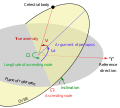
A near-equatorial orbit is an orbit that lies close to the equatorial plane of the primary body orbited. Such an orbit has an inclination near 0°. On Earth...
5 KB (689 words) - 18:00, 15 March 2025
satellites into polar orbit requires a larger launch vehicle to launch a given payload to a given altitude than for a near-equatorial orbit at the same altitude...
11 KB (1,231 words) - 07:37, 4 June 2025
Equatorial orbit: A non-inclined orbit with respect to the equator. Near equatorial orbit: An orbit whose inclination with respect to the equatorial plane...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
cases of the Sun-synchronous orbit are the noon/midnight orbit, where the local mean solar time of passage for equatorial latitudes is around noon or midnight...
14 KB (1,657 words) - 03:51, 6 July 2025
on orbit height. Satellites in orbits that reach altitudes below 300 km (190 mi) decay quickly due to atmospheric drag. Equatorial low Earth orbits (ELEO)...
19 KB (2,128 words) - 14:45, 18 June 2025
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35,786 km (22,236 mi) in altitude...
49 KB (4,893 words) - 06:24, 20 May 2025
In orbital mechanics a near-rectilinear halo orbit (NRHO) is a halo orbit that passes close to the smaller of two bodies and has nearly stable behavior...
9 KB (931 words) - 09:29, 28 June 2025
satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that...
11 KB (1,470 words) - 02:33, 8 May 2025
An areostationary orbit, areosynchronous equatorial orbit (AEO), or Mars geostationary orbit is a circular areosynchronous orbit (ASO) approximately...
8 KB (794 words) - 23:54, 7 July 2025
that its orbital plane is closer to the ecliptic plane instead of its primary's (in this case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital plane is...
38 KB (4,679 words) - 21:56, 14 June 2025
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi), or 8.317 light-minutes, in a counterclockwise direction as viewed...
17 KB (1,863 words) - 22:40, 1 July 2025
heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface...
4 KB (383 words) - 10:01, 12 July 2025
satellite reaches its final orbit. The orbital inclination of a GTO is the angle between the orbit plane and the Earth's equatorial plane. It is determined...
13 KB (1,789 words) - 19:22, 30 March 2025
the orbit passes crosses the reference plane, represented by the green angle i in the diagram). Inclinations near zero indicate equatorial orbits, and...
40 KB (5,776 words) - 18:28, 3 July 2025
In astrodynamics, an orbit equation defines the path of orbiting body m 2 {\displaystyle m_{2}\,\!} around central body m 1 {\displaystyle m_{1}\,\!}...
8 KB (1,317 words) - 19:17, 9 December 2024
Parabolic trajectory (redirect from Escape orbit)
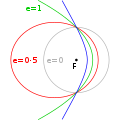
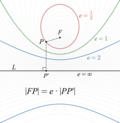
mechanics a parabolic trajectory is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity (e) equal to 1 and is an unbound orbit that is exactly on the border between elliptical...
9 KB (1,232 words) - 00:48, 8 July 2025
A high Earth orbit is a geocentric orbit with an apogee farther than that of the geosynchronous orbit, which is 35,786 km (22,236 mi) away from Earth....
9 KB (790 words) - 11:14, 26 April 2025
Hyperbolic trajectory (redirect from Hyperbolic orbit)
astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, a hyperbolic trajectory or hyperbolic orbit (from Newtonian theory: hyperbola shape) is the trajectory of any object...
14 KB (1,701 words) - 03:05, 8 July 2025
In astrodynamics and celestial dynamics, the orbital state vectors (sometimes state vectors) of an orbit are Cartesian vectors of position ( r {\displaystyle...
6 KB (833 words) - 11:13, 26 March 2025
graveyard orbit, also called a junk orbit or disposal orbit, is an orbit that lies away from common operational orbits. One significant graveyard orbit is a...
9 KB (1,036 words) - 14:31, 22 June 2025
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between 2,000...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024
Trans-lunar injection (redirect from Lunar transfer orbit)
approximates an elliptical orbit about the Earth with an apogee near to the radius of the Moon's orbit. The TLI burn is sized and timed to precisely target the...
12 KB (1,326 words) - 13:53, 27 June 2025
a small orbiting body relative to a larger orbiting body. The osculating (instantaneous) orbital period of the smaller body remains very near that of...
11 KB (1,408 words) - 04:50, 10 July 2025
thruster burns to keep the active craft in the same orbit as its target. For many low Earth orbit satellites, the effects of non-Keplerian forces, i.e...
14 KB (1,760 words) - 07:14, 7 May 2025
However, a synchronous orbit need not be equatorial; nor circular. A body in a non-equatorial synchronous orbit will appear to oscillate north and south...
8 KB (813 words) - 03:33, 1 June 2025
Halo orbit A halo orbit is a periodic, non-planar orbit associated with one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics...
11 KB (1,131 words) - 07:35, 16 June 2025
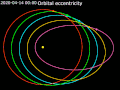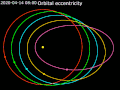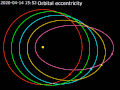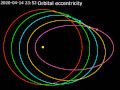
an elliptical orbit or eccentric orbit is an orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity...
18 KB (2,716 words) - 21:03, 10 June 2025
trajectory In orbital mechanics, a Lissajous orbit (pronounced [li.sa.ʒu]), named after Jules Antoine Lissajous, is a quasi-periodic orbital trajectory that...
8 KB (766 words) - 02:34, 13 November 2024
in the equatorial plane). But: conic sections may occur on surfaces of higher order, too (see image). In celestial mechanics, for bound orbits in a spherical...
11 KB (1,373 words) - 05:16, 22 March 2025
An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least...
13 KB (1,543 words) - 23:50, 6 July 2025