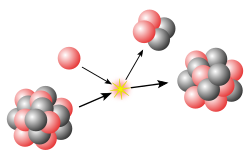
mechanics, the spin–orbit interaction (also called spin–orbit effect or spin–orbit coupling) is a relativistic interaction of a particle's spin with its motion...
29 KB (4,408 words) - 09:19, 3 April 2025
Angular momentum coupling (redirect from Orbit-orbit coupling)
orbit and spin of a single particle can interact through spin–orbit interaction, in which case the complete physical picture must include spin–orbit coupling...
17 KB (2,228 words) - 20:09, 21 February 2024
Quantum number (redirect from Quantum numbers with spin-orbit interaction)
outermost orbital). These rules are empirical but they can be related to electron physics.: 10 : 260 When one takes the spin–orbit interaction into consideration...
30 KB (3,266 words) - 21:56, 5 March 2025
m_{\text{j}}} too form a set of good quantum numbers. To take the spin-orbit interaction is taken into account, we have to add an extra term in Hamiltonian...
9 KB (1,409 words) - 11:34, 8 March 2024
Nuclear shell model (redirect from Nuclear orbital)
approximating the model with a three-dimensional harmonic oscillator plus a spin–orbit interaction. A more realistic but complicated potential is known as the Woods–Saxon...
30 KB (4,120 words) - 04:28, 2 March 2025
Pd, where the spin-orbit interaction is strong). A transformation of spin currents consisting in interchanging (swapping) of the spin and flow directions...
13 KB (1,548 words) - 17:40, 21 September 2024
spin resonance (EDSR) is a method to control the magnetic moments inside a material using quantum mechanical effects like the spin–orbit interaction....
22 KB (3,235 words) - 18:26, 23 February 2025
Dresselhaus effect is a phenomenon in solid-state physics in which spin–orbit interaction causes energy bands to split. It is usually present in crystal systems...
5 KB (753 words) - 01:09, 17 June 2023
Angular momentum (redirect from Spin-down)
angular momentum applies to J, but not to L or S; for example, the spin–orbit interaction allows angular momentum to transfer back and forth between L and...
93 KB (13,465 words) - 10:52, 25 March 2025
and m is the vacuum mass of the electron. (This equation neglects the spin–orbit effect; see below.) In a crystalline solid, V is a periodic function,...
12 KB (1,975 words) - 08:09, 19 December 2024
of SU(2) Spin angular momentum of light Spin engineering Spin-flip Spin isomers of hydrogen Spin–orbit interaction Spin tensor Spintronics Spin wave Yrast...
72 KB (10,572 words) - 12:18, 3 April 2025
in the Dirac Hamiltonian. The splitting is a combined effect of spin–orbit interaction and asymmetry of the crystal potential, in particular in the direction...
21 KB (2,843 words) - 10:51, 17 October 2024
electrons is much greater than the spin–orbit interaction, which is in turn stronger than any other remaining interactions. This is referred to as the LS...
12 KB (1,584 words) - 08:57, 5 March 2025
solution of the hydrogen atom with spin–orbit interaction. The spinor spherical harmonics Yl, s, j, m are the spinors eigenstates of the total angular momentum...
4 KB (592 words) - 19:15, 20 June 2024
Spintronics (redirect from Spin computing)
technique was used to overcome the lack of spin-orbit interaction and materials issues to achieve spin transport in silicon. Because external magnetic...
30 KB (3,343 words) - 17:21, 1 March 2025
electrostatic potential, additional relativistic terms include the spin–orbit interaction, electron gyromagnetic ratio, and Darwin term. In ordinary QM these...
86 KB (10,157 words) - 20:06, 29 December 2024
Hydrogen-like atom (redirect from Hydrogenic orbital)
a phenomenon known as spin–orbit interaction. When one takes this coupling into account, the spin and the orbital angular momentum are no longer conserved...
28 KB (5,292 words) - 01:24, 22 March 2025
B_{\text{SO}}} is the spin–orbit characteristic field which can be considered a measure of the strength of the spin–orbit interaction and B e {\displaystyle...
9 KB (1,505 words) - 21:11, 20 November 2024
effect from the non-relativistic calculation due to effects like spin–orbit interaction, zitterbewegung, and corrections to the kinetic energy. Chemistry...
2 KB (152 words) - 07:02, 21 February 2025
Tidal locking (redirect from Spin-orbit resonance)
locking, captured rotation, and spin–orbit locking. The effect arises between two bodies when their gravitational interaction slows a body's rotation until...
47 KB (5,091 words) - 00:08, 18 March 2025
Thomas precession (section In electron orbitals)
Lorentz transformations. Thomas precession gives a correction to the spin–orbit interaction in quantum mechanics, which takes into account the relativistic...
33 KB (4,713 words) - 04:08, 3 April 2025
arise, largely due to spin–orbit interaction—the mutual interaction between the motion and spin of electrons. The spin–orbit interaction is especially strong...
70 KB (11,069 words) - 06:21, 18 March 2025
in most cases from the simultaneous action of magnetization and spin–orbit interaction (exceptions related to non-collinear magnetic order notwithstanding)...
16 KB (1,863 words) - 22:16, 2 March 2025
Azimuthal quantum number (redirect from Orbital quantum number)
momenta. Due to the spin–orbit interaction in an atom, the orbital angular momentum no longer commutes with the Hamiltonian, nor does the spin. These therefore...
19 KB (2,143 words) - 18:41, 21 November 2024
their lighter homologues in the periodic table. Spin–orbit interaction splits the p subshell: one p orbital is relativistically stabilized and shrunken (it...
251 KB (27,130 words) - 17:25, 26 March 2025
Effect in Paramagnetic Resonance Spectra – Orbital Reduction Factors and Partial Quenching of Spin–Orbit Interaction". Physical Review. 138 (6A): A1727 – A1740...
61 KB (7,955 words) - 19:13, 14 March 2025
An orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin m s {\displaystyle m_{s}} . The simple names s orbital, p...
84 KB (10,942 words) - 02:20, 14 January 2025
106 kcal/mol of which about 46 kcal/mol come from these interactions. For comparison, the spin–orbit interaction for the similar molecule RnF 2 is about 10 kcal/mol...
64 KB (10,403 words) - 20:09, 17 March 2025
the spin–orbit interaction allows angular momentum to transfer back and forth between L and S, with the total J remaining constant. The orbital angular...
42 KB (6,685 words) - 17:59, 23 February 2025
key achievements include calculating relativistic effects on the spin-orbit interaction in a hydrogenic atom (Thomas precession), creating an approximate...
10 KB (888 words) - 10:28, 24 February 2025