Cyanobacteria (/saɪˌænoʊbækˈtɪəri.ə/), also called Cyanobacteriota or Cyanophyta, are a phylum of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological...
179 KB (17,664 words) - 14:50, 27 August 2024
Cyanotoxin (redirect from Cyanobacteria bloom)
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes...
47 KB (5,160 words) - 02:56, 13 September 2024
by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy...
109 KB (11,779 words) - 23:18, 7 September 2024
Great Oxidation Event (section Cyanobacteria evolution)
supplies at the end of the GOE. The GOE is inferred to have been caused by cyanobacteria, which evolved chlorophyll-based photosynthesis that releases dioxygen...
85 KB (9,541 words) - 00:28, 7 September 2024
Cyanobacterium (genus) (redirect from Cyanobacterium (cyanobacteria))
Cyanobacterium is a genus belonging to the phylum Cyanobacteria. Komárek J, Kaštovský J, Mareš J, Johansen JR (2014). "Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes...
809 bytes (37 words) - 09:33, 11 July 2023
Cyanobacterial morphology (redirect from Filamentous cyanobacteria)
Cyanobacterial morphology refers to the form or shape of cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are a large and diverse phylum of bacteria defined by their unique...
69 KB (6,986 words) - 15:14, 22 August 2024
LY-kən, UK also /ˈlɪtʃən/ LITCH-ən) is a hybrid colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among filaments of multiple fungi species, along...
130 KB (14,225 words) - 16:44, 20 August 2024
Rivularia is a genus of cyanobacteria of the family Rivulariaceae. Rivularia is found growing on submerged stones, moist rocks, and damp soils near the...
5 KB (505 words) - 19:44, 27 October 2022
ancestor, and although their plastids seem to have a single origin, from cyanobacteria, they were acquired in different ways. Green algae are examples of algae...
91 KB (10,500 words) - 01:17, 28 August 2024
Spirulina (genus) (redirect from Spirulina (cyanobacteria))
Spirulina is a genus of cyanobacteria. It is not classed as algae, despite the common name of cyanobacteria being blue-green algae. Spirulina is commonly...
4 KB (242 words) - 17:04, 5 August 2024
Light-dependent reactions (section Cyanobacteria)
same transmembrane structures are also found in cyanobacteria. Unlike plants and algae, cyanobacteria are prokaryotes. They do not contain chloroplasts;...
28 KB (3,452 words) - 18:15, 8 August 2024
bacteriological code. However, cyanobacteria were still covered by the botanical code. Starting in 1999, cyanobacteria were covered by both the botanical...
11 KB (1,299 words) - 20:05, 22 August 2024
Gloeocapsa genus of cyanobacteria, an ancient line of photosynthesizing bacteria, which photolyze water generating oxygen gas. Ancient cyanobacteria were ancestral...
4 KB (528 words) - 08:11, 2 September 2024
energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water, using the green pigment...
95 KB (8,057 words) - 06:07, 5 September 2024
Spirulina (dietary supplement) (category Cyanobacteria)
Spirulina is the dried biomass of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) that can be consumed by humans and animals. The three species are Arthrospira platensis...
32 KB (3,469 words) - 09:25, 31 August 2024
Nostoc (category Cyanobacteria genera)
as witches' butter), and witch's jelly, is the most common genus of cyanobacteria found in a variety of both aquatic and terrestrial environments that...
24 KB (1,469 words) - 16:27, 6 December 2023
Cyanophages are viruses that infect cyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta or blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their...
36 KB (4,106 words) - 08:12, 19 August 2024
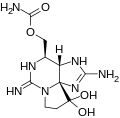
derives from saxitoxin produced by cyanobacteria. The biosynthesis of saxitoxin is well-defined in cyanobacteria, while within dinoflagellates it remains...
14 KB (1,429 words) - 08:26, 14 September 2024
photosynthesis, and examples of such organisms include plants, algae and cyanobacteria. Eukaryotic photoautotrophs absorb photonic energy through the photopigment...
7 KB (690 words) - 06:24, 16 August 2024
from endosymbionts, in this case cyanobacteria. They usually take the form of chloroplasts which, like cyanobacteria, contain chlorophyll and produce...
61 KB (6,138 words) - 17:30, 6 September 2024
freshwater species of cyanobacteria of the genus Aphanizomenon found around the world, including the Baltic Sea and the Great Lakes. Cyanobacteria were the first...
16 KB (1,643 words) - 12:42, 3 June 2024
beneficial symbiotic relationship of green algae and/or blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) living among filaments of a fungus, forming lichen. Living as a symbiont...
12 KB (1,433 words) - 02:10, 20 May 2024
Rickettsiales bacteria, while chloroplasts are thought to be related to cyanobacteria. The idea that chloroplasts were originally independent organisms that...
70 KB (7,517 words) - 19:12, 17 July 2024
Moss (section Relationship with cyanobacteria)
the ecosystem due to their relationship with nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria colonize moss and receive shelter in return for providing fixed...
61 KB (6,983 words) - 17:38, 5 August 2024
responsible for the abundant green seen in nature. Like plants, the cyanobacteria use water as an electron donor for photosynthesis and therefore liberate...
4 KB (406 words) - 05:48, 24 June 2024
Biological soil crust (section Cyanobacteria)
Biological soil crusts are most often composed of fungi, lichens, cyanobacteria, bryophytes, and algae in varying proportions. These organisms live...
34 KB (4,087 words) - 02:00, 6 September 2024
organisms. Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Examples of plastids include chloroplasts (used for photosynthesis);...
29 KB (3,219 words) - 22:25, 7 September 2024
Lechevalier (1926–2015). Geosmin is produced by various blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) and filamentous bacteria in the class Actinomyces, and also some other...
15 KB (1,544 words) - 21:11, 18 May 2024
Butanol fuel (section Cyanobacteria)
aldehydes. Isobutanol-producing species of cyanobacteria offer several advantages as biofuel synthesizers: Cyanobacteria grow faster than plants and also absorb...
40 KB (4,367 words) - 03:04, 15 September 2024
Harmful algal bloom (section Cyanobacteria)
driven Langmuir circulation and their biological effects. HABs from cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) can appear as a foam, scum, or mat on or just below...
163 KB (18,175 words) - 14:24, 21 August 2024