In logic and philosophy, a formal fallacy is a pattern of reasoning rendered invalid by a flaw in its logical structure that can neatly be expressed in...
10 KB (1,128 words) - 04:15, 26 September 2024
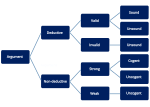
the context in which they are made. Fallacies are commonly divided into "formal" and "informal". A formal fallacy is a flaw in the structure of a deductive...
47 KB (5,578 words) - 11:02, 2 November 2024
contain fallacies. Because of their variety, fallacies are challenging to classify. They can be classified by their structure (formal fallacies) or content...
65 KB (6,805 words) - 08:23, 3 November 2024
of the argument, as is the case for formal fallacies, but can also be due to their content and context. Fallacies, despite being incorrect, usually appear...
39 KB (4,871 words) - 09:20, 2 November 2024
same set, in violation of the laws of probability. It is a type of formal fallacy. I am particularly fond of this example [the Linda problem] because...
19 KB (2,306 words) - 11:25, 28 June 2024
Argument from fallacy is the formal fallacy of analyzing an argument and inferring that, since it contains a fallacy, its conclusion must be false. It...
6 KB (727 words) - 00:28, 24 September 2024
The fallacy of four terms (Latin: quaternio terminorum) is the formal fallacy that occurs when a syllogism has four (or more) terms rather than the requisite...
5 KB (647 words) - 03:15, 29 October 2024
An ecological fallacy (also ecological inference fallacy or population fallacy) is a formal fallacy in the interpretation of statistical data that occurs...
19 KB (2,789 words) - 17:02, 21 September 2024
The association fallacy is a formal logical fallacy that asserts that properties of one thing must also be properties of another thing if both things...
8 KB (855 words) - 05:10, 25 October 2024
Irrelevant conclusion (redirect from Logical fallacy/Ignoratio elenchi)
be confused with formal fallacy, an argument whose conclusion does not follow from its premises; instead, it is that despite its formal consistency it is...
9 KB (1,017 words) - 18:26, 16 September 2024
The existential fallacy, or existential instantiation, is a formal fallacy. In the existential fallacy, one presupposes that a class has members when one...
3 KB (321 words) - 09:43, 2 November 2024
Logical reasoning (section Fallacies)
called fallacies. For formal fallacies, like affirming the consequent, the error lies in the logical form of the argument. For informal fallacies, like...
70 KB (7,319 words) - 05:56, 28 October 2024
Affirming a disjunct – Formal fallacy Essentialism – View that entities have identifying attributes Fallacy of composition – Fallacy of inferring on the...
2 KB (245 words) - 16:05, 21 February 2024
Affirming the consequent (redirect from Fallacy of the Consequent)
sometimes called converse error, fallacy of the converse, or confusion of necessity and sufficiency, is a formal fallacy of taking a true conditional statement...
7 KB (963 words) - 18:39, 1 November 2024
The fallacy of the undistributed middle (Latin: non distributio medii) is a formal fallacy that is committed when the middle term in a categorical syllogism...
5 KB (683 words) - 20:30, 26 October 2024
gambler's fallacy, named by philosopher Ian Hacking, is a formal fallacy of Bayesian inference which is an inverse of the better known gambler's fallacy. It...
5 KB (785 words) - 07:30, 13 August 2023
Logic (redirect from Formal logic)
informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses...
145 KB (16,445 words) - 14:44, 9 October 2024
False dilemma (redirect from Logical fallacy/False dilemma)
usually divided into formal and informal fallacies. Formal fallacies are unsound because of their structure, while informal fallacies are unsound because...
18 KB (2,165 words) - 09:43, 2 November 2024
In philosophical logic, the masked-man fallacy (also known as the intensional fallacy or epistemic fallacy) is committed when one makes an illicit use...
5 KB (690 words) - 11:28, 29 October 2024
Post hoc ergo propter hoc (redirect from Logical fallacy/Post hoc)
informal fallacy which one commits when one reasons, "Since event Y followed event X, event Y must have been caused by event X." It is a fallacy in which...
6 KB (671 words) - 11:05, 2 November 2024
Begging the question (redirect from Fallacy of Circular Reasoning)
question or assuming the conclusion (Latin: petītiō principiī) is an informal fallacy that occurs when an argument's premises assume the truth of the conclusion...
26 KB (3,267 words) - 05:11, 29 October 2024
Denying the antecedent (redirect from Fallacy of denying the antecedent)
the antecedent, sometimes also called inverse error or fallacy of the inverse, is a formal fallacy of inferring the inverse from an original statement....
4 KB (495 words) - 21:12, 12 March 2024
(also known as concretism, hypostatization, or the fallacy of misplaced concreteness) is a fallacy of ambiguity, when an abstraction (abstract belief...
13 KB (1,604 words) - 13:27, 14 October 2024
Deductive reasoning (section Fallacies)
deductive arguments, which do not follow a rule of inference, are called formal fallacies. Rules of inference are definitory rules and contrast with strategic...
70 KB (8,484 words) - 11:01, 2 November 2024
contentious Formal fallacy, reasoning of invalid structure Informal fallacy, the complement Informal mathematics, also called naïve mathematics Formal cause...
4 KB (466 words) - 20:01, 2 January 2024
The gambler's fallacy, also known as the Monte Carlo fallacy or the fallacy of the maturity of chances, is the belief that, if an event (whose occurrences...
39 KB (5,475 words) - 07:17, 23 October 2024
Illicit major (category Syllogistic fallacies)
Illicit major is a formal fallacy committed in a categorical syllogism that is invalid because its major term is undistributed in the major premise but...
1 KB (206 words) - 10:28, 26 July 2022
Affirmative conclusion from a negative premise (category Syllogistic fallacies)
Affirmative conclusion from a negative premise (illicit negative) is a formal fallacy that is committed when a categorical syllogism has a positive conclusion...
1 KB (188 words) - 09:41, 2 November 2024
Illicit minor (category Syllogistic fallacies)
Illicit minor is a formal fallacy committed in a categorical syllogism that is invalid because its minor term is undistributed in the minor premise but...
1 KB (178 words) - 08:12, 15 March 2023
Affirming a disjunct (category Propositional fallacies)
The formal fallacy of affirming a disjunct also known as the fallacy of the alternative disjunct or a false exclusionary disjunct occurs when a deductive...
3 KB (300 words) - 17:02, 21 September 2024