wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function...
99 KB (13,558 words) - 10:37, 19 November 2024
In quantum mechanics, wave function collapse, also called reduction of the state vector, occurs when a wave function—initially in a superposition of several...
23 KB (2,717 words) - 18:16, 21 November 2024
Bloch's theorem (redirect from Bloch Function)
{\displaystyle \psi } is the wave function, u {\displaystyle u} is a periodic function with the same periodicity as the crystal, the wave vector k {\displaystyle...
36 KB (6,052 words) - 07:43, 21 May 2024
function. Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll off much faster than in a square wave...
7 KB (979 words) - 03:40, 15 November 2024
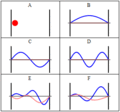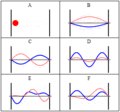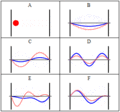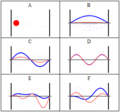
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space...
47 KB (6,567 words) - 17:46, 17 October 2024
a deterministic theory, and avoids issues such as wave–particle duality, instantaneous wave function collapse, and the paradox of Schrödinger's cat by...
27 KB (3,436 words) - 18:07, 21 November 2024
Tollmien–Schlichting wave, in fluid dynamics Wind wave Bloch's theorem Matter wave Pilot wave theory, in Bohmian mechanics Wave function Wave packet Wave–particle...
61 KB (7,802 words) - 10:47, 21 November 2024
A periodic function also called a periodic waveform (or simply periodic wave), is a function that repeats its values at regular intervals or periods....
12 KB (1,704 words) - 08:14, 18 August 2024
Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile...
39 KB (5,916 words) - 08:18, 18 November 2024
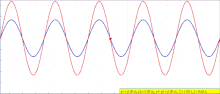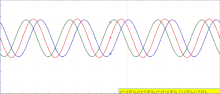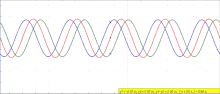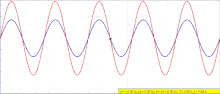
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a...
10 KB (1,332 words) - 20:42, 20 November 2024
This article mostly focuses on the scalar wave equation describing waves in scalars by scalar functions u = u (x, y, z, t) of a time variable t (a variable...
60 KB (10,757 words) - 16:20, 20 September 2024
Universal wavefunction (redirect from Universal Wave Function)
thesis: The Theory of the Universal Wave Function, pp 3–140. Stephen W Hawking, James B Hartle "The Wave Function of the Universe," Physical Review D...
5 KB (609 words) - 11:08, 8 August 2024
Particle in a box (section Position wave function)
calling k the wave number is that it enumerates the number of crests that the wave function has inside the box, and in this sense it is a wave number. This...
36 KB (5,882 words) - 11:38, 4 November 2024
DMX Krew (redirect from The Collapse of the Wave Function LP)
the Wave Function LP (2004) Many Worlds (The Collapse Of The Wave Function Volume 4) (2005) The Transactional Interpretation (The Collapse Of The Wave Function...
6 KB (583 words) - 22:28, 8 September 2024
function. A classical wave at any point can be positive or negative; the quantum probability function is non-negative. Any two different real waves in...
33 KB (4,602 words) - 11:48, 16 November 2024
mathematical formalisms. In one of them, a mathematical entity called the wave function provides information, in the form of probability amplitudes, about what...
99 KB (12,082 words) - 22:47, 20 November 2024
Particle in a ring (redirect from Ring wave guide)
the wave function be periodic in θ {\displaystyle \ \theta } with a period 2 π {\displaystyle 2\pi } (from the demand that the wave functions be single-valued...
4 KB (674 words) - 15:02, 7 November 2024
Quantum state (section Wave function representations)
for different kinds of systems or problems. Two broad categories are wave functions describing quantum systems using position or momentum variables and...
41 KB (5,491 words) - 04:08, 16 November 2024
delta. A set of orthonormal wave functions is complete in the space of square-integrable functions if any wave function |ψ⟩ can be expressed as a linear...
94 KB (14,090 words) - 11:39, 17 November 2024
In mathematics, a Coulomb wave function is a solution of the Coulomb wave equation, named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. They are used to describe...
10 KB (1,970 words) - 14:47, 23 October 2024
Hartle–Hawking state (redirect from Hawking-Hartle Wave Function)
The Hartle–Hawking state, also known as the no-boundary wave function is a proposal in theoretical physics concerning the state of the universe prior...
4 KB (375 words) - 14:46, 30 August 2024
Spheroidal wave functions are solutions of the Helmholtz equation that are found by writing the equation in spheroidal coordinates and applying the technique...
2 KB (232 words) - 00:01, 6 April 2021
Probability amplitude (redirect from Probability wave)
first proposed by Max Born, in 1926. Interpretation of values of a wave function as the probability amplitude is a pillar of the Copenhagen interpretation...
27 KB (3,513 words) - 20:37, 1 March 2024
Dirac equation (redirect from Dirac wave)
the introduction of several component wave functions in Pauli's phenomenological theory of spin. The wave functions in the Dirac theory are vectors of four...
78 KB (13,035 words) - 14:51, 5 November 2024
mechanics, a Slater determinant is an expression that describes the wave function of a multi-fermionic system. It satisfies anti-symmetry requirements...
14 KB (2,550 words) - 17:58, 21 September 2024
equation that treated the electron as a wave, and Born discovered that the way to successfully interpret the wave function that appeared in the Schrödinger equation...
81 KB (9,933 words) - 13:31, 6 November 2024
Schrödinger equation (redirect from Schrödinger Wave Equation)
Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a non-relativistic quantum-mechanical system.: 1–2 Its discovery...
74 KB (10,231 words) - 22:06, 19 November 2024
orbital (/ˈɔːrbɪtəl/) is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes an electron's charge...
84 KB (10,942 words) - 01:33, 19 November 2024
Basis set (chemistry) (redirect from Polarization function)
chemistry, a basis set is a set of functions (called basis functions) that is used to represent the electronic wave function in the Hartree–Fock method or...
36 KB (4,967 words) - 01:47, 12 October 2024
the universal wavefunction is objectively real, and that there is no wave function collapse. This implies that all possible outcomes of quantum measurements...
68 KB (8,281 words) - 19:02, 30 October 2024