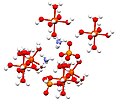
Ferrous oxalate (iron(II) oxalate) are inorganic compound with the formula FeC2O4(H2O)x where x is 0 or 2. These are orange compounds, poorly soluble...
5 KB (342 words) - 03:54, 5 February 2024
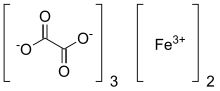
Ferric oxalate, also known as iron(III) oxalate, refers to inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(C2O4)3(H2O)x but could also refer to salts of [Fe(C2O4)3]3-...
5 KB (491 words) - 14:30, 9 March 2024
decomposition of iron(II) oxalate. FeC2O4 → FeO + CO2 + CO The procedure is conducted under an inert atmosphere to avoid the formation of iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3)...
7 KB (548 words) - 13:43, 13 August 2024
Copper(II) oxalate are inorganic compounds with the chemical formula CuC2O4(H2O)x. The value of x can be 0, 0.44, and 1. Two of these species are found...
6 KB (481 words) - 18:30, 24 September 2024
Potassium ferrioxalate (redirect from Potassium ferric oxalate)
ammonium iron(III) citrate, but potassium ferrioxalate is also used. A number of other iron oxalates are known: Iron(II) oxalate Iron(III) oxalate Sodium...
10 KB (1,020 words) - 07:07, 25 June 2024
Tin(II) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of tin and oxalic acid with the chemical formula SnC 2O 4. The compound looks like colorless crystals...
4 KB (373 words) - 01:58, 1 December 2023
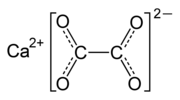
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula CaC2O4 or Ca(COO)2. It forms hydrates...
16 KB (1,485 words) - 23:11, 27 September 2024
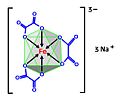
Sodium ferrioxalate (category Iron complexes)
which causes the decomposition of one oxalate to carbon dioxide CO2 and reduction of the iron(III) atom to iron(II). Sodium ferrioxalate can be obtained...
4 KB (318 words) - 17:53, 30 January 2024
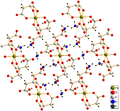
processes. The dihydrate of iron(II) oxalate has a polymeric structure with co-planar oxalate ions bridging between iron centres with the water of crystallisation...
150 KB (17,056 words) - 12:22, 24 August 2024
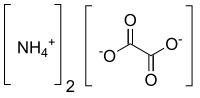
ammonium cations ([NH4]+) and oxalate anions (C2O2−4). The structure of ammonium oxalate is ([NH4]+)2[C2O4]2−. Ammonium oxalate sometimes comes as a monohydrate...
4 KB (310 words) - 22:30, 1 May 2024
Manganese oxalate is a chemical compound, a salt of manganese and oxalic acid with the chemical formula MnC 2O 4. The compound creates light pink crystals...
7 KB (614 words) - 04:25, 17 June 2024
processes. The dihydrate of iron(II) oxalate has a polymeric structure with co-planar oxalate ions bridging between iron centres with the water of crystallisation...
27 KB (2,957 words) - 03:23, 7 August 2024
Potassium ferrooxalate (category Iron(II) compounds)
bisoxalatoferrate(II), is a salt with the formula K2Fe(C2O4)2(H2O)x. The anion is a transition metal oxalate complex, consisting of an atom of iron in the +2...
4 KB (307 words) - 16:25, 30 January 2024
Chromium(II) oxalate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrC2O4. According to Nikumbh et al., CrC2O4·2H2O can be prepared from chromium(II) sulfate...
4 KB (291 words) - 19:43, 25 September 2023
Ferric (redirect from Ferric iron)
is used instead for iron(II) salts, containing the cation Fe2+. The word ferric is derived from the Latin word ferrum, meaning "iron". Although often abbreviated...
8 KB (1,039 words) - 16:20, 6 July 2024
Humboldtine (category Oxalate minerals)
composition FeC2O4•2H2O and is therefore a water-containing iron(II) oxalate or the iron salt of oxalic acid. Humboldtine crystallizes in the monoclinic...
6 KB (564 words) - 07:50, 17 February 2024
Fe2+Nb2O6 Iron(II) chloride – FeCl2 Iron(II) oxalate – FeC2O4 Iron(II) oxide – FeO Iron(II) selenate – FeSeO4 Iron(II) sulfate – FeSO4 Iron(III) chloride...
119 KB (8,735 words) - 14:26, 16 September 2024
134 Iron(II) oxalate FeC2O4·2H2O 0.008 Iron(II) perchlorate Fe(ClO4)2·6H2O 299 Iron(II) sulfate FeSO4 28.8 40 48 60 73.3 101 79.9 Iron(III) arsenate...
84 KB (193 words) - 18:48, 2 September 2024
Transition metal oxalate complexes are coordination complexes with oxalate (C2O42−) ligands. Some are useful commercially, but the topic has attracted...
9 KB (931 words) - 07:08, 25 June 2024
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate, or Mohr's salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2SO4.Fe(SO4).6H2O. Containing two different cations, Fe2+ and...
6 KB (432 words) - 06:38, 29 May 2024
Beryllium oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of beryllium metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula C 2BeO 4. It forms colorless crystals...
4 KB (293 words) - 17:38, 25 September 2023
The ultrafine particles can be prepared by thermal decomposition of iron(III) oxalate. Several other phases have been identified or claimed. The beta phase...
22 KB (2,076 words) - 16:36, 18 September 2024
Ammonium ferric citrate (redirect from Iron(II) ammonium citrate)
ammoniacal ferrous citrate) has the formula [NH+4]5[Fe(C6H4O7)2]5−. The iron in this compound is trivalent. All three carboxyl groups and the central...
6 KB (333 words) - 12:40, 29 September 2024
by solid-state reaction using Li2CO3 (lithium carbonate), FeC2O4 (iron(II) oxalate), and NH4H2PO4 (ammonium dihydrogen phosphate). The compounds were...
10 KB (1,378 words) - 08:23, 30 July 2023
An oxalate chloride or oxalato chloride is a mixed anion compound contains both oxalate and chloride anions. Related compounds include oxalate fluorides...
38 KB (2,124 words) - 04:58, 1 June 2024
crystallization from a solution of ferric sulfate and ammonium sulfate. Iron(II) in ferrous sulfate is oxidized to ferric sulfate by addition of sulfuric...
7 KB (539 words) - 13:45, 3 April 2024
hydrated ferric chloride is oxophilic. For example, oxalate salts react rapidly with aqueous iron(III) chloride to give [Fe(C2O4)3]3−, known as ferrioxalate...
39 KB (3,874 words) - 22:00, 27 September 2024
quantitative presence of various chemical species, such as iron(II), manganese(II), oxalate, nitrite, and hydrogen peroxide. Depending on the conditions...
3 KB (348 words) - 07:32, 5 September 2023
Upon heating in an oxygen-free atmosphere (usually CO2), manganese(II) oxalate decomposes into MnO: MnC2O4·2H2O → MnO + CO2 + CO + 2 H2O Together with...
6 KB (546 words) - 09:55, 26 May 2024