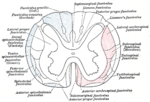
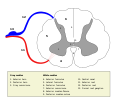
The lateral corticospinal tract (also called the crossed pyramidal tract or lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus) is the largest part of the corticospinal tract...
5 KB (560 words) - 16:48, 18 February 2024
divisions of the corticospinal tract, the lateral corticospinal tract and the anterior corticospinal tract. The lateral corticospinal tract neurons cross...
5 KB (623 words) - 04:15, 12 June 2024
The corticospinal tract conducts impulses from the brain to the spinal cord. It is made up of a lateral and anterior tract. The corticospinal tract is...
16 KB (1,678 words) - 15:49, 19 May 2024
The anterior corticospinal tract (also called the ventral corticospinal tract, medial corticospinal tract, direct pyramidal tract, or anterior cerebrospinal...
4 KB (383 words) - 16:51, 27 August 2024
and lateral corticospinal tract. It is one of the three tracts which make up the anterolateral system: anterior and lateral spinothalamic tract, spinotectal...
14 KB (1,583 words) - 03:27, 23 October 2024
Spinal cord (redirect from Spinal cord tract)
tract, the tectospinal tract and the reticulospinal tract. The rubrospinal tract descends with the lateral corticospinal tract, and the remaining three...
43 KB (5,117 words) - 05:03, 26 October 2024
Pronator quadratus muscle (section Spinal tracts)
role in that action. The lateral corticospinal tract is responsible for the motor pathway of the pronator quadratus. This tract begins in the precentral...
5 KB (577 words) - 18:09, 4 May 2024
Anterolateral corticospinal tract is a subdivision of the corticospinal tract in the spinal cord. It is formed by approximately 2% of the corticospinal fibers...
874 bytes (85 words) - 01:03, 18 November 2020
oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is...
6 KB (639 words) - 05:34, 2 January 2024
the corticospinal tract decussates and becomes the lateral corticospinal tract. The nerve signal will continue down the lateral corticospinal tract until...
8 KB (890 words) - 18:48, 25 October 2024
cord as the lateral corticospinal tract. Fibers that do not cross over in the brainstem travel down the separate ventral corticospinal tract and most of...
5 KB (590 words) - 16:45, 17 January 2024
within the lateral tegmentum medial to the spinocerebellar tract, and posterior to the spinothalamic tract. It descends with the corticospinal tract (and other...
5 KB (471 words) - 07:55, 23 October 2024
decussate (intersect) within the lower medulla oblongata to form the lateral corticospinal tract on each side of the spinal cord. The fibers that do not decussate...
6 KB (520 words) - 10:40, 12 August 2024
making up the rubrospinal tract, which runs ventral to the lateral corticospinal tract. As stated earlier, the rubrospinal tract is more important in non-primate...
8 KB (867 words) - 17:45, 9 November 2024
neck. The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, the other being the corticospinal tract. The corticobulbar tract originates in the primary...
5 KB (531 words) - 15:02, 2 September 2024
decussates, or crosses, in the medulla oblongata, specifically in the lateral corticospinal tract. The signal continues down through the anterior horn of the spinal...
7 KB (817 words) - 16:24, 4 May 2024
proprioception (joint sense). Lateral corticospinal tract dysfunction produces spasticity and dorsal spinocerebellar tract dysfunction causes ataxia.[citation...
9 KB (912 words) - 22:28, 24 February 2024
Extrapyramidal system Pyramidal tract Corticospinal tract or Cerebrospinal fibers Lateral corticospinal tract Anterior corticospinal tract Corticopontine fibers...
19 KB (1,385 words) - 14:40, 26 October 2024
is very small and runs ventral to the lateral corticospinal tract. Descending fibers of the rubro-olivary tract project from the parvocellular red nucleus...
4 KB (326 words) - 07:53, 31 October 2024
Since the corticospinal tract is interrupted, the pontine reticulospinal and the medial and lateral vestibulospinal biased extension tracts greatly overwhelm...
14 KB (1,521 words) - 20:48, 1 September 2024
Motor neuron (redirect from Motor tract)
cord: Lateral corticospinal tract Rubrospinal tract Lateral reticulospinal tract Vestibulospinal tract Medial reticulospinal tract Tectospinal tract Anterior...
26 KB (2,987 words) - 08:15, 27 April 2024
a result of compromised anterior and lateral corticospinal tract, anterior grey matter and spinocerebellar tract. There is also a loss in nociception...
28 KB (3,033 words) - 00:49, 9 December 2023
Grey columns (redirect from Lateral gray column)
Sobue G, Li M, Hashizume Y, Tanaka F, Mitsuma T (Jan 1997). "The lateral corticospinal tract and spinal ventral horn in X-linked recessive spinal and bulbar...
22 KB (2,764 words) - 14:19, 21 October 2024
associated with the following:[citation needed] Interruption of the lateral corticospinal tracts: Ipsilateral spastic paralysis below the level of the lesion...
13 KB (1,691 words) - 19:22, 2 July 2024
cord. Above the basal ganglia the corticospinal tract is a part of the corona radiata. Below the basal ganglia the tract is called cerebral crus (a part...
9 KB (1,052 words) - 11:37, 27 August 2024
including: Clinical findings mainly eyeball is down and out ipsilateral lateral squint. Ptosis present as the levator palpebrae superioris nerve supply...
4 KB (263 words) - 07:49, 8 May 2024
Once at the pyramids, the corticospinal tracts decussate and the signal goes down the lateral corticospinal tract until it reaches the ventral horns of...
8 KB (877 words) - 12:02, 23 October 2024
of the same cerebral hemisphere in which it began; the motor lateral corticospinal tract then decussates once during its descent to control movement of...
4 KB (436 words) - 08:20, 24 September 2024
premotor cortex and primary motor cortex → lateral corticospinal tract). The rubrospinal and lateral corticospinal tracts are subsequently involved in control...
4 KB (382 words) - 12:06, 9 October 2024
Extrapyramidal system (redirect from Extra-pyramidal tract)
the tracts of the motor cortex that reach their targets by traveling through the pyramids of the medulla. The pyramidal tracts (corticospinal tract and...
4 KB (457 words) - 22:24, 29 August 2024