CCIR System G, also known as the "Gerber Standard", is an analog broadcast television system used in sixty countries around the world for UHF channels...
5 KB (528 words) - 12:54, 19 November 2024
with PAL or SECAM colour. It is usually associated with CCIR System G for UHF broadcasts. System B was the first internationally accepted 625-line broadcasting...
22 KB (1,762 words) - 12:08, 19 November 2024
paired with the PAL color system (PAL-N) since 1980. It employs the 625 line/50 field per second waveform of CCIR Systems B/G, D/K, and I, but on a 6 MHz...
4 KB (265 words) - 12:54, 19 November 2024
CCIR System H is an analog broadcast television system used in Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Malta, Slovenia and Liberia on UHF bands, paired...
4 KB (441 words) - 12:10, 19 November 2024
CCIR System E is an analog broadcast television system used in France and Monaco, associated with monochrome 819-line high resolution broadcasts. Transmissions...
5 KB (418 words) - 12:55, 19 November 2024
CCIR System L is an analog broadcast television system used in France, Luxembourg, Monaco and Chausey. It was the last system to use positive video modulation...
6 KB (285 words) - 12:54, 19 November 2024
CCIR System C (originally known as the Belgian 625-line system) is an analog broadcast television system used between 1953 and 1978 in Belgium, Italy,...
4 KB (212 words) - 12:53, 19 November 2024
CCIR System K is an analog broadcast television system used in countries that adopted CCIR System D on VHF, and in Benin, Guinea, Republic of the Congo...
6 KB (298 words) - 12:10, 19 November 2024
CCIR System I is an analogue broadcast television system. It was first used in the Republic of Ireland starting in December 1961 as the 625-line broadcasting...
11 KB (956 words) - 12:26, 19 November 2024
CCIR System A was the 405-line analog broadcast television system adopted in the UK and Ireland. System A service started in 1936 and was discontinued...
7 KB (720 words) - 12:08, 19 November 2024
CCIR System D is an analog broadcast television system used in Bulgaria, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Albania...
10 KB (429 words) - 12:53, 19 November 2024
System G may refer to: System G (supercomputer), a cluster supercomputer at Virginia Tech CCIR System G, a 625-line analog television transmission format...
208 bytes (56 words) - 06:20, 30 December 2019
CCIR System M, sometimes called 525–line, NTSC, NTSC-M, or CCIR-M, is the analog broadcast television system approved by the FCC (upon recommendation by...
11 KB (1,018 words) - 12:53, 19 November 2024
former Soviet Union, Central Africa CCIR System A CCIR System B CCIR System G CCIR System H CCIR System I CCIR System M An analog video format consists...
34 KB (3,694 words) - 19:15, 16 November 2024
was adopted into the international standard CCIR 653 (now ITU-R BT.653) of 1986 as CCIR Teletext System B. WST originally stems from the UK standard...
15 KB (1,390 words) - 02:54, 12 January 2024
units in the case of CCIR System B and CCIR System G (European systems) and 7.5 IRE units in the case of CCIR System M (American system), although NTSC-J...
1 KB (197 words) - 02:15, 10 November 2024
PAL (section PAL-B/G/D/K/I)
and associated with CCIR analogue broadcast television systems B, D, G, H, I or K. The articles on analog broadcast television systems further describe frame...
64 KB (6,691 words) - 00:42, 25 November 2024
include SKYNET, Myansat and CANAL+ Myanmar. 625 lines PAL-G was never recognised as the official system by the Government of Myanmar and has never been broadcast...
10 KB (279 words) - 06:41, 22 November 2024
Engineering Society) Beaubien, William H.: A Report of FM Stereo at the CCIR Study Group X Conference in Bad Kreuznach, Germany JAES Volume 11 Issue 1...
5 KB (678 words) - 00:48, 31 August 2024
Teletext (category Legacy systems)
notably NABTS (CCIR Teletext System C) in the United States, Antiope (CCIR Teletext System A) in France and JTES (CCIR Teletext System D) in Japan, but...
50 KB (5,892 words) - 15:44, 18 November 2024
was adopted into the international standard CCIR 653 (now ITU-R BT.653) of 1986 as CCIR Teletext System C. NABTS was originally developed as a protocol...
9 KB (1,077 words) - 11:44, 2 November 2024
NTSC-J (redirect from CCIR System J)
differences. While NTSC-M is an official CCIR and FCC standard, NTSC-J or "System J" are a colloquial indicators. The system was introduced by NHK and NTV, with...
12 KB (1,279 words) - 14:24, 29 September 2024
Kong. 405-line was approved as System A in the CCIR assignment of broadcast systems. Sometimes called the Marconi-EMI system, it was developed in 1934 by...
28 KB (3,604 words) - 10:35, 24 September 2024
The first version of the standard was approved by the CCIR as Rec.709 in 1990 (there was also CCIR Rec. XA/11 MOD F in 1989), with the stated goal of a...
24 KB (3,033 words) - 00:50, 5 November 2024
television standard which was grafted onto an existing monochrome system such as CCIR System M, using gaps in the video spectrum (explained below) to allow...
47 KB (5,115 words) - 20:56, 23 October 2024
625 lines (redirect from 625-line television system)
625-line (or CCIR 625/50) is a late 1940s European analog standard-definition television resolution standard. It consists of a 625-line raster, with 576...
15 KB (965 words) - 09:25, 11 November 2024
1129 local broadcasters. Turkey uses CCIR System B in VHF Band and CCIR System G in UHF Band. The color information is superimposed by PAL method. TRT...
3 KB (351 words) - 00:32, 22 March 2021
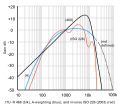
ITU-R 468 noise weighting (redirect from CCIR (ITU) 468 Noise Weighting)
(originally defined in CCIR recommendation 468-4, therefore formerly also known as CCIR weighting; sometimes referred to as CCIR-1k) is a standard relating...
15 KB (2,021 words) - 21:17, 31 January 2024
UT1R, etc.). McCarthy described the origin of the abbreviation: In 1967 the CCIR adopted the names Coordinated Universal Time and Temps Universel Coordonné...
52 KB (6,084 words) - 22:50, 13 November 2024