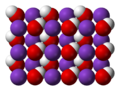
Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide or ferric oxyhydroxide is the chemical compound of iron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula FeO(OH). The compound is often encountered...
11 KB (1,227 words) - 00:12, 10 June 2024
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It occurs in nature as the mineral hematite, which serves as the primary...
22 KB (2,154 words) - 00:39, 29 October 2024
anaerobic conditions, the iron(II) hydroxide can be oxidised by the protons of water to form magnetite (iron(II,III) oxide) and molecular hydrogen. This...
7 KB (661 words) - 06:51, 17 November 2024
Iron(II,III) oxide, or black iron oxide, is the chemical compound with formula Fe3O4. It occurs in nature as the mineral magnetite. It is one of a number...
23 KB (2,169 words) - 13:28, 16 September 2024
Rust (redirect from Rust (iron oxide))
hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), Fe(OH)3), and is typically associated with the corrosion of refined iron. Given...
28 KB (3,121 words) - 12:50, 18 November 2024
Goethite (category Iron oxide pigments)
/ˈɡoʊθaɪt/) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the α-polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature...
17 KB (1,689 words) - 12:12, 26 February 2024
hydrated iron(III) oxide (ferric oxide). Iron(II) oxide also refers to a family of related non-stoichiometric compounds, which are typically iron deficient...
7 KB (548 words) - 13:43, 13 August 2024
magnetite, and hematite. Oxides of FeII FeO: iron(II) oxide, wüstite Mixed oxides of FeII and FeIII Fe3O4: Iron(II,III) oxide, magnetite Fe4O5 Fe5O6 Fe5O7...
10 KB (967 words) - 12:22, 18 November 2024
Limonite (redirect from Brown iron ore)
Limonite (/ˈlaɪməˌnaɪt/) is an iron ore consisting of a mixture of hydrated iron(III) oxide-hydroxides in varying composition. The generic formula is...
15 KB (1,669 words) - 16:49, 7 February 2024
high temperatures (e.g. above 500 °C), iron can react endothermically with sodium hydroxide to form iron(III) oxide, sodium metal, and hydrogen gas. This...
54 KB (5,925 words) - 15:03, 14 November 2024
inorganic compounds, in which carbonates, oxides, and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate. By contrast, quicklime specifically...
23 KB (2,231 words) - 10:54, 14 November 2024
bound to a strongly electron-withdrawing metal centre, hydroxide ligands tend to ionise into oxide ligands. For example, the bichromate ion [HCrO4]− dissociates...
41 KB (4,891 words) - 16:04, 20 November 2024
Nickel oxide hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NiO(OH). It is a black solid that is insoluble in all solvents but attacked...
3 KB (311 words) - 02:43, 20 November 2023
The nickel–iron battery (NiFe battery) is a rechargeable battery having nickel(III) oxide-hydroxide positive plates and iron negative plates, with an...
18 KB (2,022 words) - 23:31, 20 July 2024
hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties. Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide, AlO(OH), and aluminium oxide or...
24 KB (2,174 words) - 07:32, 23 October 2024
its oxide layer. Iron forms various oxide and hydroxide compounds; the most common are iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), and iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3). Iron(II)...
150 KB (17,078 words) - 12:22, 24 August 2024
pages 509-524. doi:10.1016/S0021-9797(78)80011-3 H. Lux (1963). "Iron (III) Hydroxide FeO(OH)". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry...
8 KB (704 words) - 12:39, 2 April 2024
Ferrous (redirect from Ferrous iron)
organisms must obtain their iron from the environment. However, iron tends to form highly insoluble iron(III) oxides/hydroxides in aerobic (oxygenated) environment...
9 KB (975 words) - 20:00, 6 November 2024
Lepidocrocite (category Iron(III) minerals)
Lepidocrocite (γ-FeO(OH)), also called esmeraldite or hydrohematite, is an iron oxide-hydroxide mineral. Lepidocrocite has an orthorhombic crystal structure, a hardness...
4 KB (201 words) - 08:55, 17 October 2024
coordinated to 4 oxide ions and oxide cubically coordinated to 8 sodium ions. Sodium oxide is produced by the reaction of sodium with sodium hydroxide, sodium...
7 KB (542 words) - 05:02, 12 September 2024
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning...
5 KB (580 words) - 02:09, 29 April 2024
iridescent layer of bismuth oxide, with a whitish-silver bismuth cube for comparison Goethite, an iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, from Polk County, Arkansas...
20 KB (1,973 words) - 09:05, 2 November 2024
low-temperature process does not oxidize the iron, but deposits a copper selenium compound. Hot baths of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), nitrates such as sodium nitrate...
11 KB (1,265 words) - 11:54, 15 September 2024
Manganese oxide is any of a variety of manganese oxides and hydroxides. These include Manganese(II) oxide, MnO Manganese(II,III) oxide, Mn3O4 Manganese(III) oxide...
2 KB (232 words) - 12:21, 27 January 2024
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula Al2O3. It is the most commonly occurring...
36 KB (3,591 words) - 07:25, 11 November 2024
Ethylene oxide was first reported in 1859 by the French chemist Charles-Adolphe Wurtz, who prepared it by treating 2-chloroethanol with potassium hydroxide: Cl...
106 KB (11,531 words) - 00:26, 22 November 2024
potassium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide. Nickel–iron batteries also use potassium hydroxide electrolyte. In food products, potassium hydroxide acts as...
21 KB (2,063 words) - 06:28, 7 October 2024
Iron oxide nanoparticles are iron oxide particles with diameters between about 1 and 100 nanometers. The two main forms are composed of magnetite (Fe3O4)...
25 KB (2,968 words) - 11:37, 20 February 2024