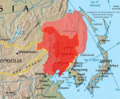
called "Jin" (or "Great Jin") in 1616 and ruled as a khan. This marks the start of the Later Jin dynasty. With the establishment of the Later Jin dynasty...
14 KB (1,464 words) - 03:31, 7 January 2025
(金朝), also known as the Jurchen Jin Later Jin (1616–1636) (後金; 1616–1636), precursor of the Qing dynasty Jin (Korean state) (辰國), precursor of the Jinhan...
5 KB (711 words) - 03:28, 8 January 2025
Later Jin may refer to two states in imperial China: Later Jin (Five Dynasties) (後晉; 936–947), one of the Five Dynasties Later Jin (1616–1636) (後金; 1616–1636)...
320 bytes (75 words) - 09:43, 8 November 2018
the first capital of the Later Jin (1616–1636) state, the predecessor of the Qing dynasty of China. It was the capital from 1616 to 1622. It was renamed...
2 KB (298 words) - 03:02, 18 July 2024
homelands of the Jurchens The traditional homelands of the Manchus Later Jin (1616–1636), the Manchu state prior to the establishment of the Qing Empire...
1 KB (160 words) - 22:16, 5 December 2023
and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Qing (1636–1912) dynasties of China were established and ruled by the...
186 KB (17,712 words) - 00:25, 6 January 2025
Jurchen took control of most of Manchuria. In 1616 Nurhaci founded the Later Jin dynasty, which later became known as the Qing dynasty. The Qing defeated...
68 KB (7,618 words) - 17:29, 22 November 2024
Qing dynasty coinage (redirect from Later Jin dynasty coinage (1616-1636))
people, while adopting policies which fostered ethnic inclusivity. In 1616, the Later Jin began producing their own cash coins; the coins issued under Nurhaci...
139 KB (15,743 words) - 22:52, 7 January 2025
founding ruler of Later Jin (1616–1636) Shi Jingtang (892–942), founding emperor of Later Jin (936–947) Taizu (disambiguation) Jin (disambiguation) This...
566 bytes (113 words) - 02:17, 7 June 2021
to: Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) Jin dynasty (266–420) Jin dynasty (1115–1234) Later Jin (1616–1636) Qing dynasty (1644–1912) Jin § States Qin § Dynasties and...
342 bytes (64 words) - 18:53, 29 March 2024
Autonomous Region, China Hetu Ala, the capital of Later Jin (1616–1636), also known as Xingjing (興京) after 1636, located in Xinbin Manchu Autonomous County...
550 bytes (97 words) - 19:07, 26 September 2022
Qizhuang (section Ming dynasty and later Jin dynasty)
bannermen and Han bannermen in Later Jin (1616–1636) territories engaged in the practice of shaving their foreheads since 1616. When the Manchu arrived in...
86 KB (8,790 words) - 06:17, 31 March 2024
of Aisin-Gioro is a Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin dynasty (1616–1636), the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), and Manchukuo (1932–1945) in the history...
48 KB (5,266 words) - 19:00, 3 January 2025
Nurhaci was Khan of Later Jin from 1616 to 1626. Hong Taiji was Khan of Later Jin from 1626 to 1636, and Emperor of the Qing dynasty from 1636 to 1643. During...
50 KB (844 words) - 05:36, 31 August 2024
Khan by the Mongols. In 1616, Nurhaci declared himself Khan and founded the Jin dynasty (aisin gurun), often called the Later Jin in reference to the legacy...
49 KB (5,541 words) - 12:00, 9 December 2024
: 60 The Manchu, Mongol bannermen and Han bannermen in Later Jin (1616–1636) territories since 1616 already shaved their foreheads. The Qing imposed the...
26 KB (3,153 words) - 01:51, 10 January 2025
technological advantage didn't last long. Kong Youde defected to the Later Jin (1616–1636) in 1631, taking with him knowledge of the hongyipao. Around 1635...
79 KB (10,888 words) - 11:29, 12 December 2024
University of California Press, 1998. Sinicization of the Manchus Later Jin (1616–1636) Conquest dynasty Qing dynasty in Inner Asia Names of the Qing dynasty...
59 KB (7,301 words) - 17:30, 11 December 2024
history Five Races Under One Union Han chauvinism Han nationalism Later Jin (1616–1636) Legacy of the Qing dynasty Little China (ideology) Names of the...
40 KB (4,092 words) - 01:12, 28 December 2024
(1559–1626), khan of the Jurchens, founded the Later Jin dynasty in 1616 in reference to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty (1115–1234) that had once ruled over...
48 KB (3,957 words) - 01:02, 9 October 2024
of this period. China Tianming (天命, 1616–1626): Later Jin—era name of Nurhaci Tiancong (天聰, 1627–1636): Later Jin—era name of Hong Taiji Ruiying (瑞應,...
4 KB (409 words) - 07:29, 29 November 2024
Qing dynasty (redirect from Manchu Empire (1636–1912))
the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital...
155 KB (18,915 words) - 16:04, 1 January 2025
was officially proclaimed in AD 1636 by the Emperor Taizong of Qing through renaming the Later Jin established in AD 1616, while the Ming imperial family...
208 KB (14,888 words) - 01:22, 3 December 2024
of Nurhaci (r. 1616–1626): Primary consort (大福晉; from 1623) During the reign of Hong Taiji (r. 1626–1643): Empress (皇后; from August 1636) During the reign...
8 KB (663 words) - 19:21, 26 June 2024
(1368–1644) Southern Ming (南明) (1644–1662) Qing dynasty (清朝) (1636–1912) Later Jin (後金) (1616–1636) Taiping Heavenly Kingdom Empire of China (1915–1916) Manchukuo...
25 KB (2,452 words) - 02:59, 16 December 2024
1610:Taipei-Kaohsiung 1611:Taipei-Tainan 1613:Taipei-Pingtung 1615:Taipei-Changhua 1616:Taipei-Yuanlin 1617:Taipei-Fengyuan—Dongshi District, Taichung 1618:Taipei-Chiayi...
6 KB (521 words) - 00:55, 18 September 2024
892–936) Later Han (AD 947–951) Later Jin (AD 936–947) Later Jin (AD 1616–1636) Later Trần dynasty (1407–1413) Later Zhou (AD 951–960) Liang dynasty (AD...
16 KB (1,297 words) - 11:42, 14 November 2024
Date Masamune (category 1636 deaths)
Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, DAH-tay; September 5, 1567 – June 27, 1636) was a Japanese daimyō during the Azuchi–Momoyama period through the early Edo period...
30 KB (3,327 words) - 09:18, 1 December 2024
Nurhaci's campaign against the Ula clan. In 1616, when Nurhaci declared himself khan and established the Later Jin dynasty, Daišan was the first selected as...
11 KB (1,367 words) - 00:38, 12 September 2024
History of Manchuria (section Liao and Jin dynasties)
Nurhaci declared himself a khan, and founded the Later Jin dynasty (which his successors renamed in 1636 to Qing dynasty). The process of unification of...
48 KB (5,936 words) - 04:10, 2 October 2024