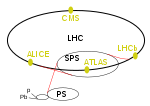
The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC /ˈrɪk/) is the first and one of only two operating heavy-ion colliders, and the only spin-polarized proton collider...
41 KB (4,768 words) - 08:07, 22 September 2024
Particle accelerator (redirect from Ring collider)
include the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and the largest accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider near Geneva...
66 KB (7,678 words) - 00:31, 30 October 2024
High-energy nuclear physics (redirect from Relativistic heavy-ion collisions)
the Brookhaven National Laboratory's Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) and at the CERN Large Hadron Collider. At RHIC the programme began with four...
10 KB (1,201 words) - 13:23, 7 August 2024
colliders Fixed-target experiment Large Electron–Positron Collider Large Hadron Collider Very Large Hadron Collider Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider International...
13 KB (1,343 words) - 18:59, 1 October 2024
contains several large research facilities, including the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and National Synchrotron Light Source II. Seven Nobel Prizes...
29 KB (2,833 words) - 03:56, 30 September 2024
List of accelerators in particle physics (redirect from List of particle colliders)
Undulator Radiation Collider: An Energy Efficient Design for a s = 15 GeV {\displaystyle {\sqrt {s}}=15~{\text{GeV}}} Collider". arXiv:1704.04469 [physics...
33 KB (657 words) - 13:15, 8 September 2024
National Laboratory's Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) on Long Island (New York, USA) and at CERN's recent Large Hadron Collider near Geneva (Switzerland)...
62 KB (7,370 words) - 00:36, 4 October 2024
An electron–ion collider (EIC) is a type of particle accelerator collider designed to collide spin-polarized beams of electrons and ions, in order to study...
8 KB (965 words) - 10:54, 24 September 2024
Safety of high-energy particle collision experiments (redirect from Safety of the Large Hadron Collider)
topical interest during the time when the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) and later the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)—currently the world's largest and...
56 KB (6,252 words) - 14:18, 2 November 2024
hadron collider 1981–1991. Tevatron, Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), in operation 1983–2011. Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC)...
1,001 bytes (113 words) - 22:18, 20 December 2021
Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC). Elliptic flow describes the azimuthal momentum space anisotropy of particle emission from non-central heavy-ion...
5 KB (471 words) - 09:34, 30 April 2022
nucleon (or 522 TeV per ion), higher than the energies reached by the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. The aim of the heavy-ion programme is to investigate...
108 KB (10,721 words) - 09:48, 19 October 2024
been an active participant with the STAR experiment at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) at Brookhaven National Laboratory, and the particle...
10 KB (820 words) - 17:00, 24 October 2024
chromodynamics. It is the object of study in the Large Hadron Collider and the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider, and is related to the so-called vacuum structure of...
25 KB (2,747 words) - 20:05, 20 September 2024
Cloud chamber (redirect from Ion cloud)
collisions, resulting in a trail of ionized gas particles. The resulting ions act as condensation centers around which a mist-like trail of small droplets...
15 KB (1,687 words) - 15:06, 24 October 2024
Archived 2008-11-20 at the Wayback Machine detector on the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine at Brookhaven National...
104 KB (12,956 words) - 19:12, 28 October 2024
Gerhard (1988). "Pair production with atomic shell capture in relativistic heavy ion collisions" (PDF). Brazilian Journal of Physics. 18: 559. Bertulani...
21 KB (2,219 words) - 20:17, 14 August 2024
Solenoidal Tracker at RHIC) is one of the four experiments at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) in Brookhaven National Laboratory, United States. The...
6 KB (761 words) - 06:40, 3 July 2024
Quark (redirect from Heavy quarks)
by CERN in the 1980s and 1990s), recent experiments at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider have yielded evidence for liquid-like quark matter exhibiting...
77 KB (7,572 words) - 14:12, 5 November 2024
one was discovered in March 2010 by the STAR detector of the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) at Brookhaven National Laboratory. "What does hypertriton...
2 KB (146 words) - 08:31, 6 February 2024
detector at Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider, Brookhaven National Laboratory and ALICE: A Large Ion Collider Experiment at the Large Hadron Collider, CERN presented...
4 KB (446 words) - 23:12, 10 September 2022
largest of the four experiments that have taken data at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) in Brookhaven National Laboratory, United States. PHENIX...
4 KB (582 words) - 19:39, 26 September 2024
development support for US government experiments at RHIC (Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider) at the Brookhaven National Laboratory to help discover the...
2 KB (145 words) - 22:54, 9 February 2024
collisions at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The strongest Higgs yield is from fusion of two gluons (via annihilation of a heavy quark pair), while two quarks...
12 KB (1,374 words) - 22:31, 2 May 2024
antimatter began in 1928, with a paper by Paul Dirac. Dirac realised that his relativistic version of the Schrödinger wave equation for electrons predicted the...
78 KB (8,023 words) - 02:06, 8 November 2024
used at both operating ion colliders: the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and in the Low Energy Ion Ring at CERN. Basically, electron cooling works as follows:...
2 KB (274 words) - 00:16, 5 November 2024
ISABELLE (section Colliding beam accelerators)
infrastructure built for ISABELLE were salvaged and reused by the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC), a US$617 million joint project of the U.S. Department...
8 KB (880 words) - 16:42, 3 May 2022
One method to reach relativistic velocities uses a matter-antimatter GeV gamma ray laser photon rocket made possible by a relativistic proton-antiproton...
25 KB (3,000 words) - 13:55, 13 September 2024
Nobel Prizes and today serves as the injector for Brookhaven's Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider; it remains the world's highest intensity high-energy proton...
6 KB (664 words) - 19:33, 26 September 2024
GeV/c2). The driving motivation for constructing the International Linear Collider is to produce the Higgs bosons (mass 125.09 GeV/c2) in this way.[citation...
7 KB (823 words) - 08:01, 13 September 2024