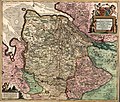
The Lower Saxon Circle (German: Niedersächsischer Reichskreis) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire. It covered much of the territory of the...
11 KB (552 words) - 08:55, 21 October 2024
imperial circles as part of the Imperial Reform: the Bavarian Circle the Franconian Circle the Saxon Circle the Swabian Circle the Upper Rhenish Circle the...
7 KB (683 words) - 13:08, 21 October 2024
In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, though by declining numbers of people. Lower Saxony borders on (from north...
65 KB (6,642 words) - 04:20, 15 November 2024
Electorate itself remained officially Protestant. Entries are listed by Imperial Circle (introduced 1500, 1512) even for territories that ceased to exist prior...
51 KB (709 words) - 22:00, 28 October 2024
Holstein-Glückstadt (category Lower Saxon Circle)
Holstein-Glückstadt or Schleswig-Holstein-Glückstadt is the historiographical name, as well as contemporary shorthand name, for the parts of the duchies...
6 KB (715 words) - 13:24, 13 November 2024
Frisians and Saxons, which would later comprise the Duchy of Saxony (est. 806), the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle (1500), and the Lower Saxon Circle (1512)...
22 KB (2,098 words) - 01:27, 21 October 2024
Duchy of Holstein (category Lower Saxon Circle)
northern border of the Carolingian Empire, after Emperor Charlemagne upon the Saxon Wars reached an agreement with King Hemming of Denmark in 811. The lands...
11 KB (1,118 words) - 02:28, 21 October 2024
maintained neutrality, as did most of the Protestant territories in the Lower Saxon Circle, a fiscal and military subsection of the Holy Roman Empire. The neighbouring...
63 KB (6,664 words) - 11:42, 21 October 2024
and the German Empire, commonly called Lower Saxony between the 14th and 17th centuries Lower Saxon Circle (1500–1806), a tax levying and army recruitment...
562 bytes (109 words) - 17:56, 14 October 2021
triplum. The figures for the contingents to be supplied by each Imperial Circle were little altered until the demise of the Empire. In practice, they were...
11 KB (1,095 words) - 20:23, 23 October 2024
April 1787 – 1790 Chargé d'affaires In Dresden. Jacob Gustaf De la Gardie 15 August 1795 – January 1796 Envoy en mission spéciale To the Saxon court....
30 KB (1,441 words) - 12:42, 23 October 2024
County of Regenstein (category Lower Saxon Circle)
was a mediaeval statelet of the Holy Roman Empire. It was ruled by the Saxon comital House of Regenstein, named after their residence at Regenstein Castle...
6 KB (497 words) - 13:38, 27 October 2024
Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim (category Lower Saxon Circle)
Louis the German, Altfrid founded Essen Abbey. During the reign of the Saxon Ottonian dynasty Hildesheim, together with the neighbouring bishoprics of...
9 KB (712 words) - 03:33, 24 October 2024
extinct. In 1701, with the endorsement of the Imperial state of the Lower Saxon Circle, the Treaty of Hamburg (1701) was signed and the final division of...
11 KB (965 words) - 12:24, 21 October 2024
Mecklenburg-Güstrow, the daughter of Gustav Adolph. The emissaries of the Lower Saxon Circle finally negotiated a compromise on March 8, 1701. The agreement created...
8 KB (567 words) - 02:18, 9 August 2024
designated as Saxon Circle, while the Wettin-ruled Saxon electorate and duchies at that time formed the Upper Saxon Circle. The naming of Lower Saxony became...
49 KB (5,512 words) - 01:38, 21 October 2024
the latter of his functions – by the Lower Saxon Circle's member territories commander-in-chief of the Lower Saxon troops. More troops were recruited and...
68 KB (8,362 words) - 14:06, 21 October 2024
member of the Lower Saxon Circle and part of the League. The same applied to the Spanish Netherlands, a member of the Burgundian Circle, but not the Kingdom...
19 KB (2,182 words) - 05:20, 21 October 2024
them in his Duchy of Holstein (in the Lower Saxon Circle of the Holy Roman Empire) and persuaded the other Lower Saxon rulers to make him the commander of...
70 KB (8,572 words) - 20:06, 12 November 2024
Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (category Lower Saxony articles missing geocoordinate data)
Germany-wide standing. In 1500 Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel became part of the Lower Saxon Circle within the Holy Roman Empire. From 1519 to 1523 the principality went...
19 KB (1,922 words) - 16:56, 21 October 2024
Christian: surrender all imperial offices, surrender his bishoprics in the Lower Saxon Circle, buy out his provinces of Holstein, Schleswig and Jutland from the...
13 KB (1,214 words) - 23:07, 22 October 2024
Thirty Years' War (redirect from Low Saxon War)
Verden Kassel Wolfenbüttel With Saxony dominating the Upper Saxon Circle and Brandenburg the Lower, both kreise had remained neutral during the campaigns in...
121 KB (14,371 words) - 15:06, 13 November 2024
Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck (category Lower Saxon Circle)
split off from Oldenburg and no bishop was appointed after 1066. After the Saxon count Henry of Badewide had campaigned in the Wagrian lands east of the...
9 KB (748 words) - 03:04, 23 October 2024
Christian IV of Denmark from having access to Kassel and to protect the Lower Saxon Circle. The Imperial German forces of Albrecht von Wallenstein handily defeated...
7 KB (694 words) - 21:40, 23 October 2024
Brunswick–Lüneburg (category Lower Saxon Circle)
imperial principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the territory of present day Lower Saxony. In 1235, Otto I was enfeoffed with the newly founded Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg...
76 KB (2,292 words) - 15:51, 21 October 2024
Dutch Low Saxon (Nederlaands Leegsaksies [ˈneːdərlaːnts ˈleːxsɑksis] or Nederlaands Nedersaksies; Dutch: Nederlands Nedersaksisch) are Low Saxon dialects...
15 KB (1,826 words) - 00:42, 7 November 2024
Sweden a vote in the Imperial Diet and enabled it to "direct" the Lower Saxon Circle alternately with Brandenburg. France and Sweden, moreover, became...
43 KB (5,647 words) - 22:26, 12 November 2024
Principality of Calenberg (category Lower Saxony articles missing geocoordinate data)
Danish troops under King Christian IV, who was then commander of the Lower Saxon Circle, was defeated by the general of the Catholic League, Tilly in the...
19 KB (2,255 words) - 12:46, 24 June 2024
House of Mecklenburg. Heavily influenced by representatives of the Lower Saxon Circle, it was agreed on 8 March 1701 in neutral Hamburg. It ended the dispute...
1 KB (103 words) - 20:20, 23 June 2023
Roman Empire than as a bishop. Wichmann sided with the emperor in the Great Saxon Revolt and was rewarded by recognising the archepiscopal and the cathedral...
19 KB (2,089 words) - 23:06, 9 October 2024