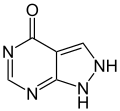
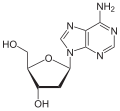
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also...
24 KB (2,505 words) - 14:56, 30 January 2025
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms. Purines are biologically synthesized...
14 KB (1,640 words) - 19:09, 27 December 2024
Purine analogues are antimetabolites that mimic the structure of metabolic purines. Nucleobase analogues Thiopurines such as thioguanine are used to treat...
2 KB (186 words) - 01:57, 24 June 2022
Purine synthesis may either refer to: in vivo purine synthesis: Purine metabolism#Biosynthesis laboratory purine synthesis: Purine#Laboratory synthesis...
188 bytes (51 words) - 20:12, 29 December 2019
Nucleotide (section Purine ribonucleotide synthesis)
linked. Purines, however, are first synthesized from the sugar template onto which the ring synthesis occurs. For reference, the syntheses of the purine and...
32 KB (3,305 words) - 04:15, 28 January 2025
Nucleotide base (section Modified purine nucleobases)
have a fused-ring skeletal structure derived of purine, hence they are called purine bases. The purine nitrogenous bases are characterized by their single...
15 KB (1,439 words) - 03:19, 11 November 2024
Caffeine (redirect from 1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6(3H,7H)-dione 3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione)
beyond usual human consumption. Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, a methylxanthine alkaloid, and is chemically related to the adenine and...
201 KB (20,111 words) - 05:50, 17 January 2025
Xanthine (redirect from 1H-purine-2,6-diol)
archaically xanthic acid; systematic name 3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione) is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids, as well as in other organisms...
14 KB (956 words) - 11:52, 24 November 2024
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase (EC 2.4.2.1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene. It catalyzes...
14 KB (1,511 words) - 15:37, 26 August 2023
Nucleoside deoxyribosyltransferase (redirect from Nucleoside:purine(pyrimidine) deoxy-D-ribosyltransferase)
class is nucleoside:purine(pyrimidine) deoxy-D-ribosyltransferase. Other names in common use include purine(pyrimidine) nucleoside:purine(pyrimidine) deoxyribosyl...
3 KB (267 words) - 16:18, 22 September 2024
In enzymology, a purine nucleosidase (EC 3.2.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction a purine nucleoside + H2O ⇌ {\displaystyle \rightleftharpoons...
5 KB (421 words) - 14:53, 22 September 2024
ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations...
40 KB (4,027 words) - 02:33, 25 January 2025
Inosinic acid (category Purines)
of hypoxanthine and the first nucleotide formed during the synthesis of purine nucleotides. It can also be formed by the deamination of adenosine monophosphate...
7 KB (600 words) - 22:40, 16 November 2024
1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) to the purine. HGPRT plays a central role in the generation of purine nucleotides through the purine salvage pathway. HGPRT catalyzes...
15 KB (1,614 words) - 05:11, 25 December 2024
Adenine (redirect from 6-Amino-purine)
Adenine (/ˈædɪniːn/, /ˈædɪnɪn/) (symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base. It is one of the nucleobases in the nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. The shape...
14 KB (1,295 words) - 02:27, 27 January 2025
Alkaloid (redirect from Purine alkaloid)
This group includes terpene-like and steroid-like alkaloids, as well as purine-like alkaloids such as caffeine, theobromine, theacrine and theophylline...
69 KB (5,413 words) - 16:40, 6 January 2025
allopurinol's effect. Allopurinol is a purine analog; it is a structural isomer of hypoxanthine (a naturally occurring purine in the body) and is an inhibitor...
31 KB (2,802 words) - 17:05, 12 January 2025
A purine riboswitch is a sequence of ribonucleotides in certain messenger RNA (mRNA) that selectively binds to purine ligands via a natural aptamer domain...
13 KB (1,346 words) - 20:41, 4 August 2024
enzymology, a diphosphate-purine nucleoside kinase (EC 2.7.1.143) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction diphosphate + a purine nucleoside ⇌ {\displaystyle...
2 KB (158 words) - 13:52, 26 August 2023
The Purine Nucleotide Cycle is a metabolic pathway in protein metabolism requiring the amino acids aspartate and glutamate. The cycle is used to regulate...
23 KB (2,658 words) - 11:45, 3 September 2024
Methylliberine Names Preferred IUPAC name 2-Methoxy-1,7,9-trimethyl-7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-6,8-dione Other names O(2),1,7,9-Tetramethylurate; Tetramethyluric acid;...
5 KB (432 words) - 17:14, 14 January 2025
Nucleoside triphosphate (section Purine synthesis)
novo. The synthesis of ATP and GTP (purines) differs from the synthesis of CTP, TTP, and UTP (pyrimidines). Both purine and pyrimidine synthesis use phosphoribosyl...
24 KB (2,518 words) - 06:30, 20 January 2025
Nucleotide salvage (redirect from Purine salvage pathway)
often refers to nucleotide salvage in particular, in which nucleotides (purine and pyrimidine) are synthesized from intermediates in their degradative...
7 KB (736 words) - 10:22, 12 August 2024
the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building blocks...
10 KB (813 words) - 19:42, 12 August 2024
Theacrine (redirect from 1,3,7,9-Tetramethyl-7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione)
Theacrine, also known as 1,3,7,9-tetramethyluric acid, is a purine alkaloid found in Cupuaçu (Theobroma grandiflorum) and in a Chinese tea known as kucha...
6 KB (524 words) - 00:12, 17 November 2024
Inosine (category Purines)
this set of white cells (which cannot operate purine salvage pathways) is selectively targeted by the purine deficiency resulting from inosine monophosphate...
13 KB (1,250 words) - 21:14, 27 January 2025
established; purine–purine pairings are energetically unfavorable because the molecules are too close, leading to overlap repulsion. Purine–pyrimidine base-pairing...
32 KB (3,701 words) - 08:12, 9 January 2025
Nucleic acid metabolism (category Purines)
phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. The bases found in nucleic acids are either purines or pyrimidines. In the more complex multicellular animals, they are both...
14 KB (1,457 words) - 14:51, 9 January 2025
humans and other hominids), it is a product of oxidation of uric acid by purine catabolism. After birth, it is the predominant means by which nitrogenous...
15 KB (1,476 words) - 08:19, 21 December 2024
reactivity was governed by physico-chemical processes. RNA is composed of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides, both of which are necessary for reliable information...
4 KB (467 words) - 14:44, 14 July 2024