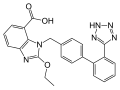
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood...
143 KB (15,593 words) - 09:45, 17 November 2024
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood...
64 KB (7,334 words) - 17:05, 11 September 2024
cardiomyopathies. Heart failure is frequently associated with weakness of the heart muscle in the ventricles (systolic heart failure), but can also be...
144 KB (17,016 words) - 04:01, 15 November 2024
Cardiology (redirect from Heart disorders)
medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians...
87 KB (9,515 words) - 16:10, 22 September 2024
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing...
24 KB (2,496 words) - 21:40, 15 October 2024
Edema (redirect from Oedema due to heart failure)
depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis...
30 KB (3,284 words) - 15:04, 20 November 2024
conditions and conditions that reduce the output of the right heart, such as right heart failure and some myocardial infarctions. Conditions that limit the...
18 KB (1,806 words) - 08:03, 29 September 2024
The main pathophysiology of heart failure is a reduction in the efficiency of the heart muscle, through damage or overloading. As such, it can be caused...
16 KB (2,166 words) - 05:57, 27 January 2023
heart disease with heart failure (I11.0) and hypertensive heart disease without heart failure (I11.9) are distinguished from chronic rheumatic heart diseases...
24 KB (2,174 words) - 20:31, 16 August 2024
Management of heart failure requires a multimodal approach. It involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and possibly the use of...
41 KB (5,139 words) - 08:07, 11 November 2024
Myocardial infarction (redirect from Heart Attack)
have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs...
129 KB (13,821 words) - 06:58, 18 November 2024
Cardiomegaly (redirect from Enlarged heart)
enlarged heart begins to affect the body's ability to pump blood, then symptoms associated with congestive heart failure may arise, including: Heart palpitations...
26 KB (2,721 words) - 09:59, 17 November 2024
Valsartan (section Heart failure)
Diovan among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It belongs to a class of medications referred...
41 KB (3,491 words) - 03:59, 30 October 2024
heart failure conditions including cardiogenic shock, as well as for long-term management of heart failure. These conditions arise when the heart's ability...
57 KB (5,106 words) - 16:11, 11 August 2024
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (redirect from Broken heart syndrome)
blood flow and oxygen to the heart muscle. Together, these events can lead to congestive heart failure and decrease the heart's output of blood with each...
52 KB (5,864 words) - 23:06, 20 November 2024
Cardiovascular disease (redirect from Heart disease)
the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive...
137 KB (14,469 words) - 14:14, 7 November 2024
Arrhythmia (redirect from Heart arryhthmia)
serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized...
43 KB (4,754 words) - 13:09, 12 November 2024
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF, hef-REF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction is reduced. This is defined as...
2 KB (173 words) - 16:24, 6 November 2024
Ejection fraction (section Heart failure categories)
ventricle of the heart. EF is widely used as a measure of the pumping efficiency of the heart and is used to classify heart failure types. It is also...
18 KB (2,219 words) - 09:45, 4 November 2024
Atrial fibrillation (section Rapid heart rate)
chest pain. Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia...
164 KB (18,163 words) - 00:55, 22 November 2024
artificial heart devices; in both cases, they are for temporary use, of less than a year, for total heart failure patients awaiting a human heart to be transplanted...
70 KB (7,749 words) - 00:19, 10 November 2024
High-output heart failure is a heart condition that occurs when the cardiac output is higher than normal because of increased peripheral demand. There...
2 KB (236 words) - 02:07, 25 May 2023
Ivabradine (section Heart failure)
symptomatic management of heart-related chest pain and heart failure. Patients who qualify for use of ivabradine for coronary heart failure are patients who have...
27 KB (2,803 words) - 18:23, 8 November 2024
hypoxemia and respiratory failure. Pulmonary edema has multiple causes and is traditionally classified as cardiogenic (caused by the heart) or noncardiogenic...
34 KB (3,812 words) - 09:59, 17 November 2024
Digoxin (section Heart failure)
used to treat various heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. Digoxin is one of the...
47 KB (4,845 words) - 09:13, 6 October 2024
Candesartan (section Heart failure)
used mainly for the treatment of high blood pressure and congestive heart failure. Candesartan has a very low maintenance dose. Like olmesartan, the metabolism...
22 KB (2,320 words) - 13:06, 15 August 2024
The Alliance for Heart Failure is a coalition of charities, patient groups, professional bodies, public sector organisations and corporate members working...
9 KB (938 words) - 02:57, 8 July 2024
Beta blocker (section Congestive heart failure)
indicated in cases of compensated, stable congestive heart failure; in cases of acute decompensated heart failure, beta blockers will cause a further decrease...
75 KB (7,463 words) - 18:51, 13 November 2024
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (redirect from Heart hypertrophy, hereditary)
may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly...
82 KB (8,830 words) - 06:28, 31 October 2024
BC-007 (section Heart failure)
clinical trials as a lead compound intended for the potential treatment of heart failure or long COVID. Since the 1990s, the binding of G protein coupled receptors...
17 KB (1,148 words) - 17:38, 23 July 2024