The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull minus the mandible is called...
7 KB (1,105 words) - 04:22, 3 January 2024
abdominal cavity, and houses the organs of reproduction. The dorsal body cavity contains the cranial cavity, and the spinal cavity. The cranial cavity is a...
12 KB (1,416 words) - 19:47, 20 October 2024
Skull fracture (section Cranial burst fracture)
structures, bringing the outside environment into contact with the cranial cavity is called a compound fracture. Compound fractures can either be clean...
22 KB (2,808 words) - 04:49, 18 October 2024
A cranial fossa is formed by the floor of the cranial cavity. There are three distinct cranial fossae: Anterior cranial fossa (fossa cranii anterior)...
3 KB (142 words) - 18:45, 18 May 2024
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid...
6 KB (563 words) - 14:57, 31 January 2024
The dorsal body cavity is located along the dorsal (posterior) surface of the human body, where it is subdivided into the cranial cavity housing the brain...
2 KB (172 words) - 21:15, 6 October 2024
Skull (redirect from Cranial bone)
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones, and ear ossicles. Two...
40 KB (4,483 words) - 13:07, 2 November 2024
Pneumocephalus is the presence of air or gas within the cranial cavity. It is usually associated with disruption of the skull: after head and facial trauma...
6 KB (631 words) - 22:50, 4 November 2023
Brain size (redirect from Cranial capacity)
the potential intelligence of the organism. Cranial capacity is often tested by filling the cranial cavity with glass beads and measuring their volume...
53 KB (6,157 words) - 05:54, 2 November 2024
Outline of human anatomy (section Thoracic cavity)
Heel Toe Big toe Sole Cavities Cranial cavity Spinal cavity Thoracic cavity Abdominopelvic cavity Abdominal cavity Pelvic cavity Planes, lines, and regions...
54 KB (4,597 words) - 06:00, 19 October 2024
and hypophysial veins. This depends upon the area of the cranial cavity: in the anterior cranial fossa the anterior meningeal artery (branch from the ethmoidal...
15 KB (1,718 words) - 20:58, 2 November 2024
Neurocranium (redirect from Cranial bones)
rest of the braincase. Animation without left parietal bone, showing cranial cavity and inner surface of base of skull. Inner surface of base of skull....
9 KB (1,044 words) - 15:25, 28 May 2024
facial vein and the cavernous sinus. The cavernous sinus lies within the cranial cavity, between layers of the meninges, and is a major conduit of venous drainage...
6 KB (733 words) - 18:36, 14 April 2024
pterygopalatine fossae or masseteric space. The spread of the cancer into the cranial cavity may lead to headaches, nerve damage, and cerebrospinal fluid leak. Cigarette...
12 KB (1,532 words) - 07:59, 6 September 2024
enters first the cranial cavity and then the nasal cavity. It provides sensory innervation to part of the meninges, parts of the nasal cavity, and part of...
5 KB (535 words) - 14:36, 3 May 2024
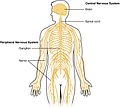
Central nervous system (section Cranial nerves)
vertebrates, the CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, while the brain is housed in the cranial cavity within the skull. The spinal cord is housed in...
34 KB (3,645 words) - 12:08, 24 October 2024
Meninges (redirect from Subarachnoid cavity)
anatomicae de durae meningis ... published in Acta Eruditorum, 1703 Cranial cavity Also rarely called meninx fibrosa or pachymeninx "meninges". Oxford...
14 KB (1,578 words) - 02:06, 23 October 2024
tympanic cavity through the petrous part of the temporal bone into the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through...
5 KB (517 words) - 16:20, 8 May 2024
"tent of the cerebellum") is one of four dural folds that separate the cranial cavity into four (incomplete) compartments. The cerebellar tentorium separates...
6 KB (663 words) - 16:11, 10 August 2024
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs...
42 KB (4,693 words) - 04:00, 23 October 2024
olfactory cells. Due to the location of the tumor and its proximity to the cranial cavity, esthesioneuroblastoma can be highly invasive and challenging to treat...
22 KB (2,029 words) - 00:14, 16 December 2023
Human nose (section Nasal cavity)
nerve into the cranial cavity. The mucosa that lines the nasal cavity extends into its chambers, the paranasal sinuses. The nasal cavity and the paranasal...
78 KB (9,078 words) - 18:43, 30 October 2024
ethmoid bone of the skull, projecting above the cribriform plate into the cranial cavity. It serves as an attachment for the membranes surrounding the brain...
3 KB (268 words) - 15:56, 16 May 2024
cerebral hemispheres are absent to a great degree and the remaining cranial cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Hydranencephaly is a type of cephalic...
11 KB (1,076 words) - 19:41, 3 October 2024
ganglion, a part of the cervical sympathetic trunk) that enters the cranial cavity through the carotid canal, then passes perpendicular to the carotid...
4 KB (359 words) - 15:53, 8 May 2024
lobe the flocculonodular lobe. The cerebellum rests at the back of the cranial cavity, lying beneath the occipital lobes, and is separated from these by the...
169 KB (18,815 words) - 15:17, 25 October 2024
carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into (the middle cranial fossa of) the cranial cavity. Observing the trajectory of the canal from exterior to interior...
8 KB (790 words) - 23:19, 20 September 2024
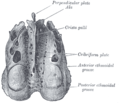
which connect the anterior cranial fossa with the nasal cavity and transmit the olfactory nerves. Animation. Anterior cranial fossa shown in green. Photo...
5 KB (595 words) - 01:52, 14 October 2019
the skull. It is the superior part of the neurocranium and covers the cranial cavity containing the brain. It forms the main component of the skull roof...
6 KB (736 words) - 02:26, 17 May 2024
34 bones and contains four cavities: the cranial cavity, the orbital cavity, oral, and the nasal cavity. The cranial cavity encloses and protects the brain...
15 KB (2,137 words) - 07:37, 9 August 2024