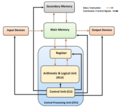
The Z3 was a German electromechanical computer designed by Konrad Zuse in 1938, and completed in 1941. It was the world's first working programmable, fully...
38 KB (3,399 words) - 13:27, 23 October 2024
Z3 may refer to: BlackBerry Z3, a smartphone Moto Z3, a smartphone Motorola Rizr Z3, a slide mobile phone Samsung Z3, a smartphone Sony Xperia Z3, a smartphone...
1 KB (178 words) - 06:00, 25 January 2024
Lusser. The Z2 and Z3 were follow-ups based on many of the same ideas as the Z1. The Z1 contained almost all the parts of a modern computer, i.e. control unit...
14 KB (1,313 words) - 05:06, 3 May 2024
2018-05-12. [1] (xii+679 pages) Zuse, Horst (2000). "Konrad Zuse's Z1 and Z3 Computers". The Life and Work of Konrad Zuse. EPE Online. Archived from the original...
7 KB (374 words) - 00:44, 1 January 2024
History of computing hardware (redirect from Computer generation)
earlier machine up with the Z3, the world's first working electromechanical programmable, fully automatic digital computer. The Z3 was built with 2000 relays...
169 KB (17,661 words) - 20:19, 11 November 2024
: 1009 the first Swiss computer, created under the direction of ETH engineer Ambros Speiser.: 1087 The Z4 was very similar to the Z3 in its design but was...
21 KB (1,847 words) - 12:45, 6 November 2024
available at that time. The Z3 was not itself a universal computer but could be extended to be Turing complete. Zuse's next computer, the Z4, became the world's...
139 KB (14,027 words) - 22:53, 12 November 2024
Konrad Zuse completed the Z3 computer. Zuse was not familiar with Turing's work on computability at the time. In particular, the Z3 lacked dedicated facilities...
29 KB (3,240 words) - 06:46, 11 November 2024
1924. The first computer to use postfix notation, though it long remained essentially unknown outside of Germany, was Konrad Zuse's Z3 in 1941 as well...
76 KB (6,743 words) - 07:41, 27 October 2024
Konrad Zuse (category Computer designers)
programmable computer; the functional program-controlled Turing-complete Z3 became operational in May 1941. Thanks to this machine and its predecessors...
45 KB (4,577 words) - 12:49, 6 November 2024
Zuse Z3 and the Harvard Mark I, or were only programmable by physical manipulation of switches and plugs, as was the case for the Colossus computer. In...
16 KB (1,671 words) - 18:58, 15 November 2024
History of computing (redirect from The History of Computers)
later developments during the age of early electronic computing. The Z3 computer, built by German inventor Konrad Zuse in 1941, was the first programmable...
59 KB (6,591 words) - 22:49, 29 October 2024
Helmut Schreyer (category German computer scientists)
German inventor. He is mostly known for his work on the Z3, the world's first programmable computer. Helmut Schreyer was the son of the minister Paul Schreyer...
8 KB (848 words) - 15:33, 10 August 2024
ENIAC (redirect from Electronic Numerical Integrator Analyzer and Computer)
considered the beginning of the modern computer era. ENIAC was, like the IBM Harvard Mark I and the German Z3, able to run an arbitrary sequence of mathematical...
74 KB (8,226 words) - 00:22, 19 November 2024
A mechanical computer is a computer built from mechanical components such as levers and gears rather than electronic components. The most common examples...
20 KB (1,743 words) - 19:23, 5 August 2024
seventh computer model Konrad Zuse developed (the first six being the Z1, Z2, Z3, Z4, Z5 and Z11, respectively). One of the early commercial computers, the...
6 KB (586 words) - 15:04, 7 August 2024
Floating-point arithmetic (category Computer arithmetic)
(including one implicit bit), and a sign bit. The more reliable relay-based Z3, completed in 1941, has representations for both positive and negative infinities;...
118 KB (14,178 words) - 10:05, 17 November 2024
American author (b. 1926) 1995 – Konrad Zuse, German engineer, designed the Z3 computer (b. 1910) 1996 – Yulii Borisovich Khariton, Russian physicist and academic...
49 KB (4,778 words) - 22:04, 4 November 2024
machines of the same era, such as Konrad Zuse's 1941 Z3 (or earlier iterations) and the Colossus computers of 1943–1945. Nor did it implement the stored-program...
23 KB (2,620 words) - 16:16, 14 November 2024
English singer (d. 2003) 1910 – Konrad Zuse, German computer scientist and engineer, invented the Z3 computer (d. 1995) 1911 – Vernon Kirby, South African tennis...
51 KB (5,237 words) - 19:33, 12 October 2024
Analytical engine (category Computer-related introductions in 1837)
was not until 1941 that Konrad Zuse built the first general-purpose computer, Z3, more than a century after Babbage had proposed the pioneering analytical...
43 KB (3,882 words) - 19:33, 9 November 2024
Information technology (redirect from Computer services)
developed. Electronic computers, using either relays or valves, began to appear in the early 1940s. The electromechanical Zuse Z3, completed in 1941, was...
39 KB (4,353 words) - 13:52, 12 November 2024
the modern computer'[who?] "Who is the Father of the Computer?". ComputerHope. Rojas, R. (1998). "How to make Zuse's Z3 a universal computer". IEEE Annals...
50 KB (5,519 words) - 00:19, 6 October 2024
In computer science and computer engineering, computer architecture is a description of the structure of a computer system made from component parts. It...
26 KB (3,176 words) - 05:34, 4 November 2024
electromechanical desk calculator 3×10−1: multiplication on Zuse Z3 and Z4, first programmable digital computers, 1941 and 1945 respectively 5×10−1: computing power...
17 KB (1,660 words) - 15:47, 1 March 2024
with connections over high-speed networks. The console of Konrad Zuse's Z3 had a keyboard in 1941, as did the Z4 in 1942–1945. However, these consoles...
54 KB (6,798 words) - 17:23, 16 November 2024
Satisfiability modulo theories (category Logic in computer science)
inputs. SMT solvers such as Z3 and cvc5 have been used as a building block for a wide range of applications across computer science, including in automated...
46 KB (4,371 words) - 16:13, 13 October 2024
Acer Aspire (category Computer-related introductions in 1999)
Z24-880 Z3100 Z3101 Z3-105 Z3-115 Z3170 Z3171 Z3280 Z3-600 Z3-601 Z3-605 Z3-610 Z3-613 Z3-615 Z3620 Z3-700 Z3-705 Z3-710 Z3-711 Z3-715 Z3730 Z3731 Z3760...
24 KB (2,584 words) - 18:41, 27 September 2024
Bletchley Park. History of computing hardware List of vacuum-tube computers Manchester Baby Z3 Z4 The two operators have been variously identified as Dorothy...
66 KB (7,148 words) - 16:18, 14 November 2024
Information Age (redirect from Computer Age)
electromechanical systems to complete in 1941 the Z3, the world's first working programmable, fully automatic digital computer. Also during World War II, Allied engineers...
98 KB (10,364 words) - 15:16, 10 November 2024