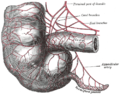
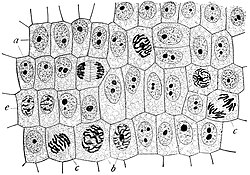
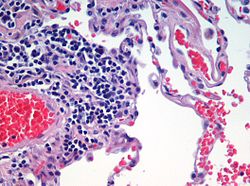
organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between...
22 KB (2,207 words) - 23:30, 15 April 2025
In biology, the electric organ is an organ that an electric fish uses to create an electric field. Electric organs are derived from modified muscle or...
25 KB (2,332 words) - 15:16, 11 March 2025
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex...
20 KB (1,993 words) - 20:22, 9 February 2025
– organ – organ system – organism – population – community – ecosystem – biosphere Approach: Reductionism – emergent property – mechanistic Biology as...
35 KB (3,176 words) - 03:05, 18 November 2024
Vestigiality (redirect from Vestigal organ)
(2005) Henderson's Dictionary of Biology. Pearson, Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-127384-1. Muller, G. B. (2002) "Vestigial Organs and Structures". in Encyclopedia...
32 KB (3,876 words) - 05:01, 7 May 2024
Look up organ in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Organ and organs may refer to: Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function...
3 KB (463 words) - 03:22, 18 December 2024
intromittent organ is any external organ of a male organism that is specialized to deliver sperm during copulation. Intromittent organs are found most...
17 KB (1,795 words) - 04:24, 2 January 2025
Sex (redirect from Sexuality (biology))
specialized sex organs to assist the transport of sperm—these male sex organs are called intromittent organs. In humans and other mammals, this male organ is known...
67 KB (7,641 words) - 22:43, 19 March 2025
The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum...
34 KB (4,107 words) - 20:29, 26 February 2025
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single,...
133 KB (13,836 words) - 13:50, 14 April 2025
derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins...
40 KB (4,069 words) - 18:15, 26 November 2024
their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct type of construction, which is to say a particular layout of organ systems...
5 KB (513 words) - 07:44, 12 April 2025
Snake (redirect from Copulatory organs of snakes)
heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side...
151 KB (15,019 words) - 13:37, 11 April 2025
Animal locomotion (redirect from Locomotory organ)
legs, wings, arms, fins, or tails are sometimes referred to as locomotory organs or locomotory structures. The term "locomotion" is formed in English from...
78 KB (8,879 words) - 23:25, 14 January 2025
more vital functions, analogous to the organs of the human body (such as the heart, lung, and kidney, with each organ performing a different function). Both...
60 KB (6,274 words) - 03:40, 27 March 2025
Sense (redirect from Sensory organ)
photoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors) in sensory organs transduct sensory information from these organs towards the central nervous system, finally arriving...
91 KB (10,760 words) - 16:50, 2 April 2025
biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. Accordingly, organs are formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues...
24 KB (3,006 words) - 23:14, 25 March 2025
Parietal eye (redirect from Parietal organ)
Light-sensitive organs that evaginate from the diencephalon - NCBI Zug, George; Vitt, Laurie Vitt; Caldwell, Janalee (2002). Herpetology: An introductory biology of...
14 KB (1,592 words) - 09:24, 10 October 2024
employing liquid medium. Organ culture technology has contributed to advances in embryology, inflammation, cancer, and stem cell biology research. In April...
11 KB (1,407 words) - 17:12, 23 December 2024
Primordium (redirect from Anlage (biology))
(/praɪˈmɔːrdiəm/; pl.: primordia; synonym: anlage), in embryology, is an organ or tissue in its earliest recognizable stage of development. Cells of the...
17 KB (2,070 words) - 15:37, 10 March 2025
Electric fish (section Electric organ)
electric fish". Journal of Experimental Biology, 202 (10): 1205–1215. Full text Kramer, Bernd (2008). "Electric Organ Discharge". In Marc D. Binder; Nobutaka...
31 KB (2,961 words) - 23:14, 6 February 2025
Life (redirect from Biota (biology))
hierarchical organization, spanning from molecular machines to cells, organs, tissues, organisms, populations, ecosystems, up to the whole biosphere...
112 KB (11,084 words) - 14:48, 14 April 2025
Involution (medicine) (redirect from Organ involution)
Involution is the shrinking or return of an organ to a former size. At a cellular level, involution is characterized by the process of proteolysis of...
3 KB (333 words) - 07:15, 27 October 2024
Pineal gland (redirect from Pineal organ)
species of amphibians and reptiles, the gland is linked to a light-sensing organ, variously called the parietal eye, the pineal eye or the third eye. Reconstruction...
53 KB (6,021 words) - 05:11, 11 April 2025
Stinger (redirect from Stinger (organ))
A stinger (or sting) is a sharp organ found in various animals (typically insects and other arthropods) capable of injecting venom, usually by piercing...
8 KB (994 words) - 21:32, 22 March 2025
Penis (category Sex organs)
sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also urinate. This organ is...
43 KB (4,056 words) - 04:01, 30 March 2025
Monotreme (redirect from Reproductive organs of monotremes)
2012). The Biology of the Monotremes. Elsevier Science. ISBN 978-0-323-15331-7. Grützner, F.; Nixon, B.; Jones, R.C. (2008). "Reproductive biology in egg-laying...
48 KB (4,754 words) - 11:48, 15 April 2025
genitals of the groin, which differ between males and females. The branch of biology dealing with the study of the bodies and their specific structural features...
3 KB (391 words) - 20:58, 31 October 2024
Gill (redirect from Gill (organ))
A gill (/ɡɪl/ ) is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills...
21 KB (2,726 words) - 04:26, 18 March 2025
Aristotle's biology is the theory of biology, grounded in systematic observation and collection of data, mainly zoological, embodied in Aristotle's books...
61 KB (6,516 words) - 19:07, 9 April 2025