Glucose transporter 1 (or GLUT1), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein that...
22 KB (2,591 words) - 01:29, 18 January 2024
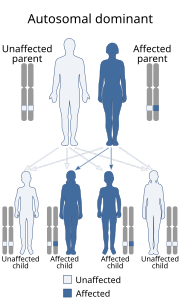
GLUT1 deficiency syndrome, also known as GLUT1-DS, De Vivo disease or Glucose transporter type 1 deficiency syndrome, is an autosomal dominant genetic...
23 KB (2,649 words) - 09:57, 25 February 2024
subclasses. Class I comprises the well-characterized glucose transporters GLUT1-GLUT4. Class II comprises: GLUT5 (SLC2A5), a fructose transporter in enterocytes...
16 KB (1,327 words) - 21:12, 2 October 2024
a fetal skeletal muscle cell line, using a GLUT1 cDNA probe and shown to share 64.4% identity with GLUT1. Although GLUT3 was found to be expressed in...
6 KB (768 words) - 17:17, 14 October 2022
Toe walking (section GLUT1 Deficiency Syndrome)
that can only manage toe walking. Toe walking is a symptom in those with GLUT1 deficiency Syndrome. There are many health professionals who assess and...
16 KB (1,919 words) - 15:00, 18 September 2024
of glucose transporters; however, the most significant for study are GLUT1-4. GLUT1 and GLUT3 are located in the plasma membrane of cells throughout the...
5 KB (773 words) - 19:45, 31 December 2023
the same cell membrane, is specific to one type or family of molecules. GLUT1 is a named carrier protein found in almost all animal cell membranes that...
25 KB (2,646 words) - 00:12, 19 June 2024
contributor to familial PED is a mutation in the GLUT1 gene, SLC2A1, which codes for the transporter GLUT1, a protein responsible for glucose entry across...
17 KB (2,208 words) - 02:17, 9 November 2024
different diseases and agents. It is a symptom of several diseases, including GLUT1 deficiency syndrome, Lesch–Nyhan syndrome, phenylketonuria, and Huntington...
2 KB (166 words) - 13:43, 18 August 2024
Tumor hypoxia (section GLUT1 transporter expression)
gradient. GLUT1 is the most abundantly expressed of the family thought to maintain basal glucose transport in almost all cell types. GLUT1 levels, in...
52 KB (5,517 words) - 00:16, 7 June 2024
lesions cause abnormal electrochemical discharges that result in seizures GLUT1 deficiency syndrome Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and other eating...
21 KB (2,196 words) - 22:03, 4 November 2024
frontal horns, is also important. Ventriculomegaly occurs in those with GLUT1 deficiency syndrome. Neuroinflammation Normal pressure hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus...
8 KB (891 words) - 03:01, 26 June 2024
fourteen GLUT proteins. Class I GLUTs include GLUT1, one of the most studied isoforms, and GLUT2. GLUT1 is found in various tissues like the red blood...
29 KB (3,180 words) - 20:49, 15 September 2024
they naturally mutate. For instance, erythrocyte-specific coexpression of GLUT1 with stomatin constitutes a compensatory mechanism in mammals that are unable...
15 KB (1,889 words) - 15:09, 11 September 2024
of tumor cells. Utilizing a mouse model, they[who?] identified that both Glut1 and glucose metabolism increased in TANs found within a mouse who possessed...
54 KB (5,770 words) - 22:58, 3 November 2024
include genetic disorders such as Down syndrome, Fragile X syndrome and GLUT1 Deficiency Syndrome; childhood infections such as meningitis or encephalitis...
9 KB (1,033 words) - 06:10, 25 July 2024
at a higher rate. An analysis of mRNA levels of GLUT1 and GLUT4 in cardiac muscles show that GLUT1 plays a larger role in cardiac muscles than it does...
25 KB (2,960 words) - 12:51, 29 August 2024
linked to mutations in the GLUT1 glucose transporter which can result in transient energy deficits in the basal ganglia. See GLUT1 deficiency syndrome. Diagnosis...
18 KB (2,290 words) - 18:42, 30 October 2024
glucose can no longer diffuse out of the cell. The glucose transporter GLUT1 is produced by most cell types and is of particular importance for nerve...
121 KB (12,789 words) - 20:45, 27 October 2024
into cells via insulin-sensitive pathways (insulin regulated transporters GLUT1 and GLUT4). Instead, fructose is taken in by GLUT5. Fructose in muscles...
17 KB (1,949 words) - 21:52, 2 September 2024
mainly in specialized cells whereas the glucose transporters, most notably GLUT1, transport DHA in most cells, where recycling back to ascorbic acid generates...
14 KB (1,277 words) - 16:44, 24 July 2024
Group; Aquaporin 1 – water transporter, defines the Colton Blood Group; Glut1 – glucose and L-dehydroascorbic acid transporter; MCT1 – Monocarboxylate...
65 KB (7,856 words) - 03:36, 10 November 2024
2% Reabsorption (mmol/day) Concentration Apical transport proteins SGLT2 SGLT1 Basolateral transport proteins GLUT2 GLUT1 Other reabsorption features...
5 KB (250 words) - 01:59, 9 October 2021
import ascorbate across plasma membranes. The Hexose Transporter proteins GLUT1, GLUT3 and GLUT4 transfer only the oxydized dehydroascorbic acid (DHA) form...
145 KB (15,192 words) - 20:29, 5 November 2024
Ehlers–Danlos syndrome Frontotemporal dementia caused by mutations in progranulin GLUT1 deficiency (DeVivo syndrome) Haploinsufficiency of A20 Haploinsufficiency...
11 KB (1,181 words) - 01:44, 9 February 2024
hypertension causes mesangial cells to stretch which causes induced expression of GLUT1 leading to increased cellular glucose. The repetition of stretching and...
14 KB (1,601 words) - 02:15, 3 December 2023
of the cell. One example of a uniport mediated transport protein is GLUT1. GLUT1 is a transmembrane protein, which means it spans the entire width of...
9 KB (939 words) - 20:56, 14 April 2024
Rab-GTPase-activating protein TBC1D1, which ultimately induces fusion of GLUT1 vesicles with the plasma membrane. AMPK stimulates glycolysis by activating...
65 KB (7,149 words) - 04:45, 26 August 2024
eye–head movements, termed aberrant gaze saccades, are an early symptom of GLUT1 deficiency syndrome in infancy.[non-primary source needed] When the brain...
29 KB (3,820 words) - 15:22, 12 September 2024
Patel; Joseph E Chen; et al. (June 11, 2013). "ATM and GLUT1-S490 phosphorylation regulate GLUT1 mediated transport in skeletal muscle". PLOS One. 8 (6):...
5 KB (515 words) - 20:05, 18 June 2024