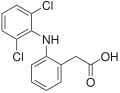
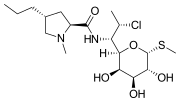
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological...
17 KB (1,857 words) - 06:00, 19 August 2024
mechanism of action of aspirin". Thrombosis Research. In Honour of Sir John Vane, F.R.S., Nobel laureate, the Discoverer of the Machanism of Action of...
15 KB (1,781 words) - 20:24, 6 November 2024
Linkage (mechanical) Mechanism of action, the means by which a drug exerts its biological effects Defence mechanism, unconscious mechanisms aimed at reducing...
1 KB (207 words) - 01:37, 1 July 2024
Anti-ulcer agents (section Mechanism of action)
Action". Martindale. Archived from the original on 2023-03-13. Retrieved 2024-04-01. "Metronidazole (systemic): Drug information. Mechanism of Action"...
44 KB (3,318 words) - 21:23, 19 October 2024
Cardiotonic agent (section Mechanism of action)
can be categorised into four distinct groups based on their unique mechanisms of action: cardiac glycosides, beta-adrenergic agonists, phosphodiesterase...
57 KB (5,106 words) - 16:11, 11 August 2024
Agonist (section Mechanism of action)
remains generally consistent however, with the primary mechanism of action requiring the binding of the agonist and the subsequent changes in conformation...
14 KB (1,622 words) - 03:21, 4 September 2024
Topical antifungal (section Mechanism of action)
to their chemical structures and their corresponding mechanism of actions. The four classes of topical antifungal drugs are azole antifungals, polyene...
28 KB (3,320 words) - 11:05, 12 October 2024
Losartan (section Mechanism of action)
olmesartan, and telmisartan. They all have the same mechanism of action and potentially inhibit the actions of angiotensin better than ACE inhibitors, such as...
41 KB (3,269 words) - 22:06, 30 August 2024
Mupirocin (section Mechanism of action)
and it's possible other species of Pseudomonas may be resistant as well. [citation needed] The mechanism of action of mupirocin differs from other clinical...
30 KB (2,609 words) - 04:22, 27 October 2024
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (redirect from Adverse effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug)
of inflammation. This mechanism of action was elucidated in 1970 by John Vane (1927–2004), who received a Nobel Prize for his work (see Mechanism of action...
111 KB (11,577 words) - 07:56, 16 November 2024
Diuretic (redirect from Adverse effects of diuretics)
retention in the filtrate. It was previously believed that the primary mechanism of osmotic diuretics such as mannitol is that they are filtered in the glomerulus...
23 KB (2,001 words) - 02:28, 23 September 2024
Drug class (redirect from Class of drugs)
class is a group of medications and other compounds that share similar chemical structures, act through the same mechanism of action (i.e., binding to...
10 KB (1,007 words) - 05:56, 14 November 2024
Minoxidil (section Mechanism of action)
antiandrogenic effect of minoxidil, shown by significant downregulation of 5α-R2 gene expression in HaCaT cells, may be one of its mechanisms of action in alopecia...
48 KB (4,625 words) - 02:15, 12 November 2024
Methotrexate (section Mechanism of action)
Bauer R (October 1993). "Mechanism of action of methotrexate: experimental evidence that methotrexate blocks the binding of interleukin 1 beta to the...
41 KB (3,770 words) - 06:26, 21 November 2024
Inclisiran (section Discovery and mechanism of action)
(siRNAs) are designed to intervene in the pathway of RNA interference (RNAi), a naturally operating mechanism, wherein they bind to a complex within the cell...
21 KB (1,744 words) - 14:15, 24 April 2024
Copper IUD (section Mechanism of action)
the mechanism of action of IUDs is abortifacient... the principal mechanism of action of the copper T 380A IUD is to interfere with sperm action, preventing...
65 KB (6,883 words) - 20:13, 4 November 2024
Clindamycin (section Mechanism of action)
prolong the effects of neuromuscular-blocking drugs, such as succinylcholine and vecuronium. Its similarity to the mechanism of action of macrolides and chloramphenicol...
44 KB (4,070 words) - 09:07, 18 October 2024
Clonazepam (section Mechanism of action)
drugs it was compared to in a study. Clonazepam's primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain, by the benzodiazepine receptor...
78 KB (7,624 words) - 13:57, 20 November 2024
Mucoactive agent (section Mechanism of action)
of respiratory diseases that are complicated by the oversecretion or inspissation of mucus. These drugs can be further categorized by their mechanism...
6 KB (555 words) - 01:07, 22 September 2024
Senna glycoside (section Mechanism of action)
color. Senna derivatives are a type of stimulant laxative and are of the anthraquinone type. While its mechanism of action is not entirely clear, senna is...
12 KB (953 words) - 14:24, 5 September 2024
Famotidine (section Mechanism of action)
effects of histamine and has some potential mechanisms of action that may contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties, including the inhibition of the...
27 KB (2,336 words) - 22:40, 9 November 2024
Drug antagonism (section Mechanism of Action)
stopping the action or effect of another substance, preventing a biological response. The stopping actions are carried out by four major mechanisms, namely...
33 KB (3,822 words) - 15:39, 25 July 2024
Acetazolamide (section Mechanism of action)
1007/978-94-007-7359-2_17. ISBN 978-94-007-7358-5. PMID 24146387. "Acetazolamide: mechanism of action". www.openanesthesia.org. Retrieved 10 May 2017. Sneader W (2005)...
27 KB (2,588 words) - 05:18, 3 July 2024
Ulotaront (section Mechanism of action)
effect profile of ulotaront differs from that of other antipsychotics because its mechanism of action does not involve antagonism of dopamine receptors...
11 KB (824 words) - 13:30, 14 November 2024
Quinine (section Mechanism of action)
hemoglobin. As with other quinoline antimalarial drugs, the precise mechanism of action of quinine has not been fully resolved, although in vitro studies indicate...
63 KB (6,755 words) - 21:54, 12 November 2024
Antiarthritics (category CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024)
response of the human body. The mechanism of action is either through interfering with the effect of cytokines, inhibiting the costimulation of T cell activation...
31 KB (3,044 words) - 03:45, 2 November 2024
Tetracycline antibiotics (section Mechanism of action)
Organization of Teratology Information Specialists. July 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-08-27. "Mechanism of Action of Tetracyclines...
44 KB (4,647 words) - 08:45, 6 May 2024
Calcium channel blocker (section Mechanism of action)
as vasodilation is minimal with the phenylalkylamines, the major mechanism of action is causing negative inotropy. Phenylalkylamines are thought to access...
29 KB (3,270 words) - 01:09, 8 October 2024
and psoriasis. It is a synthetic analog of the adrenal corticosteroids. Although its exact mechanism of action is not known, it is effective when applied...
13 KB (878 words) - 12:39, 25 April 2024
Emergency contraception (section Mechanism of action)
believed that the main mechanism of action of high-dose progestin emergency contraception is inhibition of ovulation, but other mechanisms may be involved....
96 KB (10,571 words) - 05:12, 22 November 2024