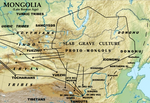
1500 the deer stones found so far are located in Mongolia. The name comes from their carved depictions of flying deer. The "Deer stones culture" relates...
81 KB (9,910 words) - 15:49, 10 August 2024
frequently reused stone material from nearby Deer stones culture sites. The replacement of the Deer stones culture by the Slab-grave culture in central and...
32 KB (3,949 words) - 23:36, 18 August 2024
the Deer stones culture of the Mongolian plateau. Daggers found in Ulaanzuukh graves have broadly similar designs to those of the Deer stones culture, with...
11 KB (1,186 words) - 09:55, 23 June 2024
Xianyun (section Deer stones culture (1400–700 BCE))
Painted Grey Ware Swat Kuru Chust Subeshi Upper Xiajiadian Siwa culture Shanma Deer stones ZHOU DYNASTY San- xingdui Ulaan- zuukh KUSH 21st Dynasty of Egypt...
39 KB (4,097 words) - 13:18, 3 August 2024
The contemporary Deer stones culture to the southeast may have been built in part by nomads from the Karasuk culture. The Karasuk culture had horse-drawn...
30 KB (3,264 words) - 12:19, 22 January 2024
petroglyphs in the region. It was followed by the Deer stones culture. At the same time the Ulaanzuukh-Tevsh culture was prospering in the steppes of southern...
4 KB (469 words) - 00:31, 24 June 2024
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age (1300–500 BC) in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia...
13 KB (1,258 words) - 13:16, 9 September 2024
burials are frequently associated with Deer Stones, to the point that the "Deer Stone culture" is often called "Deer Stone-Khirgisuur Complex” (DSK)". Archaeologically...
4 KB (470 words) - 04:16, 22 May 2024
Cycladic culture (also known as Cycladic civilisation) was a Bronze Age culture (c. 3100–c. 1000 BC) found throughout the islands of the Cyclades in the...
14 KB (1,529 words) - 23:24, 8 September 2024
Kurgan hypothesis (redirect from Kurgan culture)
the Samara and Seroglazovo cultures. Kurgan II–III, latter half of the 4th millennium BC. Stone circles, anthropomorphic stone stelae of deities. Includes...
34 KB (3,818 words) - 02:41, 26 August 2024
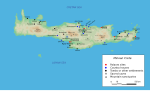
Minoan civilization (redirect from Minoan culture)
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it...
119 KB (14,038 words) - 11:57, 9 September 2024
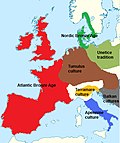
Unetice culture, Ottomány culture, British Bronze Age, Argaric culture, Nordic Bronze Age, Tumulus culture, Nuragic culture, Terramare culture, Urnfield...
27 KB (2,968 words) - 07:30, 12 September 2024
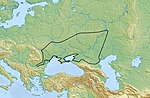
Timber-grave culture, was a Late Bronze Age 1900–1200 BC culture in the eastern part of the Pontic–Caspian steppe. It is a successor of the Yamna culture, the...
16 KB (1,622 words) - 21:21, 22 March 2024
The Tumulus culture was prevalent during the Bronze Age periods B, C1, and C2. Tumuli have been used elsewhere in Europe from the Stone Age to the Iron...
23 KB (2,064 words) - 14:52, 1 September 2024
has been interpreted as representing a deer goddess or 'Great Nature Goddess' similar to Artemis. Hallstatt culture musical instruments included harps, lyres...
77 KB (8,482 words) - 21:14, 16 August 2024
Indus Valley Civilisation (redirect from Indus Valley Culture)
edge the excavator discovered several heavily-pierced stones, similar to modern anchor stones employed by traditional seafaring communities of Western...
191 KB (21,640 words) - 15:32, 12 September 2024
Stone axes were made of a variety of stones, and other tools were made of horn and bone. The main economy was based on hunting red deer, roe deer, and...
3 KB (192 words) - 23:19, 23 September 2023
introduced through the northern steppes, probably from the area of the Deer stones culture. Contemporary oracle bone inscriptions of the character 車 depict...
19 KB (2,380 words) - 17:46, 13 August 2024
Maykop culture (Russian: майкоп, [mɐjˈkop], scientific transliteration: Majkop,), c. 3700 BC–3000 BC, is a major Bronze Age archaeological culture in the...
22 KB (2,645 words) - 04:05, 12 August 2024
The Apennine culture is a technology complex in central and southern Italy from the Italian Middle Bronze Age (15th–14th centuries BC). In the mid-20th...
10 KB (1,174 words) - 08:41, 18 March 2024
Xiajiadian Siwa culture Shanma Deer stones ZHOU DYNASTY San- xingdui Ulaan- zuukh KUSH 21st Dynasty of Egypt Amjad Jaimoukha believes the Koban culture was primarily...
10 KB (1,073 words) - 02:30, 3 March 2024
Catacomb culture. In addition to the Yamnaya culture, the Catacomb culture displays links with the earlier Sredny Stog culture, the Afanasievo culture and...
28 KB (3,366 words) - 02:02, 12 July 2024
Bronze Age Britain (section The Bell Beaker culture)
postulated for the Beaker culture, notably the Iberian Peninsula, the Netherlands and Central Europe. Part of the Beaker culture brought the skill of refining...
28 KB (2,861 words) - 21:00, 10 September 2024
The Andronovo culture is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished c. 2000–1150 BC, spanning from the southern Urals to the...
63 KB (7,073 words) - 12:24, 12 September 2024
The Urnfield culture (c. 1300–750 BC) was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield...
99 KB (10,747 words) - 13:00, 29 August 2024
Shang dynasty (redirect from Shang culture)
inscriptions and a small number of other writings on pottery, jade and other stones, horn, etc., but most prolifically on oracle bones. The complexity and sophistication...
63 KB (7,107 words) - 12:20, 5 September 2024
Afanasievo culture and the Khemtseg culture. It was contemporary with the Andronovo culture, but its very existence suggests that the Androvo culture did not...
6 KB (460 words) - 15:41, 26 June 2024
for describing Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East. The indigenous cultures of the New World did not develop an iron economy before 1500. Although...
67 KB (6,674 words) - 13:31, 8 September 2024
culture Catacomb culture Chinese Bronze Age Cycladic culture Deer stones culture Deverel–Rimbury culture Elp culture Ewart Park Phase Ezero culture Glazkov...
9 KB (191 words) - 03:18, 3 September 2024
Okunev culture (ru: Окуневская культура, romanized: Okunevskaya kul'tura, lit. 'Okunev culture'), also known as Okunevo culture, was a south Siberian archaeological...
54 KB (5,768 words) - 13:36, 25 July 2024