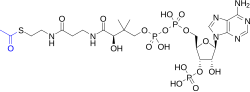
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function...
22 KB (2,097 words) - 03:05, 2 November 2024
In its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the anabolic and catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is...
26 KB (2,528 words) - 21:25, 28 August 2024
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10 /ˌkoʊkjuːˈtɛn/) also known as ubiquinone, is a naturally occurring biochemical cofactor (coenzyme) and an antioxidant produced by...
50 KB (4,992 words) - 21:34, 23 October 2024
Acetate (section Fermentation acetyl CoA to acetate)
influenzae. Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) by the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. This acetyl-CoA is then converted into acetate...
12 KB (1,257 words) - 14:37, 24 July 2024
into tissues outside the liver, where they are converted into acetyl-CoA (acetyl-Coenzyme A) – which then enters the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and...
21 KB (2,479 words) - 06:16, 27 September 2024
inhibitor herbicides Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase Tong L (August 2005). "Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase: crucial metabolic enzyme and attractive target for drug...
27 KB (2,990 words) - 21:27, 4 July 2024
Thiolase (redirect from Acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase)
Thiolases, also known as acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferases (ACAT), are enzymes which convert two units of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl CoA in the mevalonate...
19 KB (2,117 words) - 15:10, 26 February 2024
Wood–Ljungdahl pathway (redirect from Reductive acetyl CoA Pathway)
Wood–Ljungdahl pathway is a set of biochemical reactions used by some bacteria. It is also known as the reductive acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) pathway. This...
10 KB (1,077 words) - 10:03, 27 March 2024
Acetyl-coenzyme A transporter 1 also known as solute carrier family 33 member 1 (SLC33A1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC33A1 gene. The...
5 KB (630 words) - 09:28, 7 March 2022
ATP citrate synthase (redirect from Acetyl-CoA:oxaloacetate C-acetyltransferase ((pro-S)-carboxymethyl-forming, ADP-phosphorylating))
and acetyl-coenzyme A bind. In 2010, a structure of truncated human ATP citrate lyase was determined using X-ray diffraction to a resolution of 2.10 Å. In...
13 KB (1,471 words) - 17:50, 28 October 2024
formation of a new chemical bond between two large molecules. The two molecules joined that make up acetyl-CoA are acetate and coenzyme A (CoA). The complete...
17 KB (2,150 words) - 18:36, 11 September 2024
Cofactor (biochemistry) (redirect from Coenzyme)
included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or...
48 KB (4,931 words) - 15:10, 6 November 2024
Citrate synthase (redirect from Acetyl-CoA:oxaloacetate C-acetyltransferase (thioester-hydrolysing, (pro-S)-carboxymethyl forming))
two-carbon acetate residue from acetyl coenzyme A and a molecule of four-carbon oxaloacetate to form the six-carbon citrate: acetyl-CoA + oxaloacetate + H2O...
10 KB (1,161 words) - 00:10, 8 June 2024
through a two-electron transfer, and the second reaction involves ACS synthesizing acetyl-CoA using the carbon monoxide from CODH together with coenzyme-A (CoA)...
18 KB (2,194 words) - 18:27, 21 March 2024
the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other...
61 KB (6,770 words) - 15:11, 20 August 2024
2-methylacetoacetyl-CoA thiolase [misleading], 3-oxothiolase, acetyl coenzyme A thiolase, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, acetyl-CoA:N-acetyltransferase, and thiolase II. This...
4 KB (288 words) - 12:54, 26 August 2023
Pyruvic acid (section Decarboxylation to acetyl CoA)
energy, in one of two ways. Pyruvate is converted into acetyl-coenzyme A, which is the main input for a series of reactions known as the Krebs cycle (also...
16 KB (1,231 words) - 13:44, 2 November 2024
such as amino acids and carbohydrates, enter the Krebs cycle as acetyl coenzyme A and oxidize in the cycle. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)...
4 KB (338 words) - 01:13, 26 August 2024
is encoded by the ACAT1 (Acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase 1) gene. Acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase 1 is an acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase enzyme...
18 KB (2,322 words) - 21:50, 20 August 2024
N-Acetylaspartic acid (redirect from N-acetyl aspartate)
synthesized in the mitochondria from the amino acid aspartic acid and acetyl-coenzyme A. The various functions served by NAA are under investigation, but...
9 KB (745 words) - 23:35, 26 April 2024
Mechelle; Sattin, Maurizio; Powles, Stephen B. (2007). "Diversity of Acetyl-Coenzyme a Carboxylase Mutations in Resistant Lolium Populations: Evaluation...
2 KB (110 words) - 20:55, 10 October 2024
N-Acetylglutamic acid (redirect from N-Acetyl glutamate)
synthesizes N-acetylglutamic acid by catalyzing the addition of an acetyl group from acetyl-coenzyme A to glutamate. In prokaryotes with non-cyclic ornithine production...
15 KB (1,318 words) - 18:44, 17 August 2022
Metabolism (category Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback via Module:Annotated link)
smaller molecules, usually acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), which releases some energy. Finally, the acetyl group on acetyl-CoA is oxidized to water and...
113 KB (12,407 words) - 11:21, 2 November 2024
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (redirect from Coenzyme I)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two...
79 KB (9,020 words) - 21:04, 28 October 2024
when a new molecule of coenzyme A breaks the bond by nucleophilic attack on C3. This releases the first two carbon units, as acetyl CoA, and a fatty...
32 KB (3,381 words) - 18:51, 5 November 2024
HMG-CoA reductase (redirect from 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase)
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-controlling enzyme (NADH-dependent, EC 1.1.1.88;...
34 KB (4,113 words) - 16:29, 29 July 2024
are a subgroup of steroids with a hydroxyl group at the 3-position of the A-ring. They are amphipathic lipids synthesized from acetyl-coenzyme A via the...
9 KB (807 words) - 10:37, 31 October 2024
(acyl-carrier-protein) S-acetyltransferase (redirect from Acetyl-CoA:(acyl-carrier protein) S-acetyltransferase)
acetyl-CoA:[acyl-carrier-protein] S-acetyltransferase. Other names in common use include acetyl coenzyme A-acyl-carrier-protein transacylase, acetyl-CoA:ACP...
4 KB (399 words) - 14:21, 22 September 2024
Coenzyme A transferases (CoA-transferases) are transferase enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a coenzyme A group from an acyl-CoA donor to a carboxylic...
10 KB (1,316 words) - 01:10, 4 September 2024
Mupirocin (redirect from Pseudomonic acid A)
transfer an activated acetyl group from acetyl-Coenzyme A (CoA) to the first ACP domain. The chain is extended by malonyl-CoA, followed by a SAM-dependent methylation...
30 KB (2,609 words) - 04:22, 27 October 2024