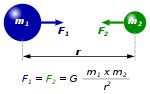
Newton's law of universal gravitation states that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the...
26 KB (3,690 words) - 13:47, 13 November 2024
gravitational constant is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of gravitational effects in Sir Isaac Newton's law of universal gravitation...
45 KB (5,204 words) - 20:19, 21 November 2024
Gauss's law for gravity, also known as Gauss's flux theorem for gravity, is a law of physics that is equivalent to Newton's law of universal gravitation. It...
15 KB (2,228 words) - 03:31, 17 May 2024
Gravity (redirect from Theory of gravitation)
for most applications, gravity is well approximated by Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity as a force causing any two bodies...
74 KB (7,487 words) - 17:13, 11 November 2024
Newton's law may refer to: Newton's laws of motion Newton's law of universal gravitation Newton's law of cooling Newton's constitutive law for a Newtonian...
265 bytes (61 words) - 13:59, 7 August 2024
mechanics, a gravitational field is a physical quantity. A gravitational field can be defined using Newton's law of universal gravitation. Determined in...
11 KB (1,307 words) - 02:50, 21 November 2024
specified, like Newton's law of universal gravitation. By inserting such an expression for F {\displaystyle \mathbf {F} } into Newton's second law, an equation...
122 KB (15,388 words) - 23:52, 11 November 2024
existence of the gravitational constant was explored by various researchers from the mid-17th century, helping Isaac Newton formulate his law of universal gravitation...
88 KB (10,802 words) - 14:05, 19 November 2024
Isaac Newton's apple tree at Woolsthorpe Manor represents the inspiration behind Sir Isaac Newton's theory of gravity. While the precise details of Newton's...
48 KB (4,270 words) - 16:48, 5 November 2024
other effects, such as buoyancy or drag. Newton's law of universal gravitation states that there is a gravitational force between any two masses that is equal...
12 KB (1,556 words) - 13:37, 13 November 2024
and hence zero outside sources. Newton's law of universal gravitation follows an inverse-square law, as do the effects of electric, light, sound, and radiation...
27 KB (3,422 words) - 23:35, 11 October 2024
General relativity (redirect from General theory of relativity)
description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing...
193 KB (22,609 words) - 23:56, 5 November 2024
Look up law of attraction in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Law of attraction may refer to: Electromagnetic attraction Newton's law of universal gravitation...
651 bytes (120 words) - 14:37, 27 October 2024
gravitational attraction between masses results from the warping of space and time by those masses. Before the advent of general relativity, Newton's...
37 KB (4,514 words) - 17:08, 11 June 2024
Action at a distance (section Categories of action)
the concept of the non-local interaction of objects that are separated in space. Coulomb's law and Newton's law of universal gravitation are based on...
27 KB (3,386 words) - 14:25, 1 November 2024
Equations for a falling body (redirect from Law of falling bodies)
gravity, Newton's law of universal gravitation simplifies to F = mg, where F is the force exerted on a mass m by the Earth's gravitational field of strength...
13 KB (1,455 words) - 20:16, 21 November 2024
Gravitoelectromagnetism (category Effects of gravity)
separate theory expanding Newton's law of universal gravitation.[better source needed] This approximate reformulation of gravitation as described by general...
29 KB (3,491 words) - 00:47, 18 November 2024
bringing forth modern science. In the Principia, Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint...
153 KB (15,774 words) - 07:09, 22 November 2024
Potential energy (redirect from Gravitation energy)
loss of potential energy. The gravitational force between two bodies of mass M and m separated by a distance r is given by Newton's law of universal gravitation...
44 KB (6,122 words) - 11:00, 4 October 2024
Copernican Revolution (category History of astronomy)
used Kepler's laws of planetary motion to derive his law of universal gravitation. Newton's law of universal gravitation was the first law he developed...
32 KB (3,966 words) - 09:55, 11 October 2024
gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does...
106 KB (12,668 words) - 03:05, 12 November 2024
conditions, Newton's law of universal gravitation may be used to obtain values that are accurate. In general, and in the presence of significant gravitation, the...
3 KB (532 words) - 15:13, 22 June 2023
observed, and the law may be found to be false when extrapolated. Ohm's law only applies to linear networks; Newton's law of universal gravitation only applies...
57 KB (5,649 words) - 14:21, 9 October 2024
include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because...
53 KB (8,201 words) - 14:56, 2 November 2024
Classical field theory (section Newtonian gravitation)
ensures that the presence of m has a negligible influence on the behavior of M. According to Newton's law of universal gravitation, F(r) is given by F ( r...
27 KB (3,848 words) - 21:31, 6 November 2024
Principia Mathematica, in which he formulates Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation 1690 - James Bernoulli shows that the cycloid...
16 KB (1,951 words) - 22:19, 8 November 2024
Entropic gravity (category Theories of gravity)
r^{2}.} From algebraic substitution of these into the above relations, one derives Newton's law of universal gravitation: F = m 2 π c k B T ℏ = m 4 π c ℏ...
24 KB (3,157 words) - 13:18, 19 August 2024
Sun or most moons and greatly simplifies equations. Under Newton's law of universal gravitation, if the distance between the bodies is r, the force exerted...
15 KB (1,461 words) - 17:20, 9 November 2024
also refer to: Newton's law of universal gravitation, the classical theory of gravitation General relativity, the theory of gravitation published by Albert...
769 bytes (118 words) - 21:47, 24 March 2024
Three-body problem (redirect from Problem of Three Bodies)
momenta) of three point masses that orbit each other in space and calculate their subsequent trajectories using Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal...
46 KB (5,814 words) - 08:09, 10 November 2024