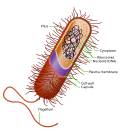
A prokaryote (/proʊˈkærioʊt, -ət/; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles...
43 KB (4,131 words) - 03:27, 21 December 2024
wall Capsule Pili Marine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments...
136 KB (12,703 words) - 13:59, 16 December 2024
Nutrition (section Prokaryote)
unavailable. Prokaryotes, including bacteria and archaea, vary greatly in how they obtain nutrients across nutritional groups. Prokaryotes can only transport...
35 KB (3,966 words) - 19:59, 3 December 2024
They constitute a major group of life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority...
62 KB (6,246 words) - 00:44, 8 January 2025
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) or Prokaryotic Code, formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or...
11 KB (1,300 words) - 17:02, 20 October 2024
In prokaryote nomenclature, Candidatus (abbreviated Ca.; Latin for "candidate of Roman office") is used to name prokaryotic taxa that are well characterized...
16 KB (1,883 words) - 04:30, 9 December 2024
prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can...
60 KB (6,269 words) - 16:45, 2 January 2025
Circular chromosome (redirect from Circular prokaryote chromosome)
of circular DNA, unlike the linear chromosome of most eukaryotes. Most prokaryote chromosomes contain a circular DNA molecule. This has the major advantage...
21 KB (2,745 words) - 08:39, 17 November 2024
animals (including protists), plants (also including algae and fungi) and prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), is Latin and binomial in form; this contrasts...
27 KB (3,131 words) - 16:41, 22 November 2024
Ribosomal RNA (section In prokaryotes)
60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can...
60 KB (7,203 words) - 11:15, 18 November 2024
traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different...
143 KB (15,576 words) - 03:46, 8 January 2025
Extremophile (redirect from Extremophilic prokaryotes)
An extremophile (from Latin extremus 'extreme' and Ancient Greek φιλία (philía) 'love') is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in...
62 KB (6,489 words) - 21:15, 27 December 2024
only from a single specimen, described in 2012. It has features of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but is apparently distinct from either group, making it...
9 KB (861 words) - 18:42, 6 January 2025
on protists, and Ruggiero et al., 2015, covering both eukaryotes and prokaryotes to the rank of Order, although both exclude fossil representatives. A...
69 KB (6,808 words) - 14:44, 9 December 2024
Phototroph (redirect from Phototrophic prokaryotes)
Phototrophs (from Ancient Greek φῶς, φωτός (phôs, phōtós) 'light' and τροφή (trophḗ) 'nourishment') are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce...
8 KB (740 words) - 06:42, 16 August 2024
antibiotics. A possible transitional form of microorganism between a prokaryote and a eukaryote was discovered in 2012 by Japanese scientists. Parakaryon...
74 KB (7,752 words) - 16:46, 15 December 2024
Prokaryotic cytoskeleton (redirect from Prokaryote cytoskeleton)
structural filaments in prokaryotes. Some of these proteins are analogues of those in eukaryotes, while others are unique to prokaryotes. Cytoskeletal elements...
20 KB (2,466 words) - 09:25, 20 December 2024
Chromosome (section Prokaryotes)
origins. The genes in prokaryotes are often organized in operons and do not usually contain introns, unlike eukaryotes. Prokaryotes do not possess nuclei...
63 KB (6,601 words) - 10:54, 23 December 2024
Unicellular organism (section Prokaryotes)
general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes...
33 KB (3,362 words) - 14:35, 17 December 2024
(mostly in eukaryotes), or aspartic acid or histidine residues (mostly in prokaryotes). The phosphorylation of proteins is a major regulatory mechanism in...
2 KB (124 words) - 17:31, 22 October 2023
divided into several different kingdoms. Originally his split of the prokaryotes was into Eubacteria (now Bacteria) and Archaebacteria (now Archaea)....
15 KB (1,625 words) - 11:52, 7 January 2025
Fission (biology) (section Fission of prokaryotes)
Binary fission in a prokaryote...
20 KB (2,236 words) - 18:20, 31 December 2024
Bacterial transcription (redirect from Transcription in prokaryotes)
Bacterial transcription is the process in which a segment of bacterial DNA is copied into a newly synthesized strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) with use of...
21 KB (2,369 words) - 18:35, 3 October 2024
Enzyme Eukaryote Fermentation Metabolism Meiosis Mitosis Photosynthesis Prokaryote Genetics DNA Epigenetics Evolutionary developmental biology Gene expression...
82 KB (9,856 words) - 13:23, 13 December 2024
the dinoflagellate protists. He first coined the terms "eukaryote" and "prokaryote" in a 1925 paper, but did not elaborate on the concept; Roger Stanier...
4 KB (305 words) - 23:27, 14 December 2024
asexually, as in single-celled organisms such as bacteria and other prokaryotes, and parthenogenetic or apomictic multi-celled organisms. DNA barcoding...
104 KB (10,511 words) - 20:12, 5 January 2025
to be names of subspecies (see International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes). As in botany, subspecies is conventionally abbreviated as "subsp."...
15 KB (1,466 words) - 21:16, 22 December 2024
prokaryotes. The set of chromosomes in a cell is collectively known as its genome. In eukaryotes, DNA is mainly in the cell nucleus. In prokaryotes,...
133 KB (13,826 words) - 03:33, 6 January 2025
"solitary") is historically a biological kingdom that is made up of prokaryotes. As such, it is composed of single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus...
22 KB (2,698 words) - 13:11, 22 November 2024
sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (Haemophilus influenzae) was published in 1995; the yeast (Saccharomyces...
44 KB (4,939 words) - 16:00, 7 January 2025