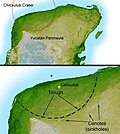
The Chicxulub crater (IPA: [t͡ʃikʃuˈluɓ] cheek-shoo-LOOB) is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore...
84 KB (8,255 words) - 14:29, 18 November 2024
7,591 inhabitants. Chicxulub Puerto is most famous for being near the geographic center of the Chicxulub crater, an impact crater discovered by geologists...
3 KB (303 words) - 01:34, 18 September 2024
population of 4,080 people. Chicxulub is most famous for being near the geographic center of the Chicxulub crater, an impact crater discovered by geologists...
7 KB (290 words) - 14:23, 4 November 2024
million years younger than Chicxulub crater in Mexico and the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary (K–Pg boundary). The Chicxulub impact is believed to have...
8 KB (938 words) - 18:21, 29 August 2023
Look up Chicxulub in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Chicxulub may refer to: Chicxulub crater, on the Yucatán Peninsula, in Mexico Chicxulub Pueblo,...
326 bytes (75 words) - 21:52, 25 August 2024
that the extinction coincided with a large meteorite impact at the Chicxulub crater and the generally accepted scientific theory is that this impact triggered...
28 KB (3,036 words) - 10:54, 22 November 2024
asteroid 10 to 15 km (6 to 9 mi) wide, 66 million years ago causing the Chicxulub crater, which devastated the global environment, mainly through a lingering...
196 KB (21,557 words) - 08:43, 23 November 2024
Deccan Traps (section Chicxulub crater)
this has been strongly disputed, with many authors suggesting that the Chicxulub impact was the primary cause of the extinction. While some scholars suggest...
31 KB (3,489 words) - 02:09, 24 October 2024
team developed their hypothesis, but later scientists discovered the Chicxulub Crater in the Yucatán Peninsula, now considered the likely impact site. Paul...
21 KB (2,437 words) - 21:32, 4 November 2024
Cenote (section Chicxulub crater)
circular alignment of cenotes overlies the measured rim of the Chicxulub crater. This crater structure, identified from the alignment of cenotes, but also...
25 KB (2,662 words) - 13:07, 17 November 2024
overlie part of it. The proposed Shiva crater and other possible impact craters along with the Chicxulub crater have led to the hypothesis that multiple...
11 KB (1,214 words) - 04:40, 12 November 2024
Yaxcopoil (section Chicxulub Crater Research)
earth on the Yucatán Peninsula 66 million years ago and created the Chicxulub crater. The first project to deep-drill and core into one of the largest and...
7 KB (809 words) - 14:09, 18 October 2022
480 km (300 mi) wide impact crater buried beneath the ice and more than 2.5 times larger than the 180 km (110 mi) Chicxulub crater. Due to the site's location...
13 KB (1,393 words) - 21:56, 11 November 2024
Peak ring (redirect from Peak-ring impact crater)
Perhaps, in the case of Chicxulub crater, an over-high central peak collapsed into the peak ring. Chicxulub is Earth's only crater to have an intact peak...
6 KB (506 words) - 20:49, 4 November 2024
boundary about 66 mya around the same time as the Chicxulub crater. Numerical simulations of crater formation suggested a sea impact at the depth of around...
6 KB (639 words) - 16:06, 6 November 2024
Caribbean Basin. The deeply buried Chicxulub crater is centered off the north coast of the peninsula near the town of Chicxulub. The now-famous "Ring of Cenotes...
25 KB (2,552 words) - 20:39, 17 November 2024
List of impact structures on Earth (redirect from Terrestrial crater)
the Pliocene. Most recorded impact craters are over 10 million years old, or have widely uncertain ages. The Chicxulub impact has been widely been considered...
42 KB (1,829 words) - 04:31, 18 November 2024
years ago, now known to be produced by the impact that formed the Chicxulub crater. Similarly, an iridium anomaly in core samples from the Pacific Ocean...
81 KB (7,815 words) - 09:58, 25 November 2024
Jacobsen, S.B.; Boynton, W.V. (1991). "Chicxulub crater: a possible Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary impact crater on the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico". Geology...
283 KB (28,273 words) - 17:02, 18 November 2024
Sudbury Basin (redirect from Sudbury Crater)
third-largest crater on Earth, after the 300 km (190 mi) Vredefort impact structure in South Africa, and the 180 km (110 mi) Chicxulub crater under Yucatán...
19 KB (2,047 words) - 07:10, 22 July 2024
boundary. In 1991, Alan Hildebrand and William Boynton reported the Chicxulub crater in the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico as a probable impact site. While...
120 KB (12,560 words) - 14:02, 2 September 2024
asteroid impact cratering, fireballs and meteorite recovery. His work has shed light on the extinction event caused by the Chicxulub asteroid at the end...
6 KB (507 words) - 03:06, 17 June 2024
Cretaceous age, the rubble from the asteroid impact that created the Chicxulub Crater. The recently discovered Sihil field (1-15,000 million barrels) contains...
13 KB (1,516 words) - 06:24, 13 November 2023
Technological Consultative Forum. The Chicxulub crater is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. The crater was discovered by Antonio...
68 KB (7,863 words) - 23:30, 6 November 2024
been reported from any of the sediment studies performed near the Chicxulub crater on the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Setting out to identify past impact...
7 KB (705 words) - 19:10, 3 November 2024
British seismologist and geophysicist known for her analyses of the Chicxulub crater the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, and the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction...
4 KB (382 words) - 19:52, 3 October 2023
leaving behind the Chicxulub crater. The impactor tore through the Earth's crust, creating huge earthquakes, giant waves, and a crater 180 kilometers (112 mi)...
31 KB (3,614 words) - 14:26, 13 November 2024
II: The nature of diatreme, karst and trappean formations, and the chicxulub crater origin". Journal of Mining Science. 48. Springer Link: 55–70. doi:10...
8 KB (814 words) - 10:01, 14 November 2024
and methane. The most notable example is the bolide that caused the Chicxulub crater 66 million years ago. Scientific consensus agrees that this event directly...
11 KB (1,075 words) - 18:16, 18 November 2024
approximately 10 kilometers (6 miles) wide is thought to have produced the Chicxulub crater and triggered the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event that is understood...
121 KB (13,415 words) - 10:33, 24 November 2024