 words) - 23:17, 16 November 2024
Old Europe (archaeology) (redirect from Old European Culture)
Gumelnița culture copper axe Hamangia culture figurine Hamangia culture ceramic sculpture Bodrogkeresztúr culture gold idol Boian culture ceramic Tiszapolgár...
27 KB (2,295 words) - 14:22, 4 October 2024
The Tiszapolgár culture (4500–4000 BC) was an Eneolithic archaeological culture in Central Europe in the Carpathian Basin, in the Great Hungarian Plain...
6 KB (470 words) - 10:22, 13 March 2024
The Baden culture or Baden-Pécel culture is a Chalcolithic archaeological culture dating to c. 3520–2690 BC. It is found in Central and Southeast Europe...
13 KB (1,202 words) - 13:20, 4 May 2024
Prehistory of Transylvania (redirect from Bodrogkeresztúr-Gorneşti culture)
the Bodrogkeresztúr-Gornești culture. The craft of pottery reaches a peak, exemplified by the great number of exquisitely decorated pots. Cultures typical...
81 KB (10,675 words) - 07:53, 4 August 2024
modified their culture. Varna culture, Bulgaria, 4500 BC Cucuteni-Trypillia pottery, Ukraine Maidanetske, Ukraine, c. 3800 BC Bodrogkeresztúr culture, Hungary...
84 KB (8,820 words) - 12:00, 12 November 2024
The Coţofeni culture (Serbian: Kocofeni), also known as the Baden-Coţofeni culture, and generally associated with the Usatove culture, was an Early Bronze...
8 KB (741 words) - 07:44, 6 November 2024
Neolithic samples: Transdanubian Lengyel culture, Bodrogkeresztúr culture, Kőrös culture, Alföld Linear Pottery culture. The genome of Christopher Corvinus...
38 KB (4,124 words) - 16:06, 5 September 2024
leaving credible traces of their presence. A Neolithic Tiszapolgár–Bodrogkeresztúr culture necropolis was found in Senta. The first historic population that...
23 KB (1,904 words) - 03:02, 11 November 2024
Neolithic samples: Transdanubian Lengyel culture, Bodrogkeresztúr culture, Kőrös culture, Alföld Linear Pottery culture. The genome of Christopher Corvinus...
64 KB (6,951 words) - 04:42, 27 October 2024
were highlighted fragments of pottery attributed to the Gornești–Bodrogkeresztúr culture, which attest to an important habitation, in a settlement probably...
10 KB (899 words) - 05:01, 24 October 2024
Vinča-Belo Brdo (category Vinča culture)
belonging to the Bodrogkeresztúr culture, a very small Baden culture settlement and some evidence of visits by people of the Kostolac culture. There was a...
15 KB (1,494 words) - 10:58, 6 November 2024
belongs to P. Patay’s Szakálhát type, which is typical of the Bodrogkeresztúr culture. Some of the finds from the hoard never reached Naturhistorische...
2 KB (275 words) - 09:06, 2 October 2023
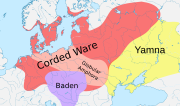
to Bodrogkeresztur. Mallory and Adams, Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, gives the bare date "fifth millennium BCE", while the Khvalynsk culture, its...
13 KB (1,336 words) - 00:51, 14 November 2024
to some underdeveloped regions existing there. Varna culture artefacts, 4500 BC Bodrogkeresztúr gold idol, 4000-3500 BC BC Cucuteni-Trypillia figurine...
13 KB (1,622 words) - 21:32, 9 November 2024
Baalberge group (redirect from Baalberge culture)
by the Baden culture (an Indo-Europeanised culture according to Gimbutas) and the Bodrogkeresztúr culture and the posture of the corpses, laid on their...
19 KB (2,456 words) - 02:56, 9 August 2023
Carpathian Basin] (PDF). Népek és kultúrák a Kárpát-medencében [Peoples and cultures in the Carpathian Basin] (in Hungarian). Magyar Nemzeti Múzeum. ISBN 978-615-5209-56-7...
52 KB (1,759 words) - 21:06, 16 October 2024
archaeological discoveries date back to the Copper Age, from the Bodrogkeresztúr culture, with evidence suggesting that people have inhabited this region...
3 KB (196 words) - 05:54, 19 October 2024
and beat Schlik in three consecutive battles at Tarcal (20 January), Bodrogkeresztúr (23 January), and Tokaj (31 January). Thanks to these victories Klapka...
58 KB (7,388 words) - 06:59, 21 October 2024
Verteba Cave (category Cucuteni–Trypillia culture)
neighbouring Badrazhy group, as well as the more distant Bodrogkeresztúr and Lublin-Volhynia cultures. Many samples of the Koshylovetska pottery group display...
40 KB (4,648 words) - 01:40, 5 November 2024
(Turkey) at Barcın(5), Chalcolithic Southeastern Europe (Romania at Bodrogkeresztur), Chalcolithic of the Levant (Israel)(70), and a Minoan from Lasithi...
92 KB (9,258 words) - 21:24, 6 November 2024
continuation of Bodrogkeresztúr-Gorneşti culture 3500 BC – Baden culture begins in Lower Tisza/Crişana as a continuation of Bodrogkeresztúr-Gorneşti culture 3000–2800...
45 KB (4,373 words) - 07:51, 6 October 2024
Ruski Krstur (section Culture)
(úr) means "lord." "Keresztúr," as seen in the Hungarian place name "Bodrogkeresztúr," likely refers to a crucifix (Our Lord on the Cross on the Bodrog...
11 KB (989 words) - 17:31, 3 November 2024
Borsod–Abaúj–Zemplén County (redirect from Culture of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén)
Bánhorváti Bánréve Becskeháza Bekecs Berente Beret Berzék Bodroghalom Bodrogkeresztúr Bodrogkisfalud Bodrogolaszi Bogács Boldogkőújfalu Boldogkőváralja Boldva...
38 KB (2,675 words) - 05:19, 3 November 2024
Sátoraljaújhely (section Culture)
occupation lasted only a few days. Skirmishes near Tarcal on January 22 and Bodrogkeresztúr on January 23 ended with Austrian withdrawals. On January 27, Captain...
94 KB (12,217 words) - 12:47, 21 November 2024