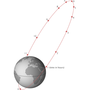
satellite to be placed in this kind of orbit was launched in 1963. Communications satellites are often placed in a geostationary orbit so that Earth-based...
49 KB (4,882 words) - 17:29, 19 November 2024
as low as low Earth orbit (LEO) and an apogee as high as geostationary orbit (GEO). Satellites that are destined for geosynchronous orbit (GSO) or GEO...
13 KB (1,801 words) - 19:57, 9 August 2024
geosynchronous Earth orbit (GEO) may be a synonym for geosynchronous equatorial orbit, or geostationary Earth orbit. The first geosynchronous satellite was designed...
33 KB (3,226 words) - 04:30, 12 November 2024
medium Earth orbit, where geostationary satellites are and where after their end of use they are parked in similar orbits, so-called graveyard orbits. Atmospheric...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024
geosynchronous satellite is the geostationary satellite, which has a geostationary orbit – a circular geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator...
9 KB (1,035 words) - 09:06, 28 July 2024
performance. In practice, a satellite in a Molniya orbit serves the same purpose for high latitudes as a geostationary satellite does for equatorial regions...
28 KB (3,117 words) - 20:57, 16 December 2024
satellites that are not in geostationary orbit are sometimes referred to as being in an inclined geostationary orbit (IGSO). Some of these satellites...
67 KB (729 words) - 03:23, 7 December 2024
An areostationary orbit, areosynchronous equatorial orbit (AEO), or Mars geostationary orbit is a circular areosynchronous orbit (ASO) approximately...
8 KB (803 words) - 16:23, 5 November 2024
periods of time. This makes these elliptical orbits useful for communications satellites. Geostationary orbits cannot serve polar latitudes because their...
3 KB (307 words) - 19:21, 6 July 2024
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy...
16 KB (1,695 words) - 17:20, 19 December 2024
re-orbiting it to a graveyard orbit only requires about 11 metres per second (36 ft/s). For satellites in geostationary orbit and geosynchronous orbits,...
8 KB (1,009 words) - 01:04, 21 December 2024
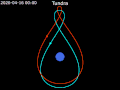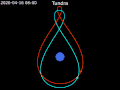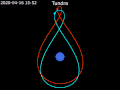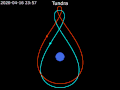
coverage for high-latitude regions, which geostationary satellites struggled to cover effectively. The Tundra orbit, while similar in its high inclination...
18 KB (1,850 words) - 08:45, 18 December 2024
system. Some communication satellites use much higher geostationary orbits and move at the same angular velocity as the Earth as to appear stationary above...
19 KB (2,168 words) - 11:41, 20 December 2024
climate of the Earth. Satellites are mainly of two types: polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously) or geostationary (hovering over the same...
30 KB (3,509 words) - 13:25, 20 December 2024
communications satellites are in geostationary orbit 22,236 miles (35,785 km) above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point...
50 KB (6,000 words) - 07:41, 18 December 2024
Geocentric orbit: An orbit around the planet Earth, such as that of the Moon or of artificial satellites. Selenocentric orbit (named after Selene): An orbit around...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
A geocentric orbit, Earth-centered orbit, or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA...
17 KB (1,997 words) - 14:43, 5 September 2024
any time everywhere on Earth at least one satellite is visible. Satellites are typically placed in sets of complementary orbital planes and connect to...
25 KB (1,753 words) - 14:14, 29 October 2024
in a paper in Wireless World in 1945. The first satellite to successfully reach geostationary orbit was Syncom3, built by Hughes Aircraft for NASA and...
68 KB (8,284 words) - 06:41, 10 December 2024
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), operated by the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s...
40 KB (4,221 words) - 00:02, 20 December 2024
Earth.[dubious – discuss] A geostationary orbit is a particular type of equatorial orbit, one which is geosynchronous. A satellite in a geostationary...
5 KB (689 words) - 02:48, 9 August 2023
communication satellite, part of the AMOS series of satellites. The satellite was positioned at 4° West longitude in the geostationary orbit. Transmission...
7 KB (509 words) - 08:42, 6 January 2023
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given...
14 KB (1,657 words) - 08:59, 12 December 2024
into geostationary orbit for testing purposes. In the early 1960s, when Europe and America were establishing geostationary communication satellites, the...
14 KB (1,302 words) - 03:42, 23 September 2024
vertical projection of the satellite's orbit onto the surface of the Earth (or whatever body the satellite is orbiting). A satellite ground track may be thought...
14 KB (1,946 words) - 02:09, 22 October 2024
about 90% of the satellites orbiting the Earth are in low Earth orbit or geostationary orbit; geostationary means the satellites stay still in the sky...
61 KB (6,358 words) - 08:36, 16 December 2024
Artemis was a geostationary earth orbit satellite (GEOS) for telecommunications, built by Alenia Spazio for ESA. The Artemis satellite operated at the...
12 KB (1,023 words) - 13:41, 9 July 2024
A satellite is said to occupy an inclined orbit around Earth if the orbit exhibits an angle other than 0° to the equatorial plane. This angle is called...
3 KB (338 words) - 20:20, 12 June 2024
Starlink (redirect from Proliferated Low Earth Orbit program)
of up to a million fixed satellite Earth stations that would communicate with its non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellite Starlink system. In June 2019...
279 KB (23,688 words) - 17:54, 21 December 2024
7 navigational satellites. Three of the satellites are placed in geostationary orbit (GEO) and the remaining 4 in geosynchronous orbit (GSO) to have a...
43 KB (4,447 words) - 23:29, 16 December 2024